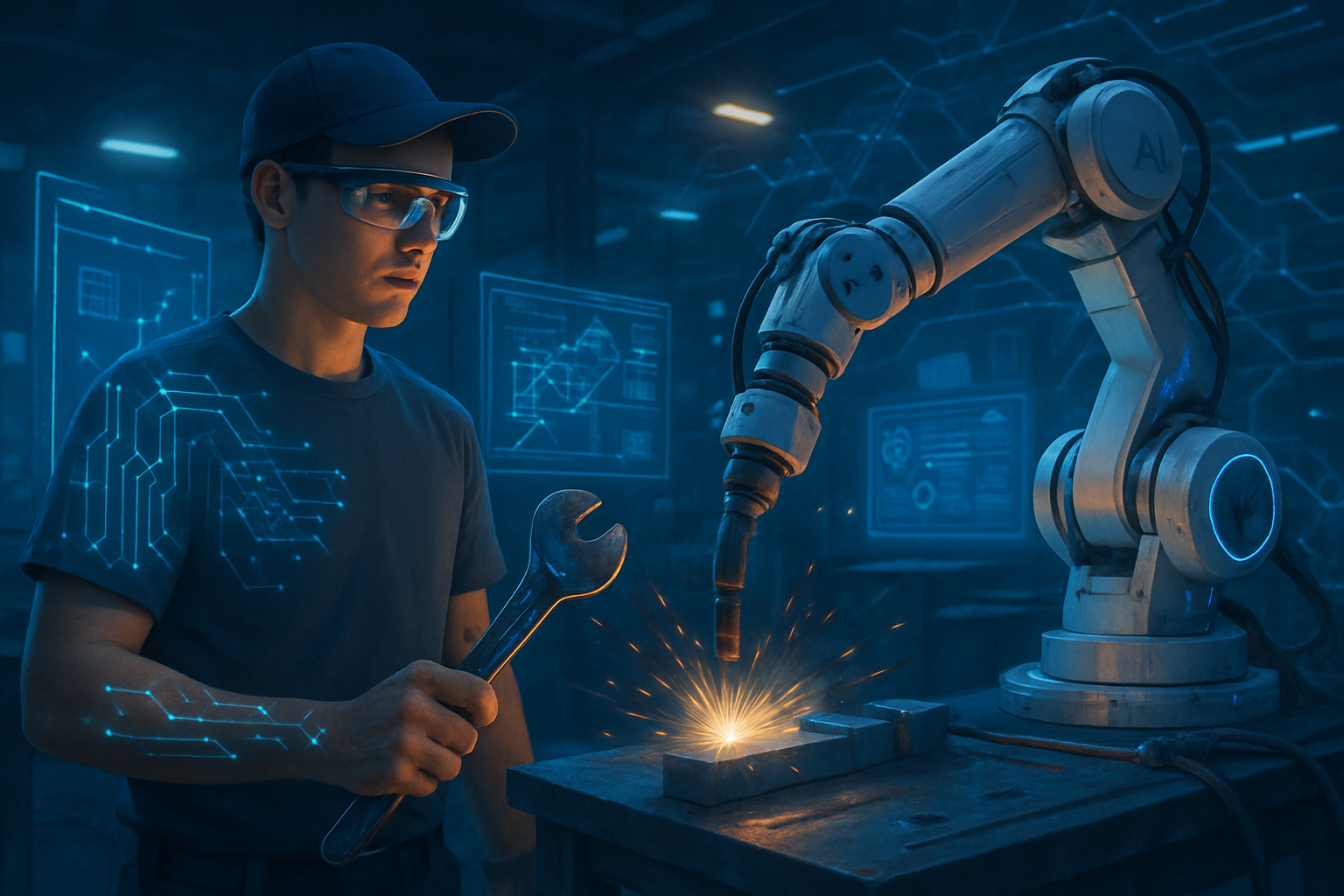
The relentless march of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is dramatically reconfiguring the global employment landscape, ushering in an era where the perceived security of traditional white-collar professions is being challenged. Far from rendering human labor obsolete, AI's increasing sophistication in automating repetitive tasks is paradoxically sparking a renaissance in blue-collar industries and skilled trades. This seismic shift is profoundly influencing career aspirations, particularly among Generation Z, who are increasingly turning away from four-year degrees in favor of vocational training, recognizing the enduring value and AI-resilience of hands-on expertise.
Recent developments indicate that while AI and advanced automation are streamlining operations in sectors like manufacturing, construction, and logistics, they are simultaneously creating a robust demand for human skills that AI cannot replicate. This includes complex problem-solving, manual dexterity, critical decision-making, and direct human interaction. As AI takes on the mundane, it elevates the human role, transforming existing jobs and creating entirely new ones that require a blend of technical acumen and practical application.
