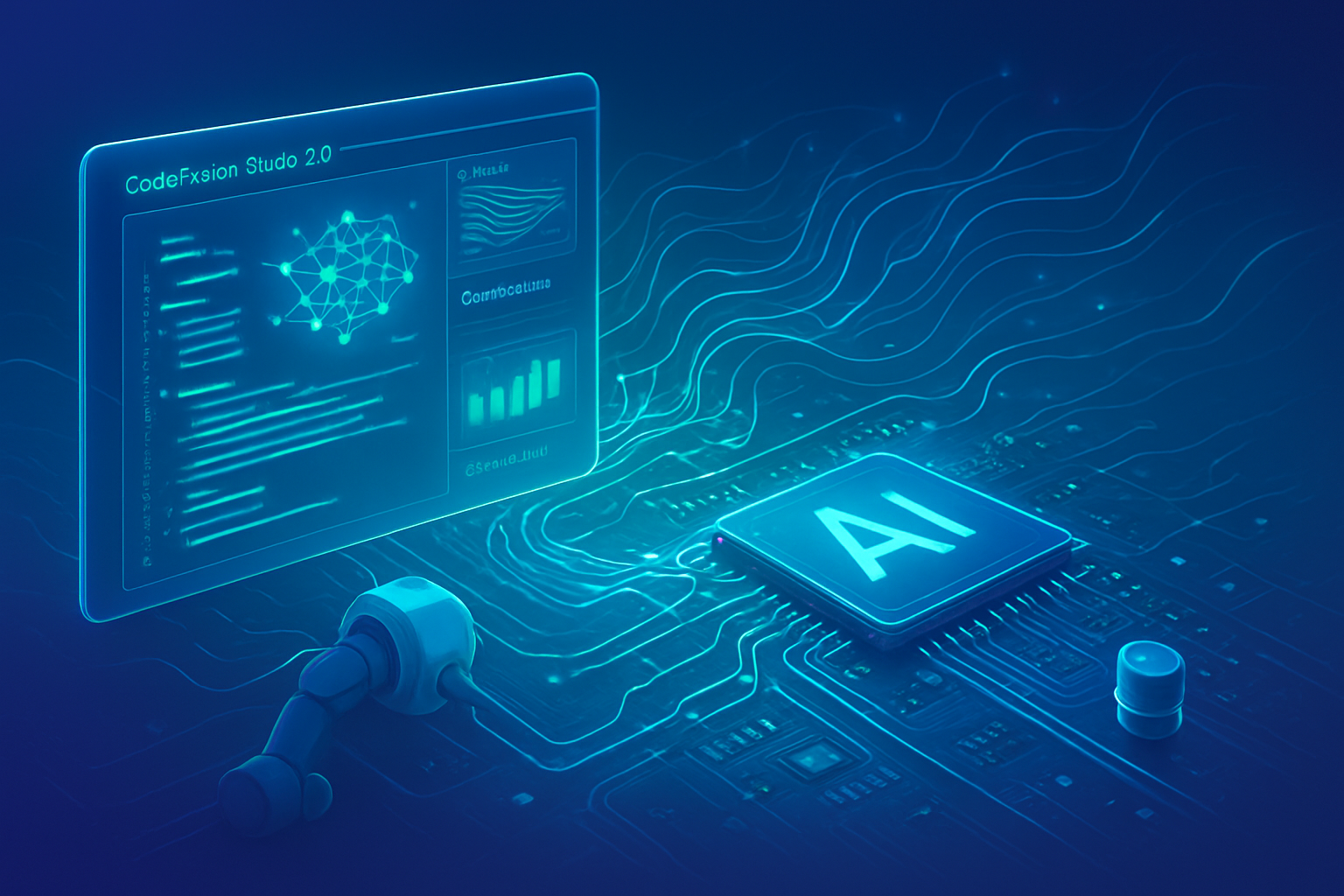
In a pivotal move for the embedded artificial intelligence landscape, Analog Devices (NASDAQ: ADI) has announced the release of CodeFusion Studio 2.0 in early November 2025. This significant upgrade to its open-source embedded development platform is engineered to dramatically streamline the creation and deployment of AI-enabled embedded systems, heralding a new era of accessibility for embedded AI. By unifying what were previously fragmented and complex AI workflows into a seamless, developer-friendly experience, CodeFusion Studio 2.0 is set to accelerate innovation at the edge, making sophisticated AI integration more attainable for engineers and developers across various industries.
