As of January 27, 2026, the global semiconductor hierarchy has undergone its most significant shift in a decade. Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) has officially announced that its 18A (1.8nm-class) manufacturing node has reached high-volume manufacturing (HVM) status, signaling the successful completion of its "five nodes in four years" roadmap. This milestone is not just a technical victory for Intel; it marks the company’s return to the pinnacle of process leadership, a position it had ceded to competitors during the late 2010s.
The arrival of Intel 18A represents a critical turning point for the artificial intelligence industry. By integrating the revolutionary RibbonFET gate-all-around (GAA) architecture with its industry-leading PowerVia backside power delivery technology, Intel has delivered a platform optimized for the next generation of generative AI and high-performance computing (HPC). With early silicon already shipping to lead customers, the 18A node is proving to be the "holy grail" for AI developers seeking maximum performance-per-watt in an era of skyrocketing energy demands.
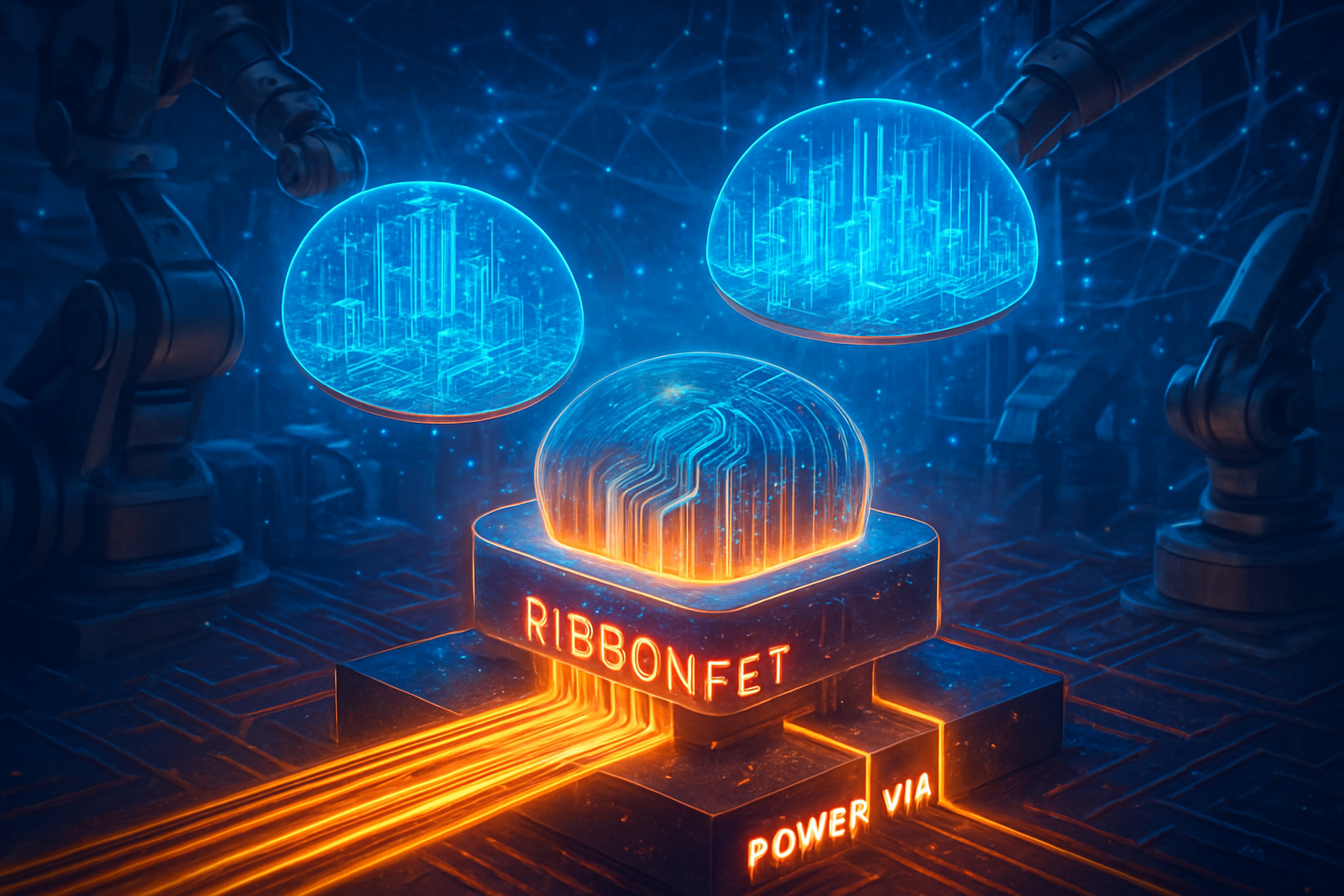
The Architecture of Leadership: RibbonFET and the PowerVia Advantage
At the heart of Intel 18A are two foundational innovations that differentiate it from the FinFET-based nodes of the past. The first is RibbonFET, Intel’s implementation of a Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistor. Unlike the previous FinFET design, which used a vertical fin to control current, RibbonFET surrounds the transistor channel on all four sides. This allows for superior control over electrical leakage and significantly faster switching speeds. The 18A node refines the initial RibbonFET design introduced in the 20A node, resulting in a 10-15% speed boost at the same power levels compared to the already impressive 20A projections.