AI's Precision Hand: Augmenting, Not Eradicating, the Trades
The technical advancements driving this transformation are multifaceted, rooted in breakthroughs in machine learning, robotics, and large language models (LLMs) that allow for unprecedented levels of automation and augmentation. Specific details reveal a nuanced integration of AI into blue-collar workflows, enhancing efficiency, safety, and precision.
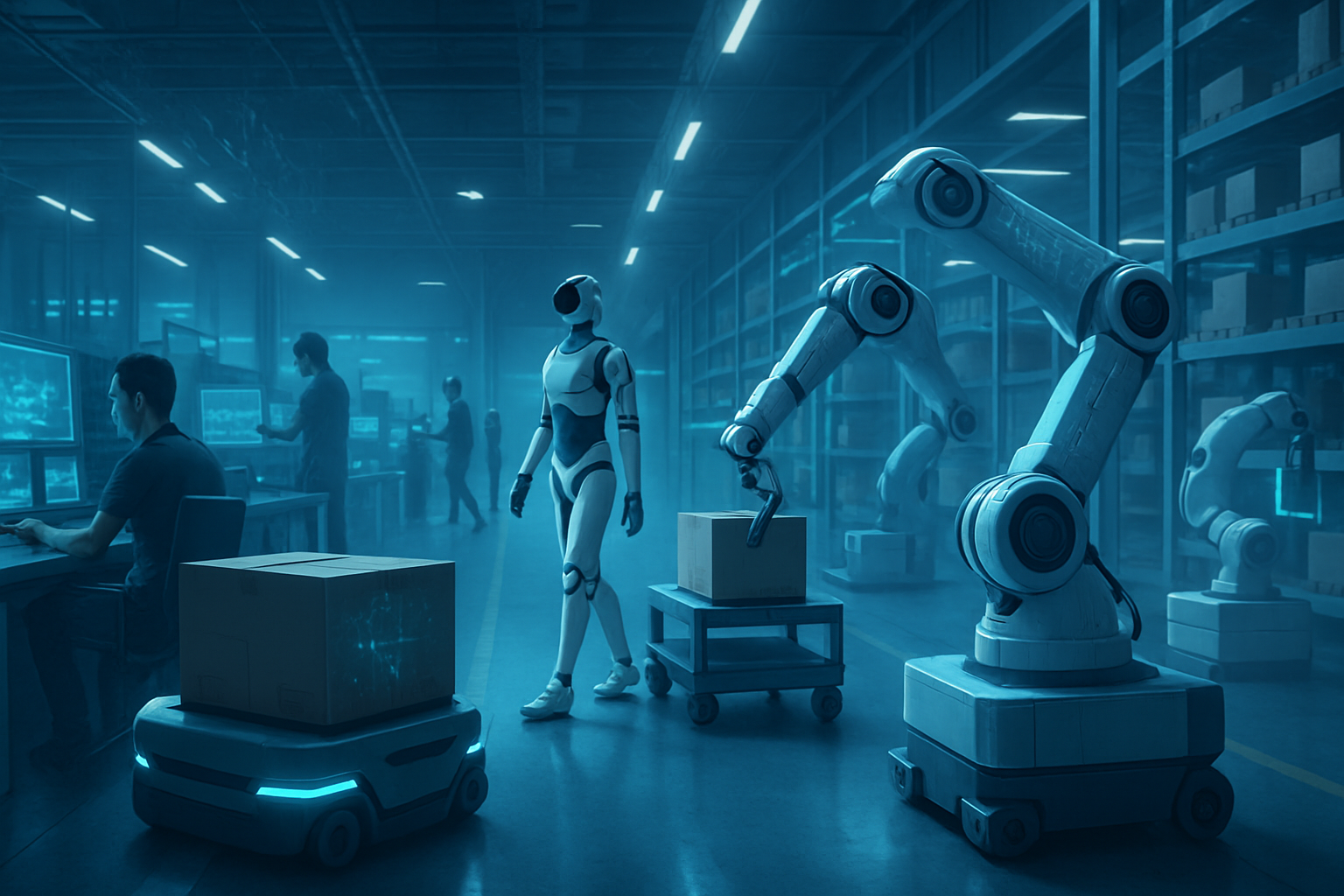
One significant area is the deployment of AI-driven robotics and automated machinery in manufacturing and construction. For instance, AI-powered Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are achieving higher precision and efficiency in material processing, from cutting intricate designs in stone to shaping metals with microscopic accuracy. In construction, robotic bricklayers, autonomous surveying drones, and AI-optimized material handling systems are becoming more common. These systems leverage computer vision and machine learning algorithms to interpret blueprints, navigate complex environments, and execute tasks with a consistency and speed that human workers cannot match. This differs from previous approaches, which often relied on simpler, pre-programmed automation, by incorporating adaptive learning and real-time decision-making capabilities. AI systems can now learn from new data, adapt to changing conditions, and even predict maintenance needs, leading to fewer errors and less downtime. Initial reactions from the AI research community and industry experts highlight this shift from mere automation to intelligent augmentation, where AI acts as a sophisticated co-worker, handling the heavy lifting and repetitive tasks while humans oversee, troubleshoot, and innovate. Experts point out that the integration of AI also significantly improves workplace safety by removing humans from hazards and predicting potential accidents.
