In a landmark moment for the semiconductor industry, Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) has officially transitioned into high-volume manufacturing (HVM) for its 18A (1.8nm-class) process node, powered by the industry’s first fleet of commercial High-Numerical Aperture (High-NA) Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines. This deployment marks the successful culmination of CEO Lip-Bu Tan’s aggressive "five nodes in four years" strategy, effectively ending a decade of manufacturing dominance by competitors and positioning Intel as the undisputed leader in the "Angstrom Era" of computing.
The immediate significance of this development cannot be overstated; by securing the first production-ready units of ASML (NASDAQ: ASML) Twinscan EXE:5200B systems, Intel has leapfrogged the traditional industry roadmap. These bus-sized machines are the key to unlocking the transistor densities required for the next generation of generative AI accelerators and ultra-efficient mobile processors. With the launch of the "Panther Lake" consumer chips and "Clearwater Forest" server processors in early 2026, Intel has demonstrated that its theoretical process leadership has finally translated into tangible, market-ready silicon.
The Technical Leap: Precision at the 8nm Limit
The transition from standard EUV (0.33 NA) to High-NA EUV (0.55 NA) represents the most significant shift in lithography since the introduction of EUV itself. The High-NA systems utilize a sophisticated anamorphic optics system that magnifies the X and Y axes differently, allowing for a resolution of just 8nm—a substantial improvement over the 13.5nm limit of previous generations. This precision enables a roughly 2.9x increase in transistor density, allowing engineers to cram billions of additional gates into the same physical footprint. For Intel, this means the 18A and upcoming 14A nodes can achieve performance-per-watt metrics that were considered impossible only three years ago.
Beyond pure density, the primary technical advantage of High-NA is the return to "single-patterning." As features shrank below the 5nm threshold, traditional EUV required "multi-patterning," a process where a single layer is exposed multiple times to achieve the desired resolution. This added immense complexity, increased the risk of stochastic (random) defects, and lengthened production cycles. High-NA EUV eliminates these extra steps for critical layers, reducing the number of process stages from approximately 40 down to fewer than 10. This streamlined workflow has allowed Intel to stabilize 18A yields between 60% and 65%, a healthy margin that ensures profitable mass production.
Industry experts have been particularly impressed by Intel’s mastery of "field-stitching." Because High-NA optics reduce the exposure field size by half, chips larger than a certain dimension must be stitched together across two exposures. Intel’s Oregon D1X facility has demonstrated an overlay accuracy of 0.7nm during this process, effectively solving the "half-field" problem that many analysts feared would delay High-NA adoption. This technical breakthrough ensures that massive AI GPUs, such as those designed by NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA), can still be manufactured as monolithic dies or large-scale chiplets on the 14A node.
Initial reactions from the research community have been overwhelmingly positive, with many noting that Intel has successfully navigated the "Valley of Death" that claimed its previous 10nm and 7nm efforts. By working in a close "co-optimization" partnership with ASML, Intel has not only received the hardware first but has also developed the requisite photoresists and mask technologies ahead of its peers. This integrated approach has turned the Oregon D1X "Mod 3" facility into the world's most advanced semiconductor R&D hub, serving as the blueprint for upcoming high-volume fabs in Arizona and Ohio.
Reshaping the Foundry Landscape and Competitive Stakes
Intel’s early adoption of High-NA EUV has sent shockwaves through the foundry market, directly challenging the hegemony of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (NYSE: TSM). While TSMC has opted for a more conservative path, sticking with 0.33 NA EUV for its N2 and A16 nodes, Intel’s move to 18A and 14A has attracted "whale" customers seeking a competitive edge. Most notably, reports indicate that Apple (NASDAQ: AAPL) has secured significant capacity for 18A-Performance (18AP) manufacturing, marking the first time in over a decade that the iPhone maker has diversified its leading-edge production away from TSMC.
The strategic advantage for Intel Foundry is now clear: by being the only provider with a calibrated High-NA fleet in early 2026, they offer a "fast track" for AI companies. Giants like Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT) and NVIDIA are reportedly in deep negotiations for 14A capacity to power the 2027 generation of AI data centers. This shift repositioned Intel not just as a chipmaker, but as a critical infrastructure partner for the AI revolution. The ability to provide "backside power delivery" (PowerVia) combined with High-NA lithography gives Intel a unique architectural stack that TSMC and Samsung are still working to match in high-volume settings.
