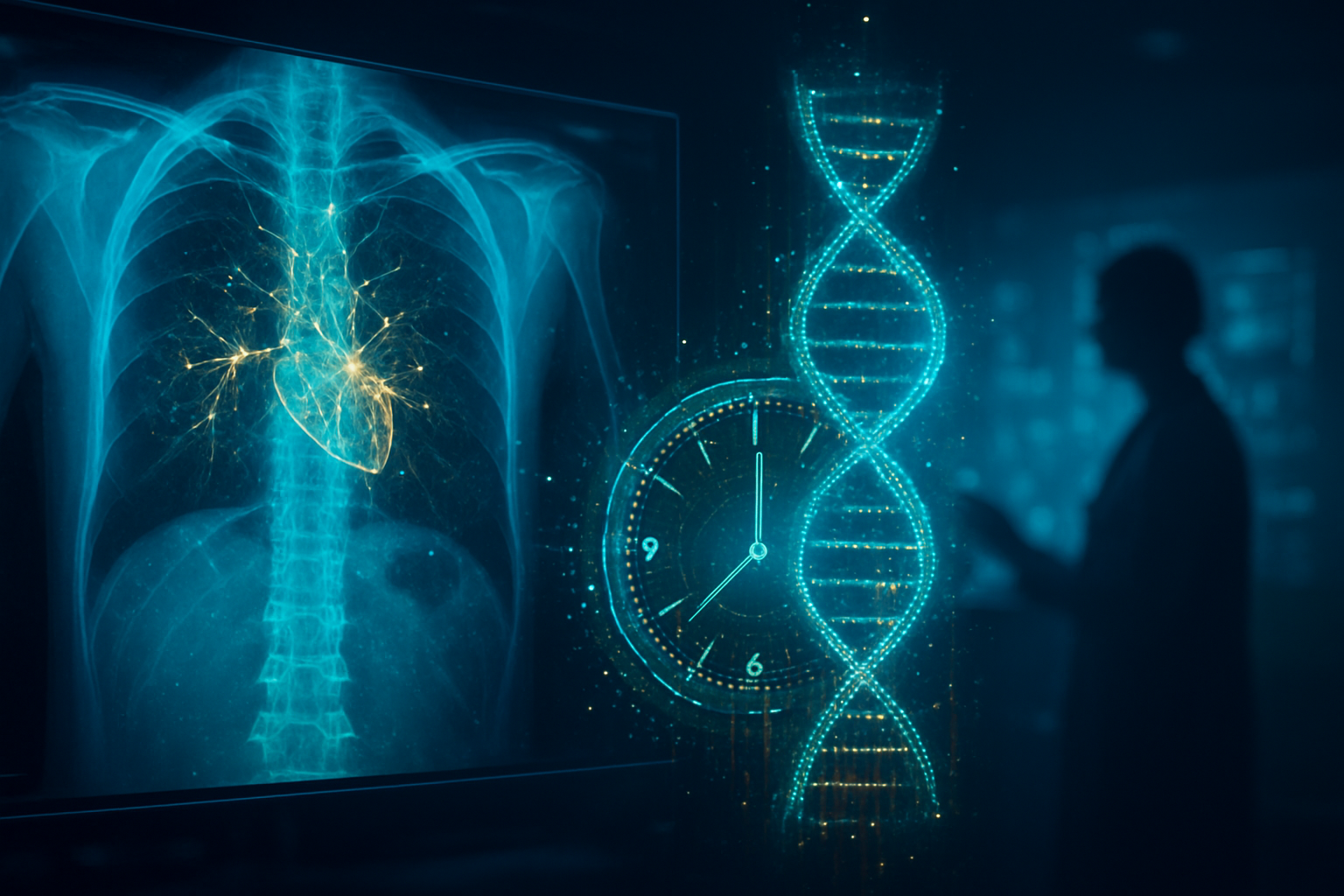
As of January 26, 2026, the medical community has officially entered the era of "Healthspan Engineering." A series of breakthroughs in artificial intelligence has transformed the humble chest X-ray—a diagnostic staple for over a century—into a sophisticated "biological clock." By utilizing deep learning models to analyze subtle anatomical markers invisible to the human eye, researchers are now able to predict a patient's biological age with startling accuracy, often revealing cardiovascular risks and mortality patterns years before clinical symptoms manifest.
This development marks a paradigm shift from reactive to proactive care. While traditional radiology focuses on identifying active diseases like pneumonia or fractures, these new AI models scan for the "molecular wear and tear" of aging. By identifying "rapid agers"—individuals whose biological age significantly exceeds their chronological years—healthcare systems are beginning to deploy targeted interventions that could potentially add decades of healthy life to the global population.
Deep Learning Under the Hood: Decoding the Markers of Aging
The technical backbone of this revolution lies in advanced neural network architectures, most notably the CXR-Age model developed by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and the ConvNeXt-based aging clocks pioneered by Osaka Metropolitan University. These models were trained on massive longitudinal datasets, including the PLCO Cancer Screening Trial, encompassing hundreds of thousands of chest radiographs paired with decades of health outcomes. Unlike human radiologists, who typically assess the "cardiothoracic ratio" (the width of the heart relative to the chest), these AI systems utilize Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) to identify micro-architectural shifts.