Analog Devices' strategic focus with CodeFusion Studio 2.0 is to "remove friction from AI development," a critical step toward realizing their vision of "Physical Intelligence"—systems capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting locally within real-world constraints. This release underscores the growing industry trend towards democratizing AI by providing robust, open-source tools that simplify complex tasks, ultimately empowering a broader community to build and deploy intelligent edge devices with unprecedented speed and confidence.
Technical Deep Dive: CodeFusion Studio 2.0's Architecture and Innovations
CodeFusion Studio 2.0 is built upon the familiar and extensible foundation of Microsoft's (NASDAQ: MSFT) Visual Studio Code, offering developers a powerful integrated development environment (IDE). Its technical prowess lies in its comprehensive support for end-to-end AI workflows, allowing developers to "bring their own models" (BYOM) via a graphical user interface (GUI) or command-line interface (CLI). These models can then be efficiently deployed across Analog Devices' diverse portfolio of processors and microcontrollers, spanning from low-power edge devices to high-performance Digital Signal Processors (DSPs).
A core innovation is the platform's integrated AI/ML tooling, which includes a model compatibility checker to verify models against ADI processors and microcontrollers. Performance profiling tools, based on a new Zephyr Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)-based modular framework, provide runtime AI/ML profiling, including layer-by-layer analysis. This granular insight into latency, memory, and power consumption enables the generation of highly optimized, inference-ready code directly within the IDE. This approach significantly differs from previous fragmented methods where developers often had to juggle multiple IDEs and proprietary toolchains, struggling with compatibility and optimization across heterogeneous systems.
The updated CodeFusion Studio System Planner further enhances the technical capabilities by supporting multi-core applications and offering broader device compatibility. It provides unified configuration tools for complex system setups, allowing visual allocation of memory, peripherals, pins, clocks, and inter-core data flows across multiple cores and devices. Coupled with integrated debugging features like GDB and Core Dump Analysis, CodeFusion Studio 2.0 offers a unified workspace that simplifies configuration, building, and debugging across all cores with shared memory maps and consistent build dependencies. Initial reactions from industry observers and ADI executives, such as Rob Oshana (SVP of Software and Digital Platforms), have been highly optimistic, emphasizing the platform's potential to accelerate time-to-market and empower developers.
Market Ripples: Impact on AI Companies, Tech Giants, and Startups
The introduction of CodeFusion Studio 2.0 is set to create significant ripples across the AI industry, benefiting a wide spectrum of players from nimble startups to established tech giants. For AI companies and startups, particularly those focused on edge AI, the platform offers a critical advantage: accelerated time-to-market. By simplifying and unifying the AI development workflow, it lowers the barrier to entry, allowing these innovators to quickly validate and deploy their AI-driven products. This efficiency translates into significant cost savings and allows smaller entities to compete more effectively by focusing on AI innovation rather than wrestling with complex embedded system integrations.
For major tech giants and AI labs, CodeFusion Studio 2.0 provides a scalable solution for deploying AI across Analog Devices' extensive hardware portfolio. Its Visual Studio Code foundation eases integration into existing enterprise development pipelines, while specialized optimization tools ensure maximum performance and efficiency for their edge AI applications. This enables these larger organizations to differentiate their products with superior embedded intelligence. The platform's ability to unify fragmented workflows also frees up valuable engineering resources, allowing them to focus on higher-level AI model development and strategic application-specific solutions.
Competitively, CodeFusion Studio 2.0 intensifies the race in the edge AI market. It could prompt other semiconductor companies and toolchain providers to enhance their offerings, leading to a more integrated and developer-friendly ecosystem across the industry. The platform's deep integration with Analog Devices' silicon could create a strategic advantage for ADI, fostering ecosystem "lock-in" for developers who invest in its capabilities. Potential disruptions include a decreased demand for fragmented embedded development toolchains and specialized embedded AI integration consulting, as more tasks become manageable within the unified studio. Analog Devices (NASDAQ: ADI) is strategically positioning itself as a leader in "Physical Intelligence," differentiating its focus on real-world, localized AI and strengthening its market position as a key enabler for intelligent edge solutions.