The second, and perhaps more consequential breakthrough, is PowerVia—Intel’s implementation of Backside Power Delivery (BSPDN). Traditionally, power and signal wires are bundled together on the "front" of the silicon wafer, leading to "routing congestion" and voltage droop. PowerVia moves the power delivery network to the backside of the wafer, using nano-TSVs (Through-Silicon Vias) to connect directly to the transistors. This decoupling of power and signal allows for much thicker, more efficient power traces, reducing resistance and reclaiming nearly 10% of previously wasted "dark silicon" area.
While competitors like TSMC (NYSE:TSM) have announced their own version of this technology—marketed as "Superpower Rail" for their upcoming A16 node—Intel has successfully brought its version to market nearly a year ahead of the competition. This "first-mover" advantage in backside power delivery is a primary reason for the 18A node's high performance. Industry analysts have noted that the 18A node offers a 25% performance-per-watt improvement over the Intel 3 node, a leap that effectively resets the competitive clock for the foundry industry.
Shifting the Foundry Balance: Microsoft, Apple, and the Race for AI Supremacy
The successful ramp of 18A has sent shockwaves through the tech giant ecosystem. Intel Foundry has already secured a backlog exceeding $20 billion, with Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) emerging as a flagship customer. Microsoft is utilizing the 18A-P (Performance-enhanced) variant to manufacture its next-generation "Maia 2" AI accelerators. By leveraging Intel's domestic manufacturing capabilities in Arizona and Ohio, Microsoft is not only gaining a performance edge but also securing its supply chain against geopolitical volatility in East Asia.
The competitive implications extend to the highest levels of the consumer electronics market. Reports from late 2025 indicate that Apple (NASDAQ:AAPL) has moved a portion of its silicon production for entry-level devices to Intel’s 18A-P node. This marks a historic diversification for Apple, which has historically relied almost exclusively on TSMC for its A-series and M-series chips. For Intel, winning an "Apple-sized" contract validates the maturity of its 18A process and proves it can meet the stringent yield and quality requirements of the world’s most demanding hardware company.
For AI hardware startups and established giants like NVIDIA (NASDAQ:NVDA), the availability of 18A provides a vital alternative in a supply-constrained market. While NVIDIA remains a primary partner for TSMC, the introduction of Intel’s 18A-PT—a variant optimized for advanced multi-die "System-on-Chip" (SoC) designs—offers a compelling path for future Blackwell successors. The ability to stack high-performance 18A logic tiles using Intel’s Foveros Direct 3D packaging technology is becoming a key differentiator in the race to build the first 100-trillion parameter AI models.
Geopolitics and the Reshoring of the Silicon Frontier
Beyond the technical specifications, Intel 18A is a cornerstone of the broader geopolitical effort to reshore semiconductor manufacturing to the United States. Supported by funding from the CHIPS and Science Act, Intel’s expansion of Fab 52 in Arizona has become a symbol of American industrial renewal. The 18A node is the first advanced process in over a decade to be pioneered and mass-produced on U.S. soil before any other region, a fact that has significant implications for national security and technological sovereignty.
The success of 18A also serves as a validation of the "Five Nodes in Four Years" strategy championed by Intel’s leadership. By maintaining an aggressive cadence, Intel has leapfrogged the standard industry cycle, forcing competitors to accelerate their own roadmaps. This rapid iteration has been essential for the AI landscape, where the demand for compute is doubling every few months. Without the efficiency gains provided by technologies like PowerVia and RibbonFET, the energy costs of maintaining massive AI data centers would likely become unsustainable.
However, the transition has not been without concerns. The immense capital expenditure required to maintain this pace has pressured Intel’s margins, and the complexity of 18A manufacturing requires a highly specialized workforce. Critics initially doubted Intel's ability to achieve commercial yields (currently estimated at a healthy 65-75%), but the successful launch of the "Panther Lake" consumer CPUs and "Clearwater Forest" Xeon processors has largely silenced the skeptics.
The Road to 14A and the Era of High-NA EUV
Looking ahead, the 18A node is just the beginning of Intel’s "Angstrom-era" roadmap. The company has already begun sampling its next-generation 14A node, which will be the first in the industry to utilize High-Numerical Aperture (High-NA) Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography tools from ASML (NASDAQ:ASML). While 18A solidified Intel's recovery, 14A is intended to extend that lead, targeting another 15% performance improvement and a further reduction in feature sizes.
The integration of 18A technology into the "Nova Lake" architecture—scheduled for late 2026—will be the next major milestone for the consumer market. Experts predict that Nova Lake will redefine the desktop and mobile computing experience by offering over 50 TOPS of NPU (Neural Processing Unit) performance, effectively making every 18A-powered PC a localized AI powerhouse. The challenge for Intel will be maintaining this momentum while simultaneously scaling its foundry services to accommodate a diverse range of third-party designs.
A New Chapter for the Semiconductor Industry
The high-volume manufacturing of Intel 18A marks one of the most remarkable corporate turnarounds in recent history. By delivering 10-15% speed gains and pioneering backside power delivery via PowerVia, Intel has not only caught up to the leading edge but has actively set the pace for the rest of the decade. This development ensures that the AI revolution will have the "silicon fuel" it needs to continue its exponential growth.
As we move further into 2026, the industry's eyes will be on the retail performance of the first 18A devices and the continued expansion of Intel Foundry's customer list. The "Angstrom Race" is far from over, but with 18A now in production, Intel has firmly re-established itself as a titan of the silicon world. For the first time in a generation, the fastest and most efficient transistors on the planet are being made by the company that started it all.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.