In a move that has fundamentally redefined the trajectory of artificial general intelligence (AGI), OpenAI has officially transitioned its flagship models from mere predictive text generators to "reasoning engines." The launch of the o3 and o3-mini models marks a watershed moment in the AI industry, signaling the end of the "bigger is better" data-scaling era and the beginning of the "think longer" inference-scaling era. These models represent the first commercial realization of "System 2" thinking, allowing AI to pause, deliberate, and self-correct before providing an answer.
The significance of this development cannot be overstated. By achieving scores that were previously thought to be years, if not decades, away, OpenAI has effectively reset the competitive landscape. As of early 2026, the o3 model remains the benchmark against which all other frontier models are measured, particularly in the realms of advanced mathematics, complex coding, and visual reasoning. This shift has also birthed a new economic model for AI: the $200-per-month ChatGPT Pro tier, which caters to a growing class of "power users" who require massive amounts of compute to solve the world’s most difficult problems.
The Technical Leap: System 2 Thinking and the ARC-AGI Breakthrough
At the heart of the o3 series is a technical shift known as inference-time scaling, or "test-time compute." While previous models like GPT-4o relied on "System 1" thinking—fast, intuitive, and often prone to "hallucinating" the first plausible-sounding answer—o3 utilizes a "System 2" approach. This allows the model to utilize a hidden internal Chain of Thought (CoT), exploring multiple reasoning paths and verifying its own logic before outputting a final response. This deliberative process is powered by large-scale Reinforcement Learning (RL), which teaches the model how to use its "thinking time" effectively to maximize accuracy rather than just speed.
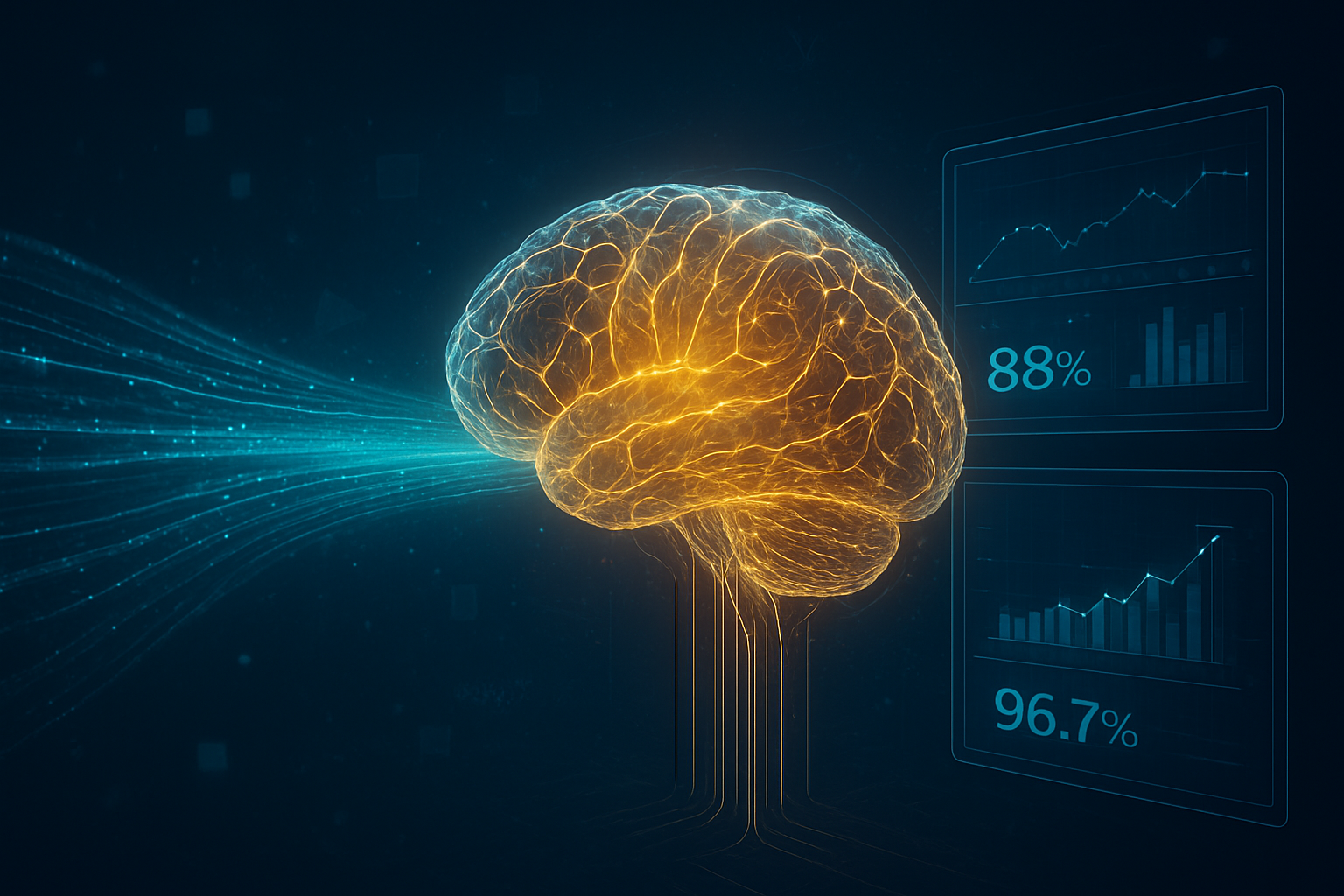
The results of this architectural shift are most evident in the record-breaking benchmarks. The o3 model achieved a staggering 88% on the Abstractions and Reasoning Corpus (ARC-AGI), a benchmark designed to test an AI's ability to learn new concepts on the fly rather than relying on memorized training data. For years, the ARC-AGI was considered a "wall" for LLMs, with most models scoring in the single digits. By reaching 88%, OpenAI has surpassed the average human baseline of 85%, a feat that many AI researchers, including ARC creator François Chollet, previously believed would require a total paradigm shift in AI architecture.
In the realm of mathematics, the performance is equally dominant. The o3 model secured a 96.7% score on the AIME 2024 (American Invitational Mathematics Examination), missing only a single question on one of the most difficult high school math exams in the world. This is a massive leap from the 83.3% achieved by the original o1 model and the 56.7% of the o1-preview. The o3-mini model, while smaller and faster, also maintains high-tier performance in coding and STEM tasks, offering users a "reasoning effort" toggle to choose between "Low," "Medium," and "High" compute intensity depending on the complexity of the task.
