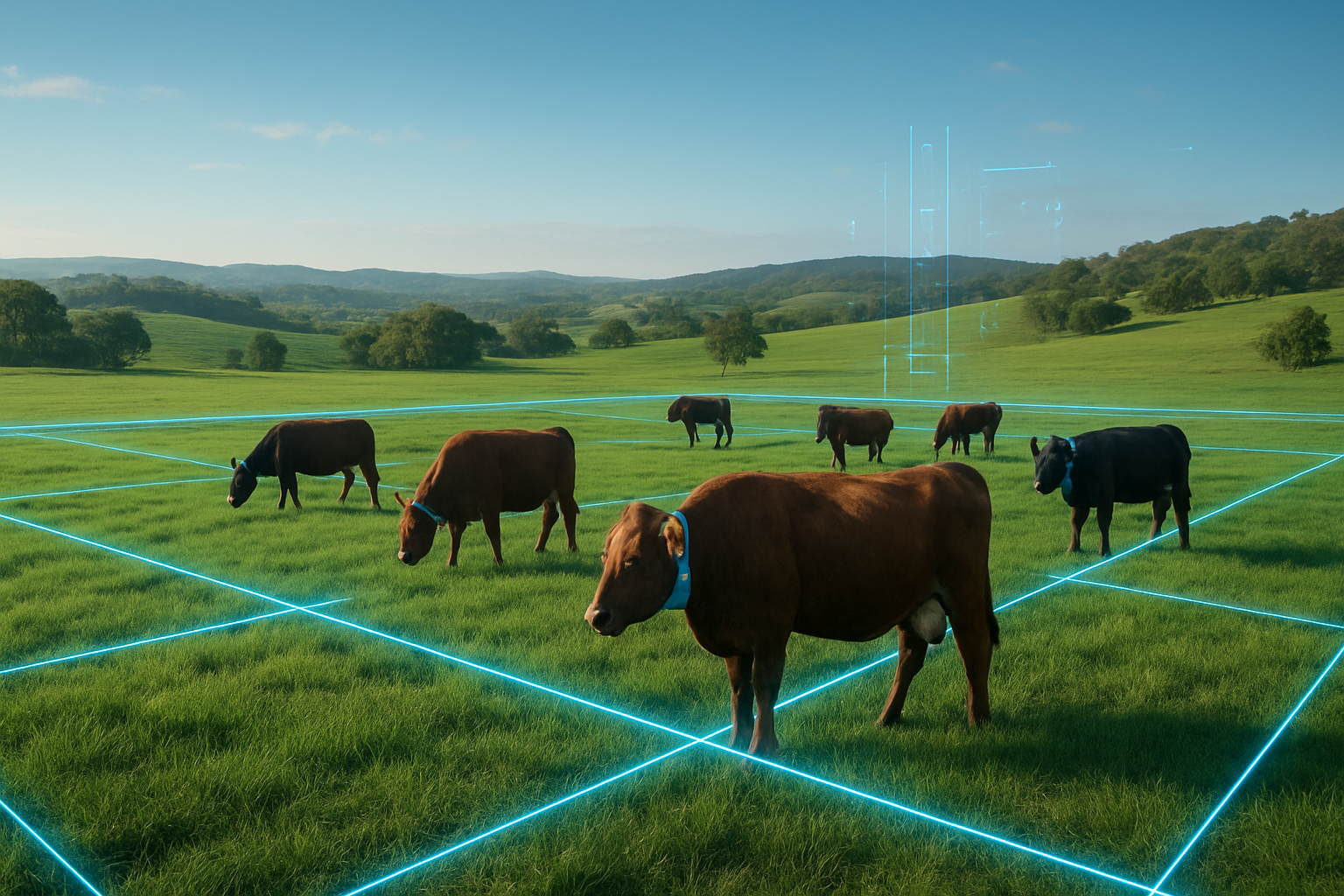
Melbourne, Victoria – December 10, 2025 – In a landmark decision set to redefine modern agriculture, the state of Victoria, Australia, has officially approved the use of virtual fencing technology for livestock management. The Allan Labor Government, through an announcement by Minister for Agriculture Ros Spence, has unveiled new regulations under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act 1986, greenlighting a technology that promises to revolutionize how farmers manage their herds. This progressive move, aligning Victoria with most other Australian states, signals a significant shift towards efficiency, enhanced animal welfare, and environmental sustainability in the agricultural sector. The immediate significance lies in empowering Victorian cattle producers with advanced tools to guide and contain livestock without the labor and cost associated with traditional physical fences, offering unprecedented flexibility in grazing patterns and a vital resource for disaster resilience.
