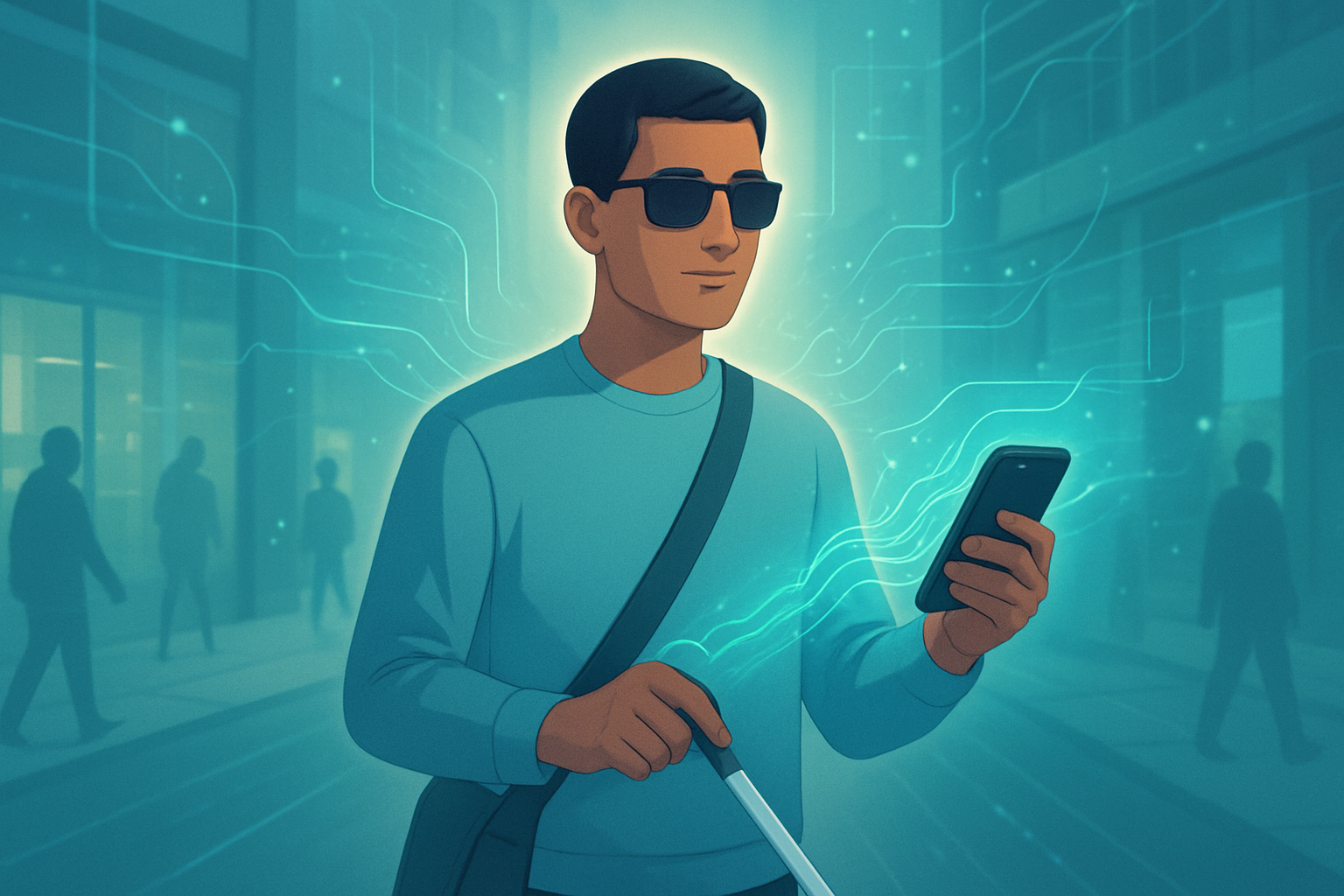
A groundbreaking new artificial intelligence tool, NaviSense, developed by researchers at Penn State, is poised to revolutionize accessibility for visually impaired individuals. Unveiled at the Association for Computing Machinery's SIGACCESS ASSETS '25 conference in October 2025, this innovative smartphone application allows users to "feel" where objects are in real-time through a sophisticated combination of audio and vibrational feedback. By leveraging cutting-edge large-language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), NaviSense offers an unprecedented level of real-time environmental understanding and guidance, marking a significant leap forward in fostering independent navigation and enhancing the quality of life for millions.
This development signifies a pivotal moment in assistive technology, moving beyond static, pre-programmed solutions to dynamic, conversational AI assistance. The ability for visually impaired users to interact with their environment in such an intuitive and responsive manner promises to unlock new levels of autonomy, transforming daily routines from navigating public spaces to locating personal items at home. The immediate significance lies in its potential to dramatically reduce reliance on human assistance and traditional, often limited, navigation aids, thereby empowering users with greater confidence and self-sufficiency in an ever-changing world.
The Technical Marvel Behind Real-Time Haptic Perception
NaviSense stands out due to its sophisticated integration of advanced AI models. Unlike previous assistive technologies that required pre-loaded object models or were limited to recognizing a narrow set of items, NaviSense employs LLMs and VLMs to process natural language prompts from users and dynamically identify a vast array of objects in their surroundings. Users can simply ask, "Where is my coffee cup?" or "Is there a chair nearby?", and the system uses the phone's camera and AI processing to understand the visual environment in real-time. This conversational capability, which can even engage in follow-up questions for clarification, provides unparalleled flexibility and user-friendliness.
