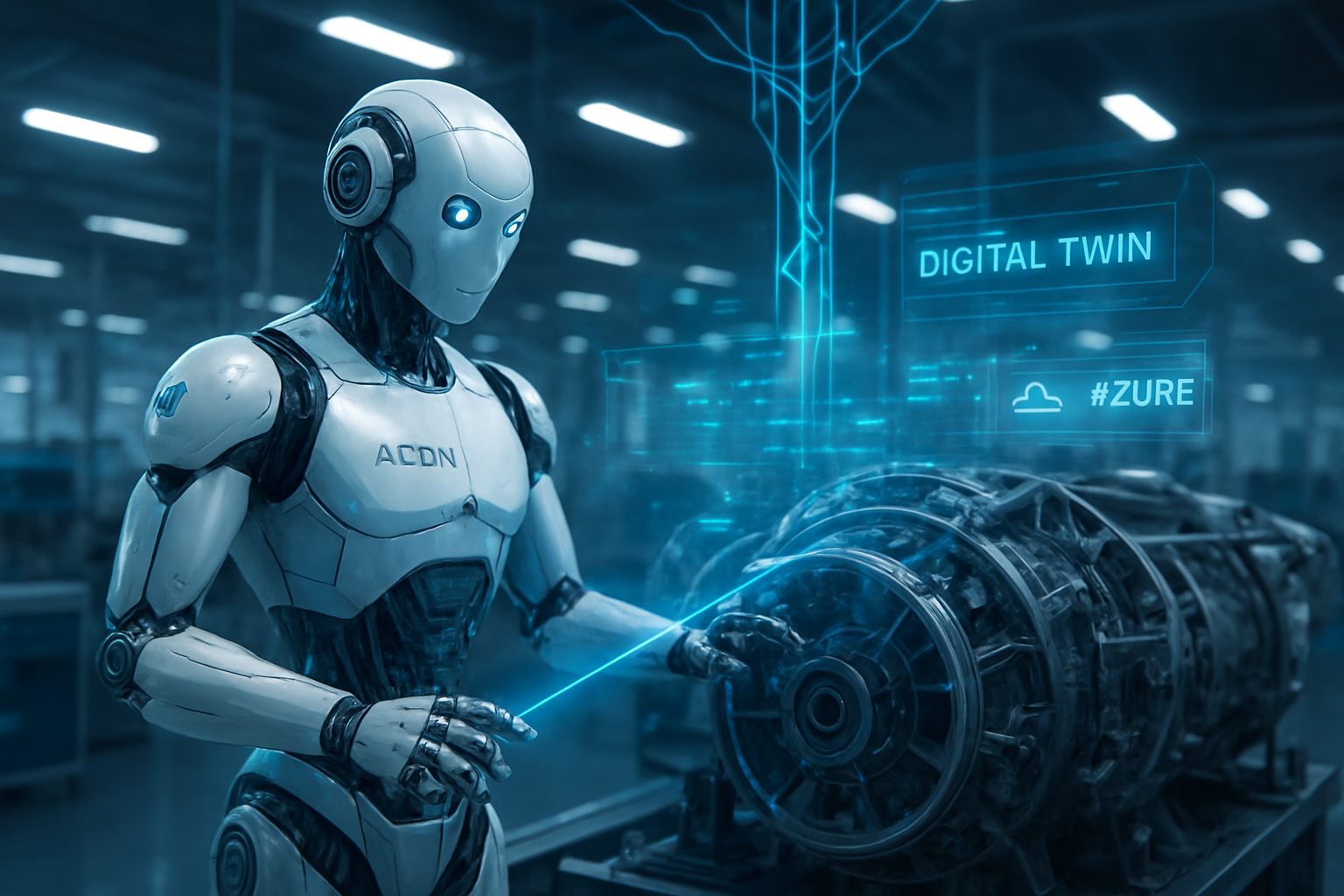
In a move that signals the transition of humanoid robotics from experimental prototypes to essential industrial tools, Hexagon Robotics—a division of the global technology leader Hexagon AB (STO: HEXA-B)—and Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT) have announced a landmark partnership to deploy production-ready humanoid robots for industrial defect detection. The collaboration centers on the AEON humanoid, a sophisticated robotic platform designed to integrate seamlessly into manufacturing environments, providing a level of precision and mobility that traditional automated systems have historically lacked.