Initial reactions from the AI research community have been a mix of awe and strategic recalibration. Experts note that OpenAI has successfully demonstrated that "compute at inference" is a viable scaling law. This means that even without more training data, an AI can be made significantly smarter simply by giving it more time and hardware to process a single query. This discovery has led to a massive surge in demand for high-performance chips from companies like Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA), as the industry shifts its focus from training clusters to massive inference farms.
The Competitive Landscape: Pro Tiers and the DeepSeek Challenge
The launch of o3 has forced a strategic pivot among OpenAI’s primary competitors. Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT), as OpenAI’s largest partner, has integrated these reasoning capabilities across its Azure AI and Copilot platforms, targeting enterprise clients who need "zero-defect" reasoning for financial modeling and software engineering. Meanwhile, Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOGL) has responded with Gemini 2.0, which focuses on massive 2-million-token context windows and native multimodal integration. While Gemini 2.0 excels at processing vast amounts of data, o3 currently holds the edge in raw logical deduction and "System 2" depth.
A surprising challenger has emerged in the form of DeepSeek R1, an open-source model that utilizes a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture to provide o1-level reasoning at a fraction of the cost. The presence of DeepSeek R1 has created a bifurcated market: OpenAI remains the "performance king" for mission-critical tasks, while DeepSeek has become the go-to for developers looking for cost-effective, open-source reasoning. This competitive pressure is likely what drove OpenAI to introduce the $200-per-month ChatGPT Pro tier. This premium offering provides "unlimited" access to the highest-compute versions of o3, as well as priority access to Sora and the "Deep Research" tool, effectively creating a "Pro" class of AI users.
This new pricing tier represents a shift in how AI is valued. By charging $200 a month—ten times the price of the standard Plus subscription—OpenAI is signaling that high-level reasoning is a premium commodity. This tier is not intended for casual chat; it is a professional tool for engineers, PhD researchers, and data scientists. The inclusion of the "Deep Research" tool, which can perform multi-step web synthesis to produce near-doctoral-level reports, justifies the price point for those whose productivity is multiplied by these advanced capabilities.
For startups and smaller AI labs, the o3 launch is both a blessing and a curse. On one hand, it proves that AGI-level reasoning is possible, providing a roadmap for future development. On the other hand, the sheer amount of compute required for inference-time scaling creates a "compute moat" that is difficult for smaller players to cross. Startups are increasingly focusing on niche "vertical AI" applications, using o3-mini via API to power specialized agents for legal, medical, or engineering fields, rather than trying to build their own foundation models.