The Invisible Revolution: Unpacking Virtual Fencing Technology
Victoria's impending full integration of virtual fencing technology marks a paradigm shift in livestock management. At its core, this innovative system relies on GPS-enabled smart collars worn by livestock, which communicate with digital boundaries defined by farmers on a mobile app or computer. As an animal approaches a designated virtual fence line, its collar emits a series of escalating sensory cues: first, auditory warnings (beeps), followed by vibrations, and finally, if the animal persists, a mild electrical pulse. Animals quickly learn to associate the audio cues with the boundary, prompting them to turn back and remain within the designated areas, thereby minimizing the need for physical stimuli.
This technology, exemplified by systems from companies like Halter and Gallagher (ASX: GAL), which commercializes CSIRO's eShepherd, offers sophisticated capabilities far beyond simple containment. The collars provide real-time monitoring of individual animal location, movement, health indicators, and even reproductive status, feeding valuable data back to farmers. Many are solar-powered for sustained operation and utilize cellular networks or LoRa base stations for connectivity, ensuring functionality even in remote areas. Unlike the static and costly nature of traditional physical fences, virtual boundaries can be created, adjusted, or removed instantly and remotely, offering dynamic control over grazing patterns, crucial for optimizing pasture utilization and responding to environmental changes. Initial reactions from agricultural bodies like the Victorian Farmers Federation (VFF) and United Dairyfarmers of Victoria (UDV) have been overwhelmingly positive, hailing the decision as a "win for common sense" and a vital step towards modernizing farming practices, while also emphasizing the stringent animal welfare safeguards embedded in the new regulations.
AgTech's New Frontier: Corporate Beneficiaries and Market Shifts
The Victorian approval of virtual fencing technology opens a fertile new market for a range of AI companies, tech giants, and startups within the burgeoning AgTech sector. Prominent beneficiaries include Halter, the New Zealand-based startup currently trialing its technology at Agriculture Victoria's Ellinbank SmartFarm, and Gallagher (ASX: GAL), the commercial partner for CSIRO's patented eShepherd virtual fencing system. CSIRO, a world leader in virtual fencing R&D since 2005, also benefits through its intellectual property and ongoing partnerships. Tech giants like Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT), through collaborations with CSIRO on projects like "SpaceCows" utilizing AI and cloud technologies for feral herd management, demonstrate a clear interest in providing underlying AI services, cloud infrastructure, and data analytics platforms to the sector. Victoria's robust digital technology ecosystem, with its significant AI cluster and university research centers, also provides fertile ground for local startups to innovate and contribute.
The competitive landscape will see a shift, with increased demand for AI and machine learning expertise to process GPS data, analyze animal behavior, and optimize grazing algorithms. Cloud computing providers like Amazon (NASDAQ: AMZN) (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), and Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL) (Google Cloud) stand to gain from hosting the vast data generated by these systems. Companies offering integrated solutions—combining hardware, software, and data analytics—and those prioritizing animal welfare and sustainability in their AI development will gain a strategic advantage. This development is poised to disrupt the traditional fencing industry, potentially leading to a decline in demand for physical fencing materials and services. It will also necessitate a shift in farm labor skills from manual construction to digital management and data interpretation. New business models, such as subscription-based virtual fencing services, are likely to emerge, lowering the barrier to entry for farmers and further reshaping the market.