Broader Horizon: CodeFusion Studio 2.0 in the AI Landscape
CodeFusion Studio 2.0 arrives at a time when embedded AI, or edge AI, is experiencing explosive growth. The broader AI landscape in 2025 is characterized by a strong push towards decentralizing intelligence, moving processing power and decision-making capabilities closer to the data source—the edge. This shift is driven by demands for lower latency, enhanced privacy, greater autonomy, and reduced bandwidth and energy consumption. CodeFusion Studio 2.0 directly supports these trends by enabling real-time decision-making on local devices, crucial for applications in industrial automation, healthcare, and autonomous systems. Its optimization tools and support for a wide range of ADI hardware, from low-power MCUs to high-performance DSPs, are critical for deploying AI models within the strict resource and energy constraints of embedded systems.
The platform's open-source nature aligns with another significant trend in embedded engineering: the increasing adoption of open-source tools. By leveraging Visual Studio Code and incorporating a Zephyr-based modular framework, Analog Devices promotes transparency, flexibility, and community collaboration, helping to reduce toolchain fragmentation. This open approach is vital for fostering innovation and avoiding vendor lock-in, enabling developers to inspect, modify, and distribute the underlying code, thereby accelerating the proliferation of intelligent edge devices.
While CodeFusion Studio 2.0 is not an algorithmic breakthrough like the invention of neural networks, it represents a pivotal enabling milestone for the practical deployment of AI. It builds upon the advancements in machine learning and deep learning, taking the theoretical power of AI models and making their efficient deployment on constrained embedded devices a practical reality. Potential concerns, however, include the risk of de facto vendor lock-in despite its open-source claims, given its deep optimization for ADI hardware. The complexity of multi-core orchestration and the continuous need to keep pace with rapid AI advancements also pose challenges. Security and privacy in AI-driven embedded systems remain paramount, requiring robust measures that extend beyond the development platform itself.
The Road Ahead: Future of Embedded AI with CodeFusion Studio 2.0
The future for CodeFusion Studio 2.0 and embedded AI is dynamic, marked by continuous innovation and expansion. In the near term, Analog Devices (NASDAQ: ADI) is expected to further refine the platform's AI workflow integration, enhancing model compatibility and optimization tools for even greater efficiency. Expanding hardware support for newly released ADI silicon and improving debugging capabilities for complex multi-core systems will also be key focuses. As an open-source platform, increased community contributions are anticipated, leading to extended functionalities and broader use cases.
Long-term developments will be guided by ADI's vision of "Physical Intelligence," pushing for deeper hardware-software integration and expanded support for emerging AI frameworks and runtime environments. Experts predict a shift towards more advanced automated optimization techniques, potentially leveraging AI itself to fine-tune model architectures and deployment configurations. The platform is also expected to evolve to support agentic AI, enabling autonomous AI agents on embedded systems for complex tasks. This will unlock potential applications in areas like predictive maintenance, quality control in manufacturing, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), wearable health monitoring, and smart agriculture, where real-time, local AI processing is critical.
However, several challenges persist. The inherent limitations of computational power, memory, and energy in embedded systems necessitate ongoing efforts in model optimization and hardware acceleration. Real-time processing, security, and the need for rigorous validation of AI outputs remain critical concerns. A growing skills gap in engineers proficient in both AI and embedded systems also needs addressing. Despite these challenges, experts predict the dominance of edge AI, with more devices processing AI locally. They foresee the rise of self-learning and adaptive embedded systems, specialized AI hardware (like NPUs), and the continued standardization of open-source frameworks. The ultimate goal is to enable AI to become more pervasive, intelligent, and autonomous, profoundly impacting industries and daily life.
Conclusion: A New Era for Embedded Intelligence
Analog Devices' (NASDAQ: ADI) CodeFusion Studio 2.0 marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of embedded AI. By offering a unified, open-source, and developer-first platform, ADI is effectively dismantling many of the traditional barriers to integrating artificial intelligence into physical devices. The key takeaways are clear: streamlined AI workflows, robust performance optimization, a unified development experience, and a strong commitment to open-source principles. This development is not merely an incremental update; it represents a significant step towards democratizing embedded AI, making sophisticated "Physical Intelligence" more accessible and accelerating its deployment across a multitude of applications.
In the grand tapestry of AI history, CodeFusion Studio 2.0 stands as an enabler—a tool-chain breakthrough that operationalizes the theoretical advancements in AI models for real-world, resource-constrained environments. Its long-term impact will likely be seen in the proliferation of smarter, more autonomous, and energy-efficient edge devices, driving innovation across industrial, consumer, and medical sectors. It sets a new benchmark for how semiconductor companies integrate software solutions with their hardware, fostering a more holistