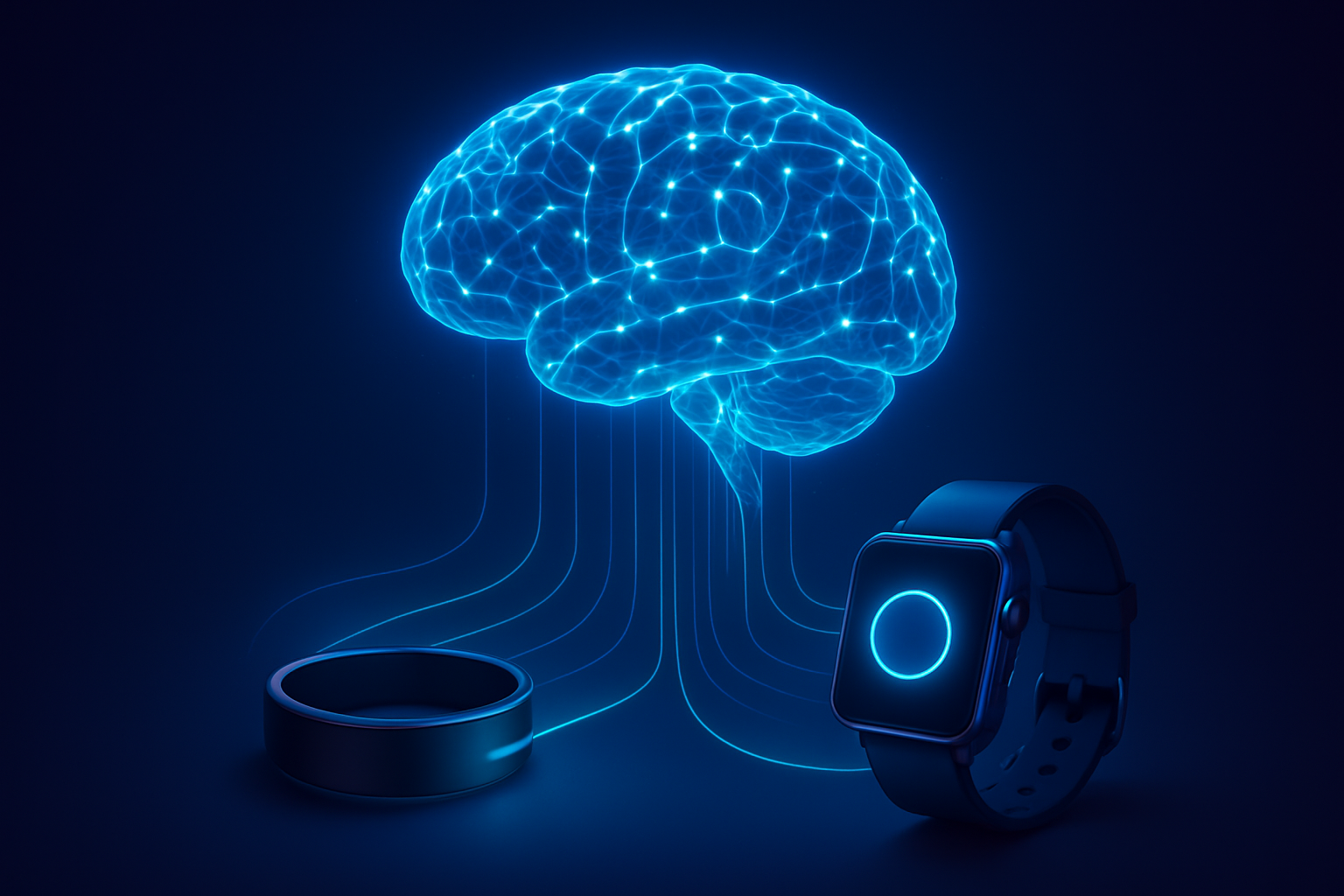
In a landmark shift for the intersection of consumer technology and geriatric medicine, Samsung Electronics (KRX: 005930) and Stanford Medicine have unveiled a sophisticated AI-driven "Brain Health" suite designed to detect the earliest indicators of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Announced at CES 2026, the system leverages a continuous stream of physiological data from the Galaxy Watch and the recently popularized Galaxy Ring to identify "digital biomarkers"—subtle behavioral and biological shifts that occur years, or even decades, before a clinical diagnosis of cognitive decline is traditionally possible.
This development marks a transition from reactive to proactive healthcare, turning ubiquitous consumer electronics into permanent medical monitors. By analyzing patterns in gait, sleep architecture, and even the micro-rhythms of smartphone typing, the Samsung-Stanford collaboration aims to bridge the "detection gap" in neurodegenerative diseases, allowing for lifestyle interventions and clinical treatments at a stage when the brain is most receptive to preservation.
Deep Learning the Mind: The Science of Digital Biomarkers
The technical backbone of this initiative is a multimodal AI system capable of synthesizing disparate data points into a cohesive "Cognitive Health Score." Unlike previous diagnostic tools that relied on episodic, in-person cognitive tests—often influenced by a patient's stress or fatigue on a specific day—the Samsung-Stanford AI operates passively in the background. According to research presented at the IEEE EMBS 2025 conference, one of the most predictive biomarkers identified is "gait variability." By utilizing the high-fidelity sensors in the Galaxy Ring and Watch, the AI monitors stride length, balance, and walking speed. A consistent 10% decline in these metrics, often invisible to the naked eye, has been correlated with the early onset of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI).
Furthermore, the system introduces an innovative "Keyboard Dynamics" model. This AI analyzes the way a user interacts with their smartphone—monitoring typing speed, the frequency of backspacing, and the length of pauses between words. Crucially, the model is "content-agnostic," meaning it analyzes how someone types rather than what they are writing, preserving user privacy while capturing the fine motor and linguistic planning disruptions typical of early-stage Alzheimer's.
Initial reactions from the AI research community have been overwhelmingly positive, particularly regarding the system's focus on "Sleep Architecture." Working with Stanford’s Dr. Robson Capasso and Dr. Clete Kushida, Samsung has integrated deep learning models that analyze REM cycle fragmentation and oxygen desaturation levels. These models were trained using federated learning—a decentralized AI training method that allows the system to learn from global datasets without ever accessing raw, identifiable patient data, addressing a major hurdle in medical AI: the balance between accuracy and privacy.
The Wearable Arms Race: Samsung’s Strategic Advantage
The introduction of the Brain Health suite significantly alters the competitive landscape for tech giants. While Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL) has long dominated the health-wearable space with its Apple Watch and ResearchKit, Samsung’s integration of the Galaxy Ring provides a distinct advantage in the quest for longitudinal dementia data. The "high compliance" nature of a ring—which users are more likely to wear 24/7 compared to a bulky smartwatch that requires daily charging—ensures an unbroken data stream. For a disease like dementia, where the most critical signals are found in long-term trends rather than isolated incidents, this data continuity is a strategic moat.
Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL), through its Fitbit and Pixel Watch lines, has focused heavily on generative AI "Health Coaches" powered by its Gemini models. However, Samsung’s partnership with Stanford Medicine provides a level of clinical validation that pure-play software companies often lack. By acquiring the health-sharing platform Xealth in 2025, Samsung has also built the infrastructure for users to share these AI insights directly with healthcare providers, effectively positioning the Galaxy ecosystem as a legitimate extension of the hospital ward.
Market analysts predict that this move will force a pivot among health-tech startups. Companies that previously focused on stand-alone cognitive assessment apps may find themselves marginalized as "Big Tech" integrates these features directly into the hardware layer. The strategic advantage for Samsung (KRX: 005930) lies in its "Knox Matrix" security, which processes the most sensitive cognitive data on-device, mitigating the "creep factor" associated with AI that monitors a user's every move and word.
A Milestone in the AI-Human Symbiosis
The wider significance of this breakthrough cannot be overstated. In the broader AI landscape, the focus is shifting from "Generative AI" (which creates content) to "Diagnostic AI" (which interprets reality). This Samsung-Stanford system represents a pinnacle of the latter. It fits into the burgeoning "longevity" trend, where the goal is not just to extend life, but to extend the "healthspan"—the years lived in good health. By identifying the biological "smoke" before the "fire" of full-blown dementia, this AI could fundamentally change the economics of aging, potentially saving billions in long-term care costs.
However, the development brings valid concerns to the forefront. The prospect of an AI "predicting" a person's cognitive demise raises profound ethical questions. Should an insurance company have access to a "Cognitive Health Score"? Could a detected decline lead to workplace discrimination before any symptoms are present? Comparisons have been drawn to the "Black Mirror" scenarios of predictive policing, but in a medical context. Despite these fears, the medical community views this as a milestone equivalent to the first AI-powered radiology tools, which transformed cancer detection from a game of chance into a precision science.
The Horizon: From Detection to Digital Therapeutics
Looking ahead, the next 12 to 24 months will be a period of intensive validation. Samsung has announced that the Brain Health features will enter a public beta program in select markets—including the U.S. and South Korea—by mid-2026. Experts predict that the next logical step will be the integration of "Digital Therapeutics." If the AI detects a decline in cognitive biomarkers, it could automatically tailor "brain games," suggest specific physical exercises, or adjust the home environment (via SmartThings) to reduce cognitive load, such as simplifying lighting or automating medication reminders.
The primary challenge remains regulatory. While Samsung’s sleep apnea detection already received FDA De Novo authorization in 2024, the bar for a "dementia early warning system" is significantly higher. The AI must prove that its "digital biomarkers" are not just correlated with dementia, but are reliable enough to trigger medical intervention without a high rate of false positives, which could cause unnecessary psychological distress for millions of aging users.
Conclusion: A New Era of Preventative Neurology
The collaboration between Samsung and Stanford represents one of the most ambitious applications of AI in the history of consumer technology. By turning the "noise" of our daily movements, sleep, and digital interactions into a coherent medical narrative, they have created a tool that could theoretically provide an extra decade of cognitive health for millions.
The key takeaway is that the smartphone and the wearable are no longer just tools for communication and fitness; they are becoming the most sophisticated diagnostic instruments in the human arsenal. In the coming months, the tech industry will be watching closely as the first waves of beta data emerge. If Samsung and Stanford can successfully navigate the regulatory and ethical minefields, the "Brain Health" suite may well be remembered as the moment AI moved from being a digital assistant to a life-saving sentinel.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.