Beyond the Paddock: Wider Implications and Ethical Considerations
Victoria's embrace of virtual fencing is more than just an agricultural upgrade; it's a testament to the broader integration of AI into critical sectors, aligning with the global "Agriculture 4.0" trend. This precision livestock farming approach leverages AI, IoT, and data analytics to optimize land use, improve environmental outcomes, and enhance food security. Environmentally, virtual fencing offers significant benefits by allowing farmers to exclude livestock from sensitive areas like waterways and regenerating native vegetation, preventing erosion and promoting biodiversity. It facilitates dynamic rotational grazing, improving soil health, increasing plant diversity, and optimizing forage production. Economically, it promises substantial reductions in labor and infrastructure costs associated with traditional fencing, boosting farm productivity and resilience against environmental challenges. Societally, it can improve animal welfare by reducing the stress of traditional herding and enhance farmer well-being by automating demanding tasks.
However, the technology is not without its concerns. Ethical questions persist regarding the use of mild electrical pulses, despite their design to be less intense than traditional electric fences. Animal welfare groups call for more long-term studies on potential stress levels and behavioral impacts. Privacy concerns are also significant, as the vast amounts of data collected on animal movements and farm operations raise questions about data ownership, security, and potential misuse. Technical limitations include the high initial investment cost, reliance on reliable connectivity in remote areas, and the need for continuous improvements in GPS accuracy and collar durability. Compared to previous AI milestones in agriculture, such as early expert systems or the advent of precision agriculture with GPS/GIS, virtual fencing represents a leap from analytical tools to real-time, dynamic control, actively influencing animal behavior and farm management in a responsive and adaptive manner.
The Horizon: Future Developments and Expert Predictions
The future of virtual fencing technology, both in Victoria and globally, is poised for rapid evolution and diversification. In the near term, Victoria's finalized regulations are expected to pave the way for wider commercial adoption, building on trials like the one at Ellinbank SmartFarm. Globally, the virtual fence market is projected for significant growth, driven by increasing connectivity, advanced AI algorithms for animal tracking and behavior monitoring, and improved mobile device integration. Smart collars will become even more refined, with enhanced automated containment, health monitoring, and features like collar-to-collar communication in areas with poor signal. We can expect reduced costs and complexity as the technology matures and competition increases.
Beyond basic containment, potential applications are vast. Virtual fencing will enable highly dynamic pasture management, allowing for precise rotational and strip grazing to optimize land use and promote environmental health. It will be crucial for environmental protection, creating exclusion zones for sensitive ecosystems and even assisting in firebreak creation through targeted grazing. Enhanced animal welfare and health monitoring will see collars providing 24/7 insights, alerting farmers to potential issues. Experts predict virtual fencing will become a foundational technology for 21st-century livestock management, enabling precision control in response to unpredictable weather and sustainability demands. Challenges such as high initial costs, connectivity in remote areas, and continuous refinement of animal welfare protocols remain. However, continuous R&D, strategic partnerships between tech firms and agribusinesses, and government initiatives are expected to fast-track commercialization and adoption, leading to smarter, more efficient, and environmentally friendly livestock management systems.
A New Chapter in Agricultural Innovation
Victoria's approval of virtual fencing technology marks a significant chapter in the ongoing narrative of AI's transformative impact on agriculture. This development underscores a commitment to embracing innovation for greater efficiency, economic resilience, and environmental stewardship. The key takeaways are clear: virtual fencing offers unparalleled flexibility in livestock management, substantial cost and labor savings, and critical tools for sustainable land use and disaster preparedness. While ethical considerations, data privacy, and technical challenges will require ongoing attention and refinement, the long-term impact is expected to be profoundly positive, ushering in an era of precision livestock farming that benefits farmers, animals, and the environment. As the first approved products become available in early 2026, the coming weeks and months will be crucial for observing the initial rollout, farmer adoption rates, and the continued evolution of this invisible revolution in the paddocks of Victoria and beyond.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.