Wider Significance: Toward AGI and the Ethics of "Thinking" AI
The transition to System 2 thinking fits into the broader trend of AI moving from a "copilot" to an "agent." When a model can reason through steps, verify its own work, and correct errors before the user even sees them, it becomes capable of handling autonomous workflows that were previously impossible. This is a significant step toward AGI, as it demonstrates a level of cognitive flexibility and self-awareness (at least in a mathematical sense) that was absent in earlier "stochastic parrot" models.
However, this breakthrough also brings new concerns. The "hidden" nature of the Chain of Thought in o3 models has sparked a debate over AI transparency. While OpenAI argues that hiding the CoT is necessary for safety—to prevent the model from being "jailbroken" by observing its internal logic—critics argue that it makes the AI a "black box," making it harder to understand why a model reached a specific conclusion. As AI begins to make more high-stakes decisions in fields like medicine or law, the demand for "explainable AI" will only grow louder.
Comparatively, the o3 milestone is being viewed with the same reverence as the original "AlphaGo" moment. Just as AlphaGo proved that AI could master the complex intuition of a board game through reinforcement learning, o3 has proved that AI can master the complex abstraction of human logic. The 88% score on ARC-AGI is particularly symbolic, as it suggests that AI is no longer just repeating what it has seen on the internet, but is beginning to "understand" the underlying patterns of the physical and logical world.
There are also environmental and resource implications to consider. Inference-time scaling is computationally expensive. If every query to a "reasoning" AI requires seconds or minutes of GPU-heavy thinking, the carbon footprint and energy demands of AI data centers will skyrocket. This has led to a renewed focus on energy-efficient AI hardware and the development of "distilled" reasoning models like o3-mini, which attempt to provide the benefits of System 2 thinking with a much smaller computational overhead.
The Horizon: What Comes After o3?
Looking ahead, the next 12 to 24 months will likely see the democratization of System 2 thinking. While o3 is currently the pinnacle of reasoning, the "distillation" process will eventually allow these capabilities to run on local hardware. We can expect future "o-series" models to be integrated directly into operating systems, where they can act as autonomous agents capable of managing complex file structures, writing and debugging code in real-time, and conducting independent research without constant human oversight.
The potential applications are vast. In drug discovery, an o3-level model could reason through millions of molecular combinations, simulating outcomes and self-correcting its hypotheses before a single lab test is conducted. In education, "High-Effort" reasoning models could act as personal Socratic tutors, not just giving students the answer, but understanding the student's logical gaps and guiding them through the reasoning process. The challenge will be managing the "latency vs. intelligence" trade-off, as users decide which tasks require a 2-second "System 1" response and which require a 2-minute "System 2" deep-dive.
Experts predict that the next major breakthrough will involve "multi-modal reasoning scaling." While o3 is a master of text and logic, the next generation will likely apply the same inference-time scaling to video and physical robotics. Imagine a robot that doesn't just follow a script, but "thinks" about how to navigate a complex environment or fix a broken machine, trying different physical strategies in a mental simulation before taking action. This "embodied reasoning" is widely considered the final frontier before true AGI.
Final Assessment: A New Era of Artificial Intelligence
The launch of OpenAI’s o3 and o3-mini represents more than just a seasonal update; it is a fundamental re-architecting of what we expect from artificial intelligence. By breaking the ARC-AGI and AIME records, OpenAI has demonstrated that the path to AGI lies not just in more data, but in more deliberate thought. The introduction of the $200 ChatGPT Pro tier codifies this value, turning high-level reasoning into a professional utility that will drive the next wave of global productivity.
In the history of AI, the o3 release will likely be remembered as the moment the industry moved beyond "chat" and into "cognition." While competitors like DeepSeek and Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL) continue to push the boundaries of efficiency and context, OpenAI has claimed the high ground of pure logical performance. The long-term impact will be felt in every sector that relies on complex problem-solving, from software engineering to theoretical physics.
In the coming weeks and months, the industry will be watching closely to see how users utilize the "High-Effort" modes of o3 and whether the $200 Pro tier finds a sustainable market. As more developers gain access to the o3-mini API, we can expect an explosion of "reasoning-first" applications that will further integrate these advanced capabilities into our daily lives. The era of the "Thinking Machine" has officially arrived.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.