Artificial Intelligence is ushering in an unprecedented era of scientific discovery in one of Earth's most challenging and least understood environments: the Antarctic seafloor. Far from being a distant theoretical concept, AI is now actively supercharging expeditions, transforming how researchers collect, analyze, and interpret vast quantities of data from the icy depths. This technological leap is not merely an incremental improvement; it represents a fundamental shift in our capacity to explore the Southern Ocean, offering critical insights into marine biodiversity, ice sheet dynamics, and the global climate system.
The immediate significance of AI's deployment in Antarctic exploration is profound. It enables scientists to overcome logistical and environmental barriers that have long hampered research, vastly accelerating the pace of discovery. From autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) navigating beneath colossal ice shelves to sophisticated algorithms rapidly identifying marine species in millions of images, AI is providing access to previously unreachable areas and delivering real-time, actionable data. This rapid advancement is crucial for understanding the impacts of climate change on a fragile ecosystem that plays a pivotal role in regulating global climate, and it is already yielding breakthroughs that are reshaping our understanding of this vital continent.
AI's Deep Dive: Unveiling the Technical Marvels Beneath the Ice
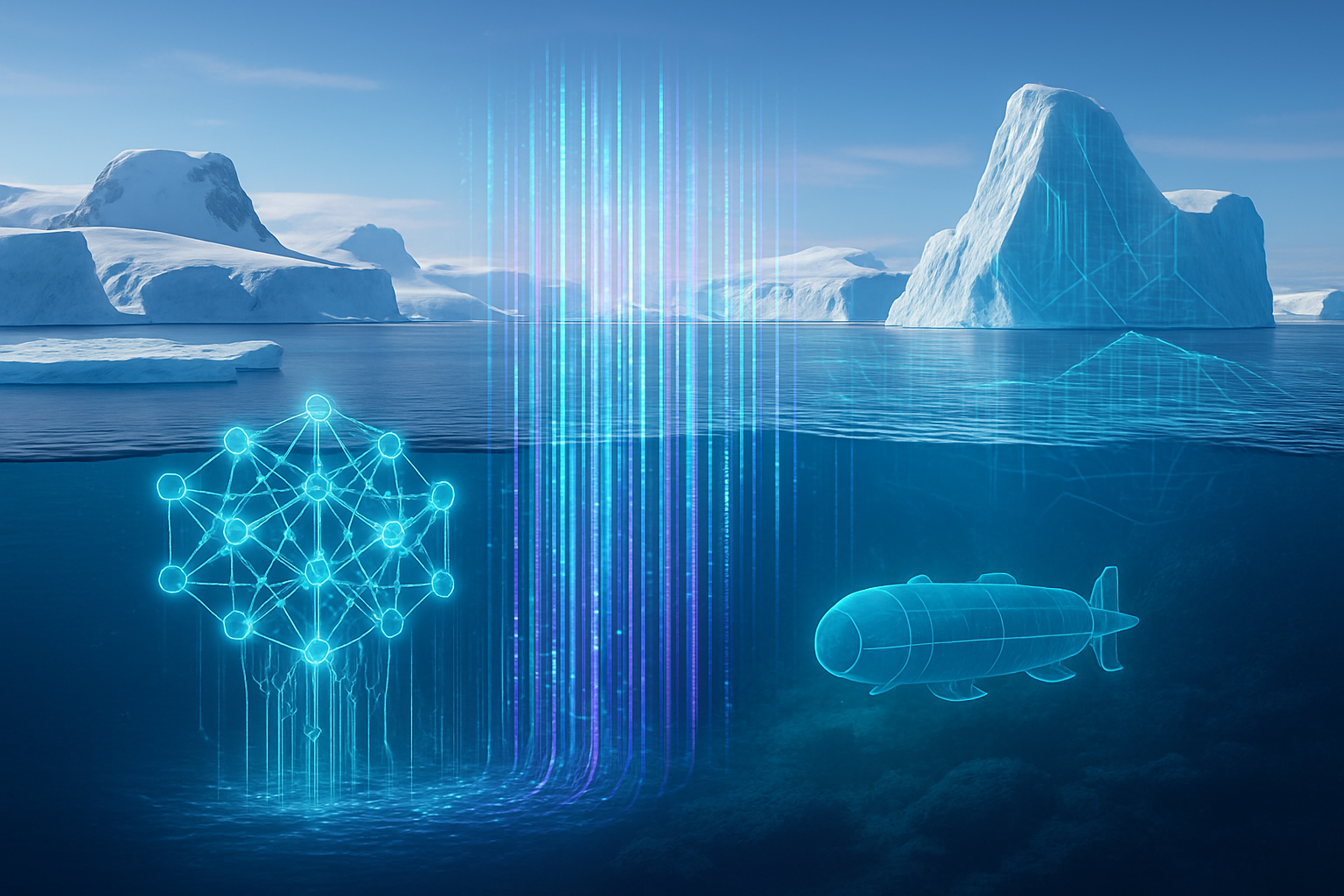
The technical advancements driving AI's success in Antarctic seafloor exploration are multifaceted, leveraging machine learning, computer vision, and autonomous robotics to tackle the unique challenges of the polar environment. A significant breakthrough, announced by scientists from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) in October 2025, involves a sophisticated AI tool designed to identify marine animals in seafloor images and videos with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This tool, trained on extensive high-resolution datasets, can classify common seafloor creatures such as starfish, corals, sponges, and various fish species in mere seconds, a task that previously required hours of painstaking human effort per image. Its capability is so robust that it can be integrated onto research vessels, allowing for real-time image labeling and immediate data interpretation while expeditions are still underway.