For Samsung, the pressure is equally intense. Although the South Korean giant received its first EXE:5200B modules in late 2025, it is currently racing to catch up with Intel’s yield stability. Samsung is targeting its SF2 (2nm) node for AI chips for Tesla and its own Exynos line, but Intel’s two-year lead in High-NA tool experience provides a significant buffer. This competitive gap has allowed Intel to command premium pricing for its foundry services, contributing to the company's first positive cash flow from foundry operations in years and driving its stock toward a two-year high near $50.
The disruption extends to the broader ecosystem of EDA (Electronic Design Automation) and materials suppliers. Companies that optimized their software for Intel's High-NA PDK 0.5 are seeing a surge in demand, as the entire industry realizes that 0.55 NA is the only viable path to 1.4nm and beyond. Intel’s willingness to take the financial risk of these $380 million machines—a risk that TSMC famously avoided early on—has fundamentally altered the power dynamics of the semiconductor supply chain, shifting the center of gravity back toward American manufacturing.
The Geopolitics of Moore’s Law and the AI Landscape
The deployment of High-NA EUV is more than a corporate milestone; it is a pivotal event in the broader AI landscape. As generative AI models grow in complexity, the demand for "compute density" has become the primary bottleneck for technological progress. Intel’s ability to manufacture 1.8nm and 1.4nm chips at scale provides the physical foundation upon which the next generation of Large Language Models (LLMs) will be trained. This breakthrough effectively extends the life of Moore’s Law, proving that the physical limits of silicon can be pushed further through extreme optical engineering.
From a geopolitical perspective, Intel’s High-NA lead represents a significant win for US-based semiconductor manufacturing. With the backing of the CHIPS Act and a renewed focus on domestic "foundry resilience," the successful ramp of 18A in Oregon and Arizona reduces the global tech industry’s over-reliance on a single geographic point of failure in East Asia. This "silicon diplomacy" has become a central theme of 2026, as governments recognize that the nation with the most advanced lithography tools effectively controls the "high ground" of the AI era.
However, the transition is not without concerns. The sheer cost of High-NA EUV tools—upwards of $380 million per unit—threatens to create a "billionaire’s club" of semiconductor manufacturing, where only a handful of companies can afford to compete. There are also environmental considerations; these machines consume massive amounts of power and require specialized chemical infrastructures. Intel has addressed some of these concerns by implementing "green fab" initiatives, but the industry-wide shift toward such energy-intensive equipment remains a point of scrutiny for ESG-focused investors.
Comparing this to previous milestones, the High-NA era is being viewed with the same reverence as the transition from 193nm immersion lithography to EUV in the late 2010s. Just as EUV enabled the 7nm and 5nm nodes that powered the first wave of modern AI, High-NA is the catalyst for the "Angstrom age." It represents a "hard-tech" victory in an era often dominated by software, reminding the world that the "intelligence" in artificial intelligence is ultimately bound by the laws of physics and the precision of the machines that carve it into silicon.