Technically, these AI models excel at detecting "invisible" markers such as subtle aortic arch calcification, thinning of the pulmonary artery walls, and shifts in the "cardiac silhouette" that suggest early-stage heart remodeling. For instance, the ConvNeXt architecture—a modern iteration of convolutional neural networks—maintains a 0.95 correlation coefficient with chronological age in healthy individuals. When a discrepancy occurs, such as an AI-predicted age that is five years older than the patient's actual age, it serves as a high-confidence signal for underlying pathologies like hypertension, COPD, or hyperuricemia. Recent validation studies published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity show that a "biological age gap" of just five years is associated with a 2.4x higher risk of cardiovascular mortality, a metric far more precise than current blood-based epigenetic clocks.
Market Disruptors: Tech Giants and Startups Racing for the 'Sixth Vital Sign'
The commercialization of biological aging clocks has triggered a gold rush among medical imaging titans and specialized AI startups. GE HealthCare (Nasdaq: GEHC) has integrated these predictive tools into its STRATUM™ platform, allowing hospitals to stratify patient populations based on their biological trajectory. Similarly, Siemens Healthineers (FWB: SHL) has expanded its AI-Rad Companion suite to include morphometry analysis that compares organ health against vast normative aging databases. Not to be outdone, Philips (NYSE: PHG) has pivoted its Verida Spectral CT systems toward "Radiological Age" detection, focusing on arterial stiffness as a primary measure of biological wear.
The startup ecosystem is equally vibrant, with companies like Nanox (Nasdaq: NNOX) leading the charge in "opportunistic screening." By running AI aging models in the background of every routine X-ray, Nanox allows clinicians to catch early signs of osteoporosis or cardiovascular decay in patients who originally came in for unrelated issues, such as a broken rib. Meanwhile, Viz.ai has expanded beyond stroke detection into "Vascular Ageing," and Lunit has successfully commercialized CXR-Age for global markets. Even Big Tech is deeply embedded in the space; Alphabet Inc. (Nasdaq: GOOGL), through its Calico subsidiary, and Microsoft Corp. (Nasdaq: MSFT), via Azure Health, are providing the computational infrastructure and synthetic data generation tools necessary to train these models on increasingly diverse demographics.
The Ethical Frontier: Privacy, Bias, and the 'Biological Underclass'
Despite the clinical promise, the rise of AI aging clocks has sparked significant ethical debate. One of the most pressing concerns in early 2026 is the "GINA Gap." While the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act protects Americans from health insurance discrimination based on DNA, it does not explicitly cover the epigenetic or radiological data used by AI aging clocks. This has led to fears that life insurance and disability providers could use biological age scores to hike premiums or deny coverage, effectively creating a "biological underclass."
Furthermore, health equity remains a critical hurdle. Many first-generation AI models were trained on predominantly Western populations, leading to "algorithmic bias" when applied to non-Western groups. Research from Stanford University and Clemson has highlighted that "aging speed" can be miscalculated by AI if the training data does not account for diverse environmental and socioeconomic factors. To address this, regulators like the FDA and EMA issued joint guiding principles in January 2026, requiring "Model Cards" that transparently detail the training demographics and potential drift of AI aging software.
The Horizon: From Hospital Scans to Ambient Sensors
Looking ahead, the integration of biological age prediction is moving out of the clinic and into the home. At the most recent tech showcases, Apple (Nasdaq: AAPL) and Samsung (KRX: 005930) previewed features that use "digital biomarkers"—analyzing gait, voice frequency, and even typing speed—to calculate daily biological age scores. This "ambient sensing" aims to detect neurological or physiological decay in real-time, potentially flagging a decline in "functional age" weeks before a catastrophic event like a fall or a stroke occurs.
The next major milestone will be the FDA's formal recognition of "biological age" as a primary endpoint for clinical trials. While aging is not yet classified as a disease, the ability to use AI clocks to measure the efficacy of "senolytic" drugs—designed to clear out aged, non-functioning cells—could shave years off the drug approval process. Experts predict that by 2028, the "biological age score" will become as common as a blood pressure reading, serving as the definitive KPI for personalized longevity protocols.
A New Era of Human Longevity
The transformation of the chest X-ray into a window into our biological future represents one of the most significant milestones in the history of medical AI. By surfacing markers of aging that have remained invisible to human specialists for over a century, these models are providing the data necessary to shift the global healthcare focus from treatment to prevention.
As we move through 2026, the success of this technology will depend not just on the accuracy of the algorithms, but on the robustness of the privacy frameworks built to protect this sensitive data. If managed correctly, the AI-driven "biological clock" could be the key to unlocking a future where aging is no longer an inevitable decline, but a manageable variable in the quest for a longer, healthier human life.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.