Once an object is identified, NaviSense translates its location into actionable guidance through the smartphone's integrated audio and vibrational capabilities. This multi-modal feedback system allows users to "feel" the direction and proximity of objects, effectively creating a real-time haptic map of their immediate environment. The intensity and pattern of vibrations, combined with spatial audio cues, guide the user directly to the desired item or around obstacles. This approach sharply contrasts with older systems that often relied on simpler sensor arrays or limited auditory descriptions, offering a much richer and more nuanced perception of space. Another recent innovation, Seismic Sense, showcased at Bitcamp 2025 in September 2025, offers a similar haptic approach using ultrasonic sonar in an ergonomic handle, where vibration intensity directly corresponds to object proximity, extending the reach beyond a traditional white cane. The initial reception for NaviSense has been overwhelmingly positive, evidenced by its receipt of the Best Audience Choice Poster Award at the SIGACCESS ASSETS '25 conference, highlighting the AI research community's recognition of its innovative potential and practical utility.
Reshaping the Landscape for AI and Assistive Tech Companies
This technological breakthrough carries profound implications for a wide spectrum of companies, from established tech giants to agile startups in the assistive technology sector. Companies specializing in AI development, particularly those at the forefront of LLM and VLM research, stand to benefit immensely. The successful application of these models in NaviSense validates their potential for real-world, high-impact accessibility solutions, likely spurring further investment and development in this area. Hardware manufacturers producing smartphones and wearable devices will also find new avenues for innovation, integrating more sophisticated sensors and haptic feedback mechanisms optimized for such AI applications.
The competitive landscape for major AI labs and tech companies like Alphabet (NASDAQ: GOOGL), Apple (NASDAQ: AAPL), and Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT) could see a renewed focus on accessibility-driven AI. These companies, with their extensive research capabilities and market reach, are well-positioned to integrate similar real-time object perception and haptic guidance features into their operating systems, smart devices, and specialized accessibility tools. This could disrupt existing products that offer more limited navigational assistance, pushing them to evolve or risk obsolescence. Startups focusing on niche assistive technologies will also find a fertile ground for innovation, potentially developing specialized hardware or software layers that enhance or complement solutions like NaviSense, carving out strategic advantages in a rapidly expanding market. The emphasis on conversational AI and real-time environmental understanding will likely become a new benchmark for assistive technologies, influencing product roadmaps and strategic partnerships across the industry.
Wider Significance in the AI Landscape
NaviSense's emergence fits perfectly within the broader AI landscape's trend towards more human-centric and embodied AI applications. It exemplifies how advanced AI, once primarily focused on abstract tasks, is increasingly being deployed to solve tangible, real-world problems that directly impact human lives. This development underscores the growing maturity of vision-language models and their ability to bridge the gap between complex visual data and intuitive human interaction. The impact on accessibility is monumental, moving beyond mere information provision to active, real-time guidance that fosters genuine independence.
Potential concerns, however, include the accuracy and reliability of real-time object recognition in diverse and challenging environments, as well as the computational demands and battery life implications for portable devices. Data privacy and security, especially concerning the continuous processing of visual and audio information, will also be critical considerations. Nevertheless, this milestone can be compared to previous AI breakthroughs such as the advent of reliable speech recognition or machine translation, which similarly democratized access to information and communication. NaviSense pushes the boundary further by offering a tangible, physical interaction with the AI-interpreted world, setting a new standard for how AI can empower individuals with disabilities. The ethical deployment and ongoing refinement of such tools will be crucial to ensure equitable access and maximize positive societal impact.
The Horizon: Future Developments and Applications
Looking ahead, the trajectory for technologies like NaviSense is one of continuous advancement and broader integration. Near-term developments are likely to focus on refining the accuracy and speed of object recognition, improving the naturalness of conversational interaction, and optimizing the haptic feedback for greater nuance and intuitiveness. We can expect to see these tools integrated into a wider array of wearable devices beyond smartphones, such as smart glasses, specialized belts, or even footwear, providing more discreet and seamless real-time perception. The Johns Hopkins system, which uses a vibrating headband for semantic mapping, offers a glimpse into such wearable integration, with clinical trial results anticipated in summer 2024 further validating this approach.
Long-term, the potential applications are vast. Beyond basic object location and navigation, these AI tools could evolve to provide richer contextual information about environments, identify people, read text in real-time, or even assist with complex tasks requiring fine motor skills by guiding hand movements. Challenges that need to be addressed include miniaturization of hardware, reducing computational latency for truly instantaneous feedback, and ensuring affordability to make these life-changing technologies accessible to all who need them. Experts predict a future where AI-powered real-time perception becomes an ubiquitous assistive layer, seamlessly blending with our physical world, transforming not just navigation but also learning, work, and social interactions for visually impaired individuals.
A New Chapter in Human-AI Collaboration for Accessibility
The unveiling of NaviSense and similar innovations marks a profound turning point in the history of artificial intelligence and accessibility. It underscores a shift from AI as a tool for automation to AI as a profound enabler of human capability, particularly for those with sensory impairments. The key takeaway is the demonstration of advanced AI's capacity to translate complex environmental data into intuitive, real-time haptic and auditory feedback, fundamentally altering how visually impaired individuals interact with and understand their surroundings. This development is not merely an incremental improvement; it represents a paradigm shift towards truly independent navigation and object perception.
Its significance in AI history lies in solidifying the role of LLMs and VLMs as powerful engines for embodied AI applications, proving their utility far beyond text generation or image recognition. The long-term impact will be measured in the increased independence, safety, and quality of life for millions globally, fostering greater social inclusion and participation. In the coming weeks and months, we should watch for further details on NaviSense's commercialization path, the results of ongoing clinical trials for similar systems like the one from Johns Hopkins, and the emergence of new startups and partnerships in the real-time haptic feedback space. This is an exciting and rapidly evolving frontier where human ingenuity and artificial intelligence are converging to create a more accessible and equitable world.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.