Future Horizons: The Roadmap to 14A and Hyper-NA
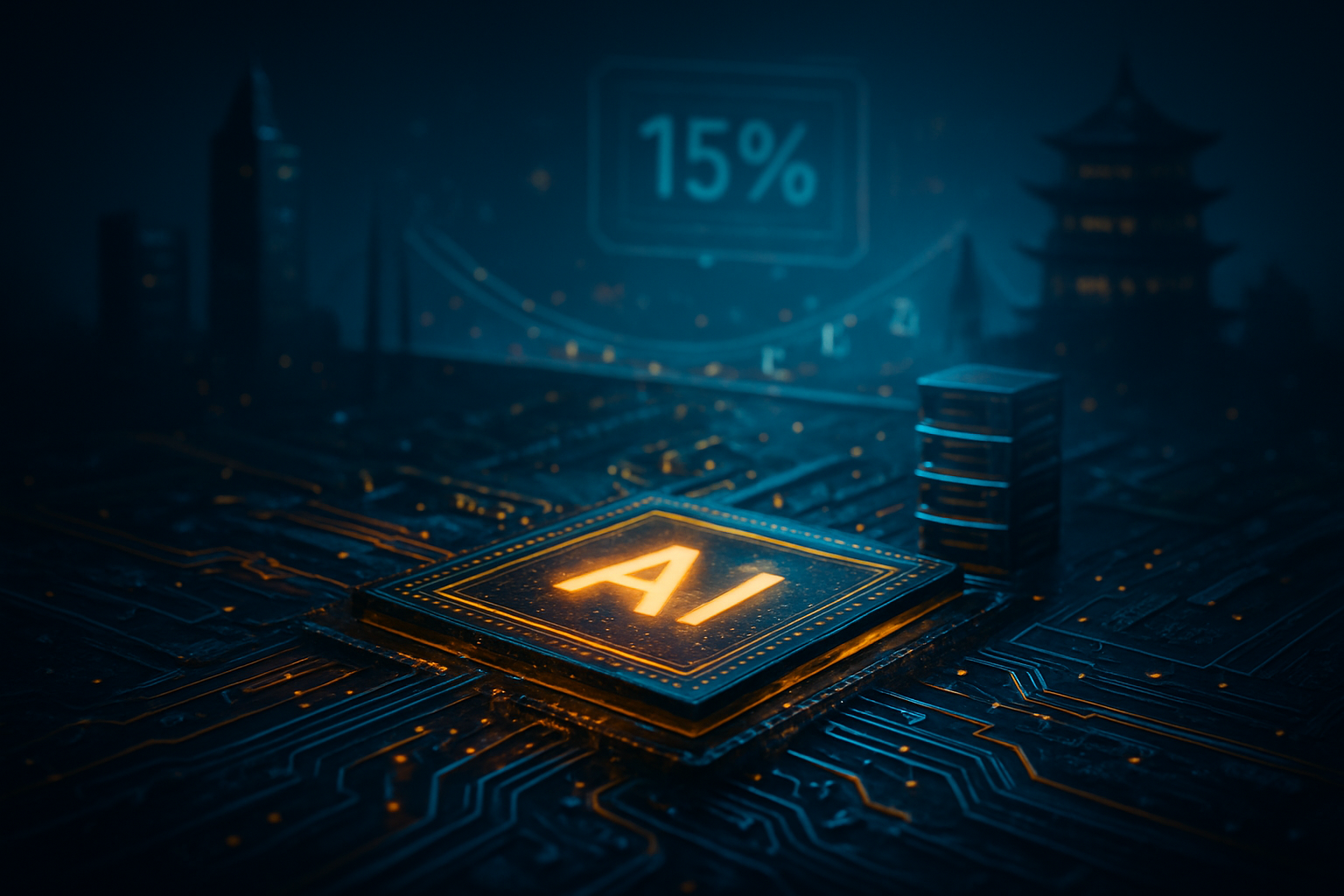
Looking ahead, the next 24 months will be defined by the transition from 18A to 14A. Intel’s 14A node, designed from the ground up to utilize High-NA EUV, is currently in the pilot phase with risk production slated for late 2026. Experts predict that 14A will offer a further 15% improvement in performance-per-watt over 18A, making it the premier choice for the autonomous vehicle and edge-computing markets. The development of 14A-P (Performance) and 14A-E (Efficiency) variants is already underway, suggesting a long and productive life for this process generation.
The long-term horizon also includes discussions of "Hyper-NA" (0.75 NA) lithography. While ASML has only recently begun exploring the feasibility of Hyper-NA, Intel’s early success with 0.55 NA has made them the most likely candidate to lead that next transition in the 2030s. The immediate challenge, however, will be managing the economic feasibility of these nodes. As Intel moves toward the 1nm (10A) mark, the cost of masks and the complexity of 3D-stacked transistors (CFETs) will require even deeper collaboration between toolmakers, foundries, and chip designers.
What experts are watching for next is the first "third-party" silicon to roll off Intel's 18A lines. While Intel’s internal "Panther Lake" is the proof of concept, the true test of their "process leadership" will be the performance of chips from customers like NVIDIA or Microsoft. If these chips outperform their TSMC-manufactured counterparts, it will trigger a massive migration of design wins toward Intel. The company's ability to maintain its "first-mover" advantage while scaling up its global manufacturing footprint will be the defining story of the semiconductor industry through the end of the decade.
A New Era for Intel and Global Tech
The successful deployment of High-NA EUV and the high-volume ramp of 18A mark the definitive return of Intel as a global manufacturing powerhouse. By betting early on ASML’s most advanced technology, Intel has not only regained its process leadership but has also rewritten the competitive rules of the foundry business. The significance of this achievement in AI history is profound; it provides the essential hardware roadmap for the next decade of silicon innovation, ensuring that the exponential growth of AI capabilities remains unhindered by hardware limitations.
The long-term impact of this development will be felt across every sector of the global economy, from the data centers powering the world's most advanced AI to the consumer devices in our pockets. Intel’s "comeback" is no longer a matter of corporate PR, but a reality reflected in its yield rates, its customer roster, and its stock price. In the coming weeks and months, the industry will be closely monitoring the first 18A benchmarks and the progress of the Arizona Fab 52 installation, as the world adjusts to a new landscape where Intel once again leads the way in silicon.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.