Furthermore, the rise of predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, is revolutionizing maintenance and operational efficiency across blue-collar sectors. AI algorithms analyze vast datasets from sensors (Internet of Things or IoT devices) embedded in machinery and equipment, such as temperature, vibration, pressure, and fluid levels. These algorithms identify subtle patterns and anomalies that indicate potential failures before they occur. For example, in HVAC, marine construction, mining, and manufacturing, ML systems predict equipment breakdowns, optimize maintenance schedules, reduce unplanned downtime, and extend equipment lifespans. This proactive approach saves costs and enhances safety, moving beyond traditional reactive or time-based scheduled maintenance. In quality control, ML-powered apps can process images of weld spatter pixel by pixel to provide quantitative, unbiased feedback to welders, accelerating competency buildup. Large language models (LLMs) are also playing a crucial role, not in direct physical labor, but in streamlining project management, generating safety protocols, and providing on-demand technical documentation, making complex information more accessible to on-site teams. Technicians can use LLMs to navigate complex repair manuals, access remote expert assistance for troubleshooting, and receive guided instructions, reducing errors and improving efficiency in the field. This blend of physical automation and intelligent information processing underscores a profound evolution in how work gets done in traditionally manual professions, offering real-time feedback and adaptive learning capabilities that far surpass static manuals or purely theoretical instruction.
Shifting Sands: Competitive Implications for Tech Giants and Skilled Labor Platforms
The evolving landscape of AI-augmented blue-collar work presents a complex web of opportunities and competitive implications for AI companies, tech giants, and startups alike. Companies specializing in industrial automation, robotics, and predictive maintenance stand to benefit immensely from this development. Firms like Boston Dynamics (privately held), known for advanced robotics, and Siemens AG (ETR: SIE), with its industrial automation solutions, are well-positioned to capitalize on the increasing demand for intelligent machines in manufacturing and logistics. Similarly, companies developing AI-powered construction technology, such as Procore Technologies (NYSE: PCOR) with its project management software integrating AI analytics, are seeing increased adoption.
The competitive implications for major AI labs and tech companies are significant. While some tech giants like Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL) and Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT) are primarily focused on LLMs and enterprise AI, their cloud platforms are crucial for hosting and processing the vast amounts of data generated by industrial AI applications. Their competitive advantage lies in providing the underlying infrastructure and AI development tools that power these specialized blue-collar solutions. Startups focusing on niche applications, such as AI for welding inspection or AR guidance for electricians, are also emerging rapidly, often partnering with larger industrial players to scale their innovations. This creates a potential disruption to existing products or services that rely on older, less intelligent automation systems, pushing them towards obsolescence unless they integrate advanced AI capabilities.
Market positioning is also critical. Companies that can offer end-to-end solutions, combining hardware (robots, sensors) with intelligent software (AI algorithms, predictive models), will gain a strategic advantage. This includes not only the developers of the AI technology but also platforms that connect skilled tradespeople with these new tools and opportunities. For instance, online platforms that facilitate apprenticeships or offer specialized training in AI-assisted trades are becoming increasingly valuable. The demand for skilled workers who can operate, maintain, and troubleshoot these advanced AI systems also creates a new market for training and certification providers, potentially drawing investment from tech companies looking to build out the ecosystem for their products. The overall trend suggests a move towards integrated solutions where AI is not just a tool but an integral part of the workflow, demanding a symbiotic relationship between advanced technology and skilled human labor.
