The University of Waterloo has unveiled a groundbreaking AI-radar system poised to redefine remote health monitoring and early disease detection. This innovative, non-invasive technology tracks subtle changes in a patient's walk and other vital signs, offering an unprecedented "invisible safety net" for individuals, particularly in vulnerable populations and busy healthcare settings. By leveraging advanced radar and artificial intelligence, the system promises to shift healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive, personalized intervention, signaling a significant leap forward in AI's application to human well-being.
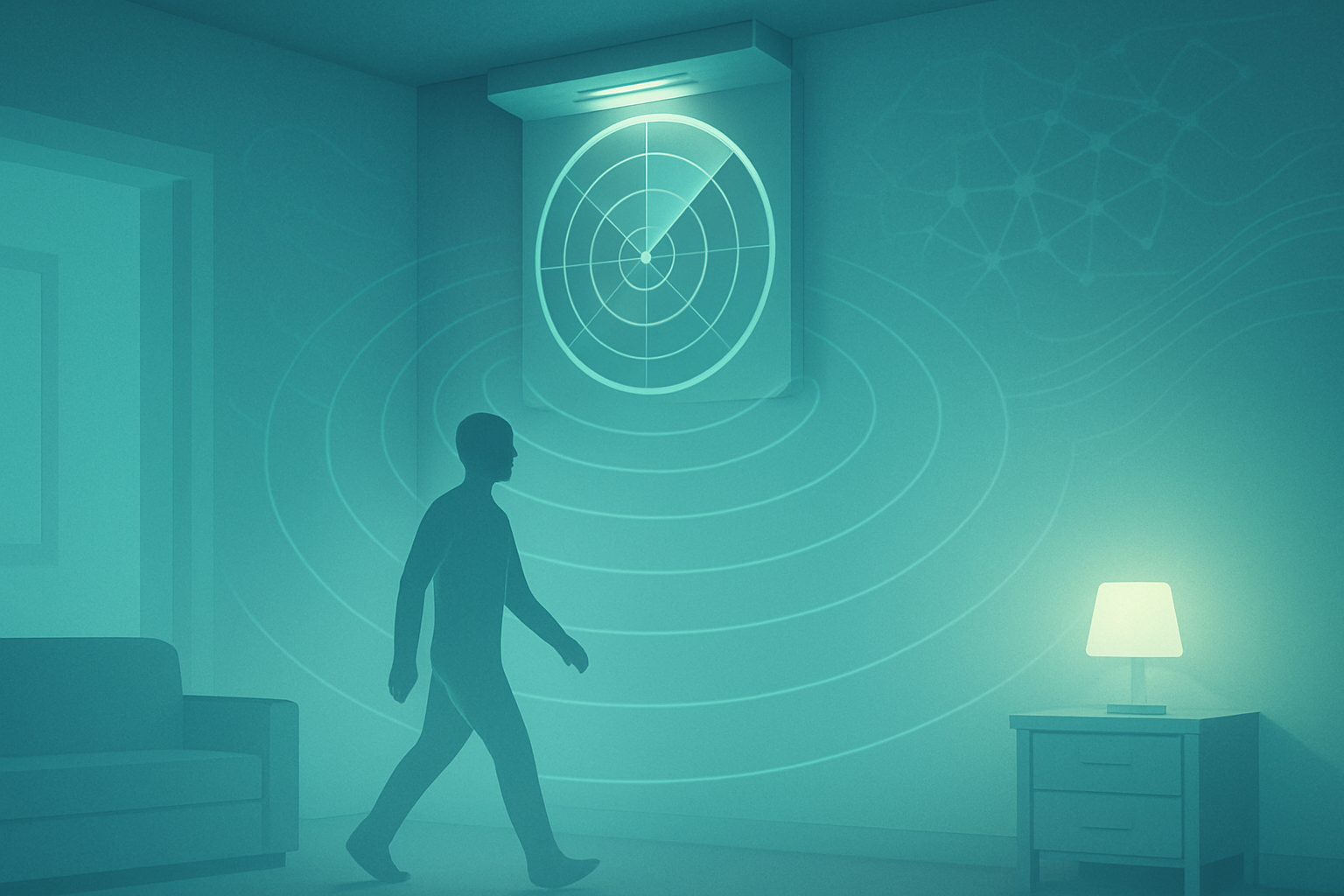
At its core, this breakthrough represents a profound evolution in how we perceive and manage health. Gone are the days of cumbersome wearables or intrusive camera-based surveillance. Instead, a discreet, wall-mounted device, no larger than a deck of cards, silently monitors individuals, detecting minute physiological changes that can signal emerging health issues long before they become critical. This capability holds immediate and profound significance for an overburdened healthcare system, offering 24/7 monitoring and the potential to save lives through early detection and intervention.
A New Era of Non-Invasive Diagnostics: How AI-Radar Works
The University of Waterloo's AI-radar system is a marvel of engineering and artificial intelligence. It operates by emitting low-power radio waves that bounce off individuals, capturing these reflections with a sensitive sensor. These signals are then converted into "heatmaps" that illustrate movement. Proprietary AI algorithms are the true intelligence behind the system, meticulously processing these heatmaps to distinguish individuals, filter out environmental noise, and precisely track each person's trajectory over time. This allows for the accurate calculation of walking speed, a crucial "functional vital sign" whose subtle decline can indicate frailty and other health problems. Beyond gait, the system can also monitor other daily activities, constructing a comprehensive picture of an individual's mobility and behavior.
The technical sophistication extends to various applications. For cardiac monitoring, the AI converts radar data into a unique heartbeat signature, trained to recognize deviations that might indicate elevated risks of serious cardiac events, such as changes in the corrected QTc interval. It also monitors heart rate variability with millisecond precision. For non-invasive glucose monitoring, machine learning algorithms analyze reflected radio waves, detecting changes based on over 500 wave features, continuously refining measurements. The radar devices themselves are highly miniaturized, ranging from "smaller than a USB thumb drive" for in-car health monitoring to a cellphone-sized box for unobtrusive heart monitoring, and the deck-of-cards-sized unit for gait analysis in care facilities. Accuracy has been impressive, with over 90% for vital signs monitoring during sleep and comparable results to medical-grade electrocardiograms (ECGs) for heart monitoring.
This approach dramatically differs from previous health monitoring technologies. Unlike wearable devices, it requires no physical contact, eliminating discomfort, charging needs, and compliance issues. Crucially, it preserves privacy by detecting movement and physiological signals without capturing identifiable video footage, a key advantage over camera systems. Its multi-person capability allows for simultaneous monitoring in crowded environments, a challenge for traditional one-on-one methods. Initial reactions from the AI research community and industry have been overwhelmingly positive, with collaborations already underway with major players like Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL) and German hardware company Infineon (FSE: IFX). A startup, Gold Sentinel, has been launched to commercialize the gait monitoring system, underscoring the strong belief in its market potential.
Reshaping the AI and Tech Landscape: A Competitive Edge
The advent of the University of Waterloo's AI-radar system carries significant implications for AI companies, tech giants, and startups across multiple sectors. Automotive manufacturers like Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA), General Motors (NYSE: GM), Ford (NYSE: F), Mercedes-Benz (ETR: MBG), and BMW (ETR: BMW) stand to benefit immensely by integrating this technology. It offers a powerful differentiator, transforming vehicles into "mobile medical hubs" capable of proactive driver and passenger health monitoring, thereby enhancing safety and well-being in an increasingly competitive market. This could lead to a new battleground for in-car experiences, with tech giants vying to offer the most comprehensive health-aware platforms.
Health tech and wearable companies, while potentially facing a shift in some use cases, could also find new avenues for collaboration. Companies specializing in remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and digital health platforms could partner with automotive and smart home providers to leverage the continuous, passive data stream. Startups focusing on AI-driven diagnostics and preventative healthcare will find fertile ground for innovation, utilizing this novel data source for more accurate and timely interventions. Even insurance companies might develop new, personalized models based on real-time health data that could predict medical emergencies.
The technology poses a subtle disruption to traditional wearables for specific scenarios like in-car monitoring, where a non-contact solution offers superior convenience. However, it is more likely to complement than replace, serving different niches. Existing in-car safety systems, often reliant on driver alertness through eye-tracking, could be significantly enhanced by direct physiological monitoring. For major AI labs, this development emphasizes the growing importance of non-contact physiological monitoring and robust AI models capable of interpreting complex biological signals from radar data, potentially leading to new R&D focuses and intellectual property. The strategic advantage lies in its non-invasive convenience, proactive health capabilities, and the richness of continuous data for further AI development, offering a powerful competitive edge for early adopters.
A Wider Lens: AI's March Towards Ambient Intelligence
This AI-radar system fits perfectly within the broader AI landscape, embodying trends such as pervasive AI, edge computing, real-time data analysis, and human-centric ambient intelligence. By embedding AI-powered sensors into everyday environments, it moves beyond traditional AI applications to create an "invisible safety net" that proactively supports human well-being. This represents a significant evolution from earlier AI milestones, which often focused on processing digital data or required direct user interaction. The system's ability to interpret subtle, continuous, and often noisy signals from a non-invasive source showcases AI's growing capability to derive meaningful insights from complex, real-world data.
The societal and healthcare impacts are profound. Beyond in-vehicle monitoring, the technology can transform long-term care facilities, providing continuous gait analysis to prevent falls and track mobility decline. It offers a new paradigm for cardiac health monitoring, potentially identifying risks before symptoms manifest. The vision of non-invasive glucose monitoring, miniaturized into a smartwatch, promises to liberate millions from daily finger pricks. This shift towards proactive, personalized healthcare could drastically reduce hospital visits, improve patient outcomes, and alleviate pressure on healthcare systems.
However, such pervasive monitoring technologies also bring critical concerns. Privacy is paramount; even without visual data, continuous monitoring of vital signs and movements can be perceived as intrusive, and AI can infer highly sensitive information from seemingly innocuous data. Data security is another major challenge, as health data is a prime target for cyberattacks, and even encrypted communications can leak inferential privacy. Ethical frameworks and robust regulatory guidelines will be essential to ensure responsible deployment, address potential biases in AI models, and prevent over-reliance on automated systems. This development, while revolutionary, underscores the ongoing need for careful consideration of privacy, security, and ethical implications as AI becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives.
The Horizon: From Smart Cars to Ubiquitous Health Guardians
The future developments for the University of Waterloo's AI-radar system are ambitious and transformative. In the near term, researchers are focused on refining prototypes, expanding testing to diverse populations and cardiovascular conditions, and enhancing the driver health monitoring system to generate comprehensive medical reports and facilitate emergency communication. For non-invasive glucose monitoring, the goal is to precisely quantify glucose levels through the skin and miniaturize the radar device for integration into a low-cost, low-power smartwatch.
The long-term vision paints a picture of ubiquitous health monitoring. Cars are envisioned as fully integrated "mobile medical hubs," continuously monitoring the health of all occupants. Smart homes will feature radar sensors embedded in furniture, silently tracking heart activity, stress, and fatigue. In healthcare facilities, the AI-radar system will evolve into an "invisible safety net," monitoring the full spectrum of mobility and behavioral changes to proactively alert caregivers. Beyond glucose, the non-invasive system is expected to track a broader range of health indicators, including blood pressure. Potential applications extend to critical care units for remote patient monitoring, child monitoring, and sophisticated early warning systems for various health events.
Challenges remain, primarily in achieving medical-grade accuracy for a wider range of health parameters, further miniaturization and power efficiency, and refining AI algorithms to filter out complex environmental noise. Commercialization and regulatory hurdles also need to be navigated. However, experts are highly optimistic. Dr. George Shaker, a lead researcher, predicts radar sensors will become as commonplace in smart homes and vehicles as seatbelts or airbags, transforming cars into future medical hubs. He hopes a wearable non-invasive glucose monitoring device could be on the market within the next five years, emphasizing the technology's "enormous potential to save lives" if widely adopted. The overarching prediction is a fundamental shift in health monitoring from invasive to seamless, non-contact, and proactive methods.
A New Chapter in AI's Health Revolution
The University of Waterloo's AI-radar system marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing AI health revolution. Its core innovation lies in providing continuous, non-invasive, and privacy-preserving health monitoring, offering an "invisible safety net" that can detect subtle health changes long before they escalate. This breakthrough stands as a testament to AI's power to move beyond reactive analysis to proactive, predictive intervention, fundamentally transforming preventive medicine and personalized healthcare.
This development's significance in AI history is profound, representing a leap towards truly ambient intelligence where technology seamlessly integrates into our environment to support human well-being. The long-term impact promises safer transportation, smarter homes, and a healthcare system better equipped for early detection and personalized care. However, as this powerful technology becomes more pervasive, ongoing vigilance regarding data privacy, security, and ethical deployment will be crucial.
In the coming weeks and months, keep a close watch for further clinical validation results, particularly expanded trials in diverse real-world settings. Announcements regarding commercialization partnerships with major automotive, health tech, and smart home companies will be key indicators of market adoption. Additionally, observe the evolving regulatory landscape as governments grapple with establishing standards for these innovative, sensitive technologies. The University of Waterloo's AI-radar system is not just a technological advancement; it's a blueprint for a healthier, more proactively monitored future, powered by the quiet vigilance of artificial intelligence.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.