This AI-powered image analysis differs dramatically from previous manual approaches, which were not only time-consuming but also limited by human capacity, making it impossible to process the sheer volume of data generated by modern seafloor imaging systems. The AI's ability to swiftly process tens of thousands of backlog images from critical regions like the Antarctic Peninsula and Weddell Sea represents a monumental leap in efficiency and data utilization. Furthermore, AI is the brain behind the increasing sophistication of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Unmanned Surface Vessels (USVs). These robotic explorers, like the forthcoming "Ran II" (expected by winter 2026/2027 to replace its predecessor lost under the Thwaites Glacier), are crucial for navigating hazardous environments inaccessible to humans, such as beneath thick sea ice and floating ice shelves. AI algorithms empower these vehicles with advanced navigation, adaptive mission planning, and real-time data processing, enabling them to operate autonomously, map vast seafloor areas, and identify critical features like hidden meltwater reservoirs – a capability highlighted by a July 2024 study that used AI to reveal significantly more meltwater in Antarctic ice shelves than previously estimated.
The initial reactions from the AI research community and industry experts have been overwhelmingly positive, recognizing these applications as a powerful demonstration of AI's potential in extreme environments. Experts commend the integration of AI with robotic platforms and advanced sensing technologies, noting that it pushes the boundaries of scientific inquiry. The ability of AI to sift through colossal datasets, identify subtle patterns, and accelerate discovery is seen as a game-changer for glaciology, oceanography, and marine biology. This collective enthusiasm underscores a growing consensus that AI is not just a tool for automation but a catalyst for entirely new forms of scientific exploration and understanding in critical, under-researched regions of the planet.
Corporate Currents: Navigating the AI Wave in Polar Science
The burgeoning application of AI in Antarctic seafloor exploration presents significant opportunities and competitive implications for a diverse array of companies, from established tech giants to specialized AI startups. Companies at the forefront of AI development, particularly those specializing in computer vision, machine learning for environmental data analysis, and autonomous robotics, stand to benefit immensely. Firms like Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA), known for its powerful GPUs essential for training complex AI models, and Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL), with its deep expertise in AI research and cloud-based data processing, are indirectly supporting these advancements by providing the foundational hardware and software infrastructure. Their continued innovation in AI frameworks and processing power directly translates into more capable and efficient research tools for polar science.
More directly, companies specializing in robust autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and unmanned surface vessels (USVs) are poised for significant growth. Manufacturers of such advanced robotics, which rely heavily on AI for navigation, data collection, and decision-making in extreme conditions, will see increased demand as scientific missions become more ambitious. This includes firms developing advanced sensor technologies, acoustic communication systems, and energy solutions for long-duration autonomous operations. The competitive landscape will likely intensify among these specialized robotics companies as they vie to produce the most reliable and intelligent platforms capable of enduring the Antarctic environment. Furthermore, startups focused on niche AI applications, such as automated image annotation for marine biology or sophisticated climate modeling algorithms, could carve out significant market positions by offering tailored solutions to research institutions and government agencies like the British Antarctic Survey.
The potential disruption to existing products or services primarily affects traditional, labor-intensive data analysis methods. As AI tools become more prevalent and efficient, the demand for manual image and data processing will diminish, necessitating a shift in skills and resources within research teams. However, this disruption is largely viewed as positive, freeing up human experts to focus on higher-level interpretation and hypothesis generation rather than repetitive tasks. Market positioning for companies will increasingly depend on their ability to integrate AI seamlessly into their offerings, demonstrating not just raw computational power but also a deep understanding of scientific research needs. Strategic advantages will be gained by those who can offer end-to-end solutions, combining advanced hardware with intelligent software, and by fostering collaborations with leading scientific institutions to co-develop cutting-edge tools.
Broader Horizons: AI's Impact on the Global Scientific Landscape
The application of AI in understanding the Antarctic seafloor fits squarely within broader AI landscape trends, particularly the increasing emphasis on AI for scientific discovery and environmental monitoring. This development is a powerful testament to the maturation of AI from theoretical models to practical tools capable of tackling real-world, grand scientific challenges. It highlights the trend of AI democratizing access to complex data analysis, allowing researchers to extract insights from massive datasets that would be intractable for human-only teams. The success in Antarctica underscores AI's role in advancing our understanding of climate change, biodiversity, and planetary processes – areas where data volume and complexity have historically been major bottlenecks.
The impacts of this development are far-reaching. Environmentally, it provides unprecedented data for conservation efforts, enabling the identification of vulnerable species and habitats with greater precision, which is crucial for informing marine protected area designations. Scientifically, it accelerates the pace of discovery, potentially leading to the identification of new species and a deeper understanding of unique ecological processes in the Southern Ocean. For climate science, AI-driven analysis of ice sheet dynamics, meltwater distribution, and ocean currents is yielding more accurate predictions of sea-level rise and future climate scenarios, as evidenced by studies revealing new insights into Antarctic ice flow in March 2025. This refined understanding is vital for global policy-making and adaptation strategies.
Potential concerns, while fewer in this specific application, primarily revolve around data privacy and ethical considerations if AI were to transition from pure scientific observation to resource exploitation, though this is not the current focus. More immediate concerns include the reliability and interpretability of AI models in making critical scientific classifications, necessitating robust validation processes. Comparisons to previous AI milestones, such as AI's breakthroughs in medical diagnostics or game-playing, reveal a common thread: AI's ability to process information at scales and speeds beyond human capability, leading to accelerated progress in fields previously limited by manual effort. This Antarctic application marks another significant milestone, demonstrating AI's capacity to extend human perception into the most extreme and vital corners of our planet, generating foundational knowledge critical for humanity's future.
Glimpsing the Future: The Next Frontier of AI in Antarctica
The trajectory of AI in Antarctic seafloor exploration points towards exciting near-term and long-term developments. In the near future, we can expect to see further integration of AI directly onto autonomous platforms, enabling more sophisticated real-time decision-making and adaptive sampling strategies. This means AUVs won't just follow pre-programmed paths but will dynamically adjust their missions based on immediate data feedback, pursuing anomalies or interesting features as they are detected. The British Antarctic Survey's AI tool, for instance, will likely evolve beyond identifying common species to recognizing rare or previously unknown organisms, and its real-time capabilities will become standard on all research vessels, drastically speeding up fieldwork. The deployment of "Ran II" by winter 2026/2027 will mark a significant step, showcasing enhanced AI capabilities for navigating and collecting high-resolution data in challenging sub-ice environments, further pushing the boundaries of autonomous exploration.
Potential applications on the horizon include the use of generative AI to simulate complex Antarctic ecosystems, allowing scientists to model the effects of climate change or human intervention with greater accuracy. AI could also be used to synthesize data from disparate sources—satellite imagery, oceanographic sensors, biological observations—to create comprehensive, dynamic models of the entire Southern Ocean system. Furthermore, AI-powered predictive analytics will become more refined, offering early warnings for changes in ice shelf stability, unusual marine animal migrations, or even localized seismic activity. Experts predict a future where AI acts as a "digital co-pilot" for polar scientists, not just processing data but actively suggesting new hypotheses, designing experiments, and even controlling fleets of autonomous robots in coordinated exploration efforts.
However, challenges remain. The extreme environmental conditions of Antarctica—freezing temperatures, immense pressures, and limited connectivity—demand incredibly robust and energy-efficient AI systems. Developing AI models that can generalize across diverse and often sparse Antarctic datasets, especially for rare species or phenomena, requires continuous innovation in machine learning techniques. Ethical considerations around data ownership and the responsible deployment of powerful AI tools will also need careful navigation. Nevertheless, experts are optimistic, foreseeing a future where AI unlocks even deeper secrets of the Antarctic, providing humanity with the critical knowledge needed to protect this invaluable global resource and understand its profound influence on our planet's future.
A New Chapter in Polar Science: AI's Enduring Legacy
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into Antarctic seafloor exploration represents a pivotal moment in both AI history and polar science. It marks a decisive shift from traditional, human-intensive research methodologies to an era of accelerated, data-driven discovery, enabling scientists to probe the mysteries of the Southern Ocean with unprecedented efficiency and scale. The ability of AI to rapidly analyze vast datasets, power autonomous vehicles in extreme environments, and uncover subtle patterns in complex ecological and glaciological systems is fundamentally reshaping our understanding of this critical region. From the British Antarctic Survey's rapid marine animal identification tool to AI's role in mapping hidden meltwater reservoirs and refining climate models, these advancements are not just incremental improvements; they are foundational shifts that promise to yield profound insights into biodiversity, oceanography, and global climate dynamics.
This development's significance in AI history lies in its demonstration of AI's capacity to extend human sensory and cognitive abilities into the most remote and challenging frontiers of our planet. It underscores the technology's potential as a powerful ally in addressing global challenges, particularly climate change. The long-term impact will be a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the Antarctic, leading to more informed conservation policies, more accurate climate predictions, and potentially the discovery of entirely new forms of life and geological processes. It also sets a precedent for how AI can be leveraged in other extreme environments, from deep-sea trenches to extraterrestrial exploration.
In the coming weeks and months, researchers and the public alike should watch for further announcements regarding the deployment of advanced AUVs like "Ran II," continued refinements in AI-powered data analysis tools, and the subsequent scientific publications detailing new discoveries facilitated by these technologies. The ongoing collaboration between AI developers and polar scientists will be crucial, fostering a symbiotic relationship that will continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in scientific exploration. The Antarctic seafloor, once largely inaccessible, is now yielding its secrets, thanks to the relentless curiosity of humanity, supercharged by the intelligence of machines.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.