The Broader Tapestry: AI, Labor, and Societal Transformation
This shift towards AI-augmented blue-collar work fits into the broader AI landscape as a critical counter-narrative to the widespread fear of mass job displacement. Instead of a dystopian vision of AI replacing all human labor, we are witnessing a more nuanced reality where AI serves as a powerful enhancer, particularly in sectors previously considered less susceptible to technological disruption. This trend aligns with the concept of "AI augmentation," where AI's primary role is to improve human capabilities and efficiency, rather than to fully automate. It also highlights the growing recognition of the economic and societal value of skilled trades, which have often been overlooked in the pursuit of white-collar careers.
The impacts are profound and far-reaching. Economically, it promises increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and potentially a more resilient workforce less vulnerable to economic downturns that disproportionately affect service-oriented or highly repetitive office jobs. Socially, it offers a pathway to stable, well-paying careers for Gen Z without the burden of crippling student debt, addressing concerns about educational accessibility and economic inequality. However, potential concerns include the need for massive reskilling and upskilling initiatives to ensure the existing workforce can adapt to these new technologies. There's also the risk of a widening gap between those who have access to such training and those who don't, potentially exacerbating existing social divides. This moment draws comparisons to previous industrial revolutions, where new technologies transformed labor markets, creating new categories of work while rendering others obsolete. The key difference now is the speed of change and the cognitive nature of AI's capabilities, demanding a more proactive and agile response from educational institutions and policymakers.
Furthermore, the environmental impact is also noteworthy. AI-driven optimization in manufacturing and logistics can lead to more efficient resource use and reduced waste. Predictive maintenance, for example, extends the lifespan of machinery, reducing the need for new equipment production. In construction, AI can optimize material usage and reduce rework, contributing to more sustainable practices. However, the energy consumption of AI systems themselves, particularly large language models and complex neural networks, remains a concern that needs to be balanced against the efficiency gains in other sectors. This broader significance underscores that the impact of AI on blue-collar jobs is not merely an economic or labor issue, but a multifaceted phenomenon with wide-ranging societal, educational, and environmental implications, demanding a holistic approach to understanding and managing its trajectory.
The Horizon of Augmentation: Future Developments and Challenges
Looking ahead, the integration of AI into skilled trades is expected to accelerate, leading to even more sophisticated applications and use cases. In the near-term, we can anticipate more widespread adoption of AI-powered diagnostic tools, augmented reality (AR) for real-time guidance in complex repairs, and collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human technicians in manufacturing and assembly. Imagine an electrician using AR glasses that overlay circuit diagrams onto a physical panel, or a plumber receiving real-time AI-driven diagnostics from a smart home system. These tools will not replace the skilled worker but empower them with superhuman precision and knowledge.
Long-term developments include fully autonomous systems capable of handling a wider range of tasks, particularly in hazardous environments, reducing human exposure to risk. AI will also play a larger role in personalized training and skill development, using adaptive learning platforms to tailor educational content to individual needs, making it easier for new entrants to acquire complex trade skills. Experts predict a future where every skilled trade will have an AI counterpart or assistant, making professions more efficient, safer, and intellectually stimulating. However, challenges remain. The development of robust, reliable, and ethically sound AI systems for critical infrastructure and safety-sensitive trades is paramount. Ensuring data privacy and security in interconnected AI systems is another significant hurdle. Furthermore, the societal challenge of bridging the skills gap and ensuring equitable access to training and job opportunities will need continuous attention. What experts predict will happen next is a continued blurring of lines between "blue-collar" and "white-collar" skills, with a new category of "new-collar" jobs emerging that demand both technical proficiency and digital literacy, making lifelong learning an imperative for all.
A New Era for Labor: Reshaping Perceptions and Pathways
In summary, the impact of AI on blue-collar jobs is not one of wholesale replacement, but rather a profound transformation that is simultaneously enhancing productivity and redirecting a new generation towards skilled trades. Key takeaways include the rise of AI as an augmentation tool, the increasing job security and financial appeal of trades for Gen Z, and the imperative for continuous reskilling and upskilling across the workforce. This development signifies a critical juncture in AI history, challenging long-held assumptions about automation's effects on employment and highlighting the enduring value of human ingenuity, adaptability, and hands-on expertise.
The significance of this development lies in its potential to rebalance the labor market, address critical skill shortages, and offer diverse, financially rewarding career paths that are resilient to future technological disruptions. It also underscores a shift in societal perception, elevating the status of skilled trades as vital, technologically advanced professions. In the coming weeks and months, we should watch for increased investment in vocational training programs, further integration of AI tools into trade-specific education, and continued public discourse on the evolving relationship between humans and intelligent machines. The blue-collar boom, powered by AI, is not just a trend; it's a fundamental reshaping of our economic and social fabric, demanding attention and proactive engagement from all stakeholders.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.