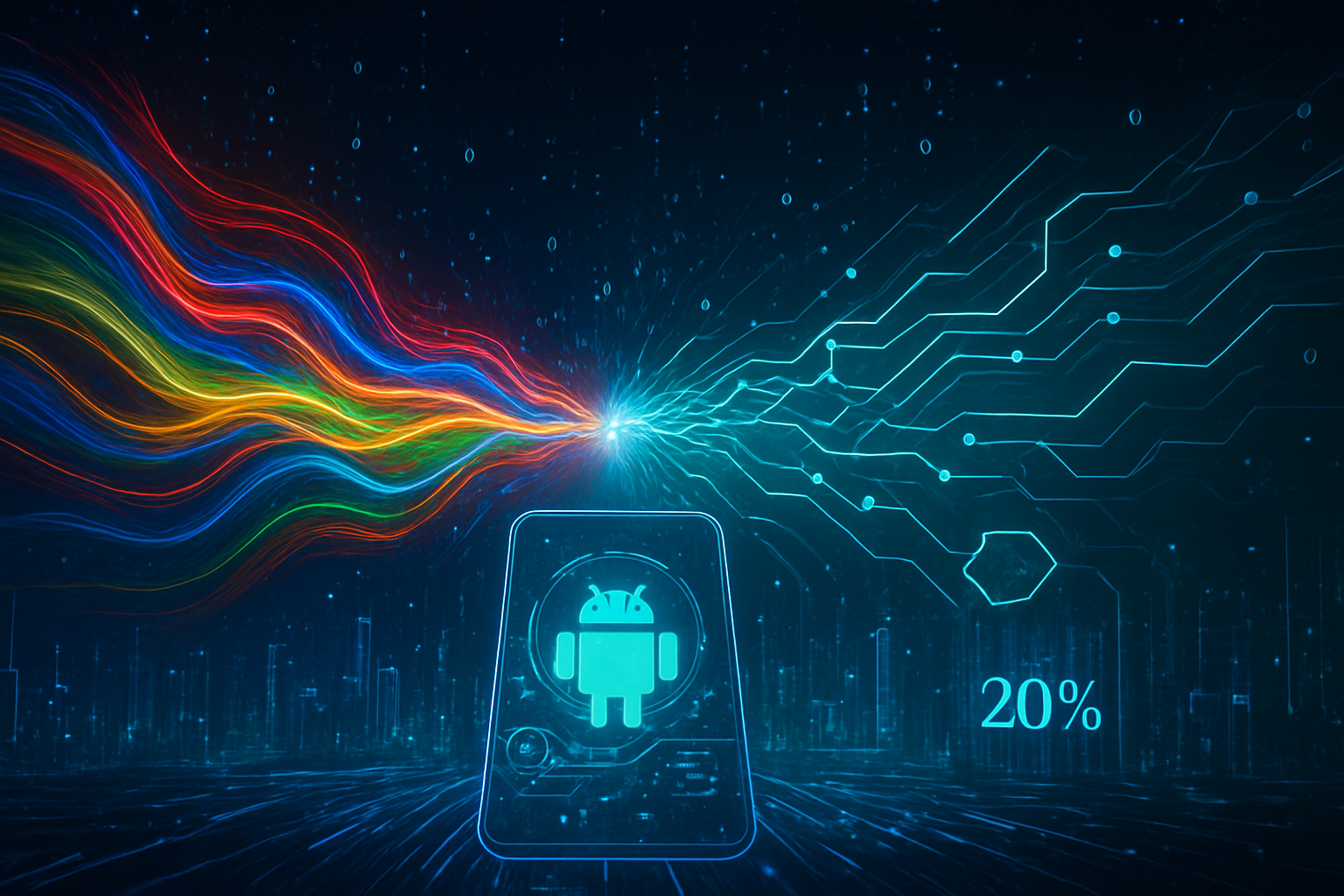
In a dramatic shift that has reshaped the artificial intelligence landscape over the past twelve months, Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOGL) has successfully leveraged its massive Android ecosystem to break the near-monopoly once held by OpenAI. As of January 26, 2026, new industry data confirms that Google Gemini has surged to a commanding 20% share of global LLM (Large Language Model) traffic, marking the most significant competitive challenge to ChatGPT since the AI boom began. This rapid ascent from a mere 5% market share a year ago signals a pivotal moment in the "Traffic War," as the battle for AI dominance moves from standalone web interfaces to deep system-level integration.
The implications of this surge are profound for the tech industry. While ChatGPT remains the individual market leader, its absolute dominance is waning under the pressure of Google’s "ambient AI" strategy. By making Gemini the default intelligence layer for billions of devices, Google has transformed the generative AI market from a destination-based experience into a seamless, omnipresent utility. This shift has forced a strategic "Code Red" at OpenAI and its primary backer, Microsoft Corp. (NASDAQ: MSFT), as they scramble to defend their early lead against the sheer distributional force of the Android and Chrome ecosystems.
The Engine of Growth: Technical Integration and Gemini 3
The technical foundation of Gemini’s 237% year-over-year growth lies in the release of Gemini 3 and its specialized mobile architecture. Unlike previous iterations that functioned primarily as conversational wrappers, Gemini 3 introduces a native multi-modal reasoning engine that operates with unprecedented speed and a context window exceeding one million tokens. This allow users to upload entire libraries of documents or hour-long video files directly through their mobile interface—a technical feat that remains a struggle for competitors constrained by smaller context windows.
Crucially, Google has optimized this power for mobile via Gemini Nano, an on-device version of the model that handles summarization, smart replies, and sensitive data processing without ever sending information to the cloud. This hybrid approach—using on-device hardware for speed and privacy while offloading complex reasoning to the cloud—has given Gemini a distinct performance edge. Users are reporting significantly lower latency in "Gemini Live" voice interactions compared to ChatGPT’s voice mode, primarily because the system is integrated directly into the Android kernel.