The significance of this announcement lies in its focus on "Physical AI"—the convergence of advanced large-scale AI models with high-precision hardware to solve real-world industrial challenges. By combining Hexagon’s century-long expertise in metrology and sensing with Microsoft’s Azure cloud and AI infrastructure, the partnership aims to address the critical labor shortages and quality control demands currently facing the global manufacturing sector. Industry experts view this as a pivotal moment where humanoid robots move beyond "walking demos" and into active roles on the factory floor, performing tasks that require both human-like dexterity and superhuman measurement accuracy.
Precision in Motion: The Technical Architecture of AEON
The AEON humanoid is a 165-cm (5'5") tall, 60-kg machine designed specifically for the rigors of heavy industry. Unlike many of its contemporaries that focus solely on bipedal walking, AEON features a hybrid locomotion system: its bipedal legs are equipped with integrated wheels in the feet. This allows the robot to navigate complex obstacles like stairs and uneven surfaces while maintaining high-speed, energy-efficient movement on flat factory floors. With 34 degrees of freedom and five-fingered dexterous hands, AEON is capable of a 15-kg peak payload, making it robust enough for machine tending and part inspection.
At the heart of AEON’s defect detection capability is an unprecedented sensor suite. The robot is equipped with over 22 sensors, including LiDAR, depth sensors, and a 360-degree panoramic camera system. Most notably, it features specialized infrared and autofocus cameras capable of micron-level inspection. This allows AEON to act as a mobile quality-control station, detecting surface imperfections, assembly errors, or structural micro-fractures that are invisible to the naked eye. The robot's "brain" is powered by the NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA) Jetson Orin platform, which handles real-time edge processing and spatial intelligence, with plans to upgrade to the more powerful NVIDIA IGX Thor in future iterations.
The software stack, developed in tandem with Microsoft, utilizes Multimodal Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models. These AI frameworks allow AEON to process natural language instructions and visual data simultaneously, enabling a feature known as "One-Shot Imitation Learning." This allows a human supervisor to demonstrate a task once—such as checking a specific weld on an aircraft wing—and the robot can immediately replicate the action with high precision. This differs drastically from previous robotic approaches that required weeks of manual programming and rigid, fixed-path configurations.
Initial reactions from the AI research community have been overwhelmingly positive, particularly regarding the integration of Microsoft Fabric for real-time data intelligence. Dr. Aris Syntetos, a leading researcher in autonomous systems, noted that "the ability to process massive streams of metrology-grade data in the cloud while the robot is still in motion is the 'holy grail' of industrial automation." By leveraging Azure IoT Operations, the partnership ensures that fleets of AEON robots can be managed, updated, and synchronized across global manufacturing sites from a single interface.
Strategic Dominance and the Battle for the Industrial Metaverse
This partnership places Microsoft and Hexagon in direct competition with other major players in the humanoid space, such as Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) with its Optimus project and Figure AI, which is backed by OpenAI and Amazon (NASDAQ: AMZN). However, Hexagon’s strategic advantage lies in its specialized focus on metrology. While Tesla’s Optimus is positioned as a general-purpose laborer, AEON is a specialized precision instrument. This distinction is critical for industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where a fraction of a millimeter can be the difference between a successful build and a catastrophic failure.
Microsoft stands to benefit significantly by cementing Azure as the foundational operating system for the next generation of robotics. By providing the AI training infrastructure and the cloud-to-edge connectivity required for AEON, Microsoft is positioning itself as an indispensable partner for any industrial firm looking to automate. This move also bolsters Microsoft’s "Industrial Metaverse" strategy, as AEON robots continuously capture 3D data to create live "Digital Twins" of factory environments using Hexagon’s HxDR platform. This creates a feedback loop where the digital model of the factory is updated in real-time by the very robots working within it.
The disruption to existing services could be profound. Traditional fixed-camera inspection systems and manual quality assurance teams may see their roles diminish as mobile, autonomous humanoids provide more comprehensive coverage at a lower long-term cost. Furthermore, the "Robot-as-a-Service" (RaaS) model, supported by Azure’s subscription-based infrastructure, could lower the barrier to entry for mid-sized manufacturers, potentially reshaping the competitive landscape of the global supply chain.
Scaling Physical AI: Broader Significance and Ethical Considerations
The Hexagon-Microsoft partnership fits into a broader trend of "Physical AI," where the digital intelligence of LLMs (Large Language Models) is finally being granted a physical form capable of meaningful work. This represents a significant milestone in AI history, moving the technology away from purely generative tasks—like writing text or code—and toward the physical manipulation of the world. It mirrors the transition of the internet from a source of information to a platform for commerce, but on a much more tangible scale.
However, the deployment of such advanced systems is not without its concerns. The primary anxiety revolves around labor displacement. While Hexagon and Microsoft emphasize that AEON is intended to "augment" the workforce and handle "dull, dirty, and dangerous" tasks, the high efficiency of these robots will inevitably lead to questions about the future of human roles in manufacturing. There are also significant safety implications; a 60-kg robot operating at high speeds in a human-populated environment requires rigorous safety protocols and "fail-safe" AI alignment to prevent accidents.
Comparatively, this breakthrough is being likened to the introduction of the first industrial robotic arms in the 1960s. While those arms revolutionized assembly lines, they were stationary and "blind." AEON represents the next logical step: a robot that can see, reason, and move. The integration of Microsoft’s AI models ensures that these robots are not just following a script but are capable of making autonomous decisions based on the quality of the parts they are inspecting.
The Road Ahead: 24/7 Operations and Autonomous Maintenance
In the near term, we can expect to see the results of pilot programs currently underway at firms like Pilatus, a Swiss aircraft manufacturer, and Schaeffler, a global leader in motion technology. These pilots are focusing on high-stakes tasks such as part inspection and machine tending. If successful, the rollout of AEON is expected to scale rapidly throughout 2026, with Hexagon aiming for full-scale commercial availability by the end of the year.
The long-term vision for the partnership includes "autonomous maintenance," where AEON robots could potentially identify and repair their own minor mechanical issues or perform maintenance on other factory equipment. Challenges remain, particularly regarding battery life and the "edge-to-cloud" latency required for complex decision-making. While the current 4-hour battery life is mitigated by a hot-swappable system, achieving true 24-hour autonomy without human intervention is the next major technical hurdle.
Experts predict that as these robots become more common, we will see a shift in factory design. Future manufacturing plants may be optimized for humanoid movement rather than human comfort, with tighter spaces and vertical storage that AEON can navigate more effectively than traditional forklifts or human workers.
A New Chapter in Industrial Automation
The partnership between Hexagon Robotics and Microsoft marks a definitive shift in the AI landscape. By focusing on the specialized niche of industrial defect detection, the two companies have bypassed the "uncanny valley" of general-purpose robotics and delivered a tool with immediate, measurable value. AEON is not just a robot; it is a mobile, intelligent sensor platform that brings the power of the cloud to the physical factory floor.
The key takeaway for the industry is that the era of "Physical AI" has arrived. The significance of this development in AI history cannot be overstated; it represents the moment when artificial intelligence gained the hands and eyes necessary to build the world around it. As we move through 2026, the tech community will be watching closely to see how these robots perform in the high-pressure environments of aerospace and automotive assembly.
In the coming months, keep an eye on the performance metrics released from the Pilatus and Schaeffler pilots. These results will likely determine the speed at which other industrial giants adopt the AEON platform and whether Microsoft’s Azure-based robotics stack becomes the industry standard for the next decade of manufacturing.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.