Industry experts have been particularly impressed by Gemini’s "Screen Awareness" capabilities. By integrating with the Android operating system at a system level, Gemini can "see" what a user is doing in other apps. Whether it is summarizing a long thread in a third-party messaging app or extracting data from a mobile banking statement to create a budget in Google Sheets, the model’s ability to interact across the OS has turned it into a true digital agent rather than just a chatbot. This "system-level" advantage is a moat that standalone apps like ChatGPT find nearly impossible to replicate without similar OS ownership.
A Seismic Shift in Market Positioning
The surge to 20% market share has fundamentally altered the competitive dynamics between AI labs and tech giants. For Alphabet Inc., this represents a successful defense of its core Search business, which many predicted would be cannibalized by AI. Instead, Google has integrated AI Overviews into its search results and linked them directly to Gemini, capturing user intent before it can migrate to OpenAI’s platforms. This strategic advantage is further bolstered by a reported $5 billion annual agreement with Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL), which utilizes Gemini models to enhance Siri’s capabilities, effectively placing Google’s AI at the heart of the world’s two largest mobile operating systems.
For OpenAI, the loss of nearly 20 points of market share in a single year has triggered a strategic pivot. While ChatGPT remains the preferred tool for high-level reasoning, coding, and complex creative writing, it is losing the battle for "casual utility." To counter Google’s distribution advantage, OpenAI has accelerated the development of its own search product and is reportedly exploring "SearchGPT" as a direct competitor to Google Search. However, without a mobile OS to call its own, OpenAI remains dependent on browser traffic and app downloads, a disadvantage that has allowed Gemini to capture the "middle market" of users who prefer the convenience of a pre-installed assistant.
The broader tech ecosystem is also feeling the ripple effects. Startups that once built "wrappers" around OpenAI’s API are finding it increasingly difficult to compete with Gemini’s free, integrated features. Conversely, companies within the Android and Google Workspace ecosystem are seeing increased productivity as Gemini becomes a native feature of their existing workflows. The "Traffic War" has proven that in the AI era, distribution and ecosystem integration are just as important as the underlying model’s parameters.
Redefining the AI Landscape and User Expectations
This milestone marks a transition from the "Discovery Phase" of AI—where users sought out ChatGPT to see what was possible—to the "Utility Phase," where AI is expected to be present wherever the user is working. Gemini’s growth reflects a broader trend toward "Ambient AI," where the technology fades into the background of the operating system. This shift mirrors the early days of the browser wars or the transition from desktop to mobile, where the platforms that controlled the entry points (the OS and the hardware) eventually dictated the market leaders.
However, Gemini’s rapid ascent has not been without controversy. Privacy advocates and regulatory bodies in both the EU and the US have raised concerns about Google’s "bundling" of Gemini with Android. Critics argue that by making Gemini the default assistant, Google is using its dominant position in mobile to stifle competition in the nascent AI market—a move that echoes the antitrust battles of the 1990s. Furthermore, the reliance on "Screen Awareness" has sparked intense debate over data privacy, as the AI essentially has a constant view of everything the user does on their device.
Despite these concerns, the market’s move toward 20% Gemini adoption suggests that for the average consumer, the convenience of integration outweighs the desire for a standalone provider. This mirrors the historical success of Google Maps and Gmail, which used similar ecosystem advantages to displace established incumbents. The "Traffic War" is proving that while OpenAI may have started the race, Google’s massive infrastructure and user base provide a "flywheel effect" that is incredibly difficult to slow down once it gains momentum.
The Road Ahead: Gemini 4 and the Agentic Future
Looking toward late 2026 and 2027, the battle is expected to evolve from simple text and voice interactions to "Agentic AI"—models that can take actions on behalf of the user. Google is already testing "Project Astra" features that allow Gemini to navigate websites, book travel, and manage complex schedules across both Android and Chrome. If Gemini can successfully transition from an assistant that "talks" to an agent that "acts," its market share could climb even higher, potentially reaching parity with ChatGPT by 2027.
Experts predict that OpenAI will respond by doubling down on "frontier" intelligence, focusing on the o1 and GPT-5 series to maintain its status as the "smartest" model for professional and scientific use. We may see a bifurcated market: OpenAI serving as the premium "Specialist" for high-stakes tasks, while Google Gemini becomes the ubiquitous "Generalist" for the global masses. The primary challenge for Google will be maintaining model quality and safety at such a massive scale, while OpenAI must find a way to secure its own distribution channels, possibly through a dedicated "AI phone" or deeper partnerships with hardware manufacturers like Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (KRX: 005930).
Conclusion: A New Era of AI Competition
The surge of Google Gemini to a 20% market share represents more than just a successful product launch; it is a validation of the "ecosystem-first" approach to artificial intelligence. By successfully transitioning billions of Android users from the legacy Google Assistant to Gemini, Alphabet has proven that it can compete with the fast-moving agility of OpenAI through sheer scale and integration. The "Traffic War" has officially moved past the stage of novelty and into a grueling battle for daily user habits.
As we move deeper into 2026, the industry will be watching closely to see if OpenAI can reclaim its lost momentum or if Google’s surge is the beginning of a long-term trend toward AI consolidation within the major tech platforms. The current balance of power suggests a highly competitive, multi-polar AI world where the winner is not necessarily the company with the best model, but the company that is most accessible to the user. For now, the "Traffic War" continues, with the Android ecosystem serving as Google’s most powerful weapon in the fight for the future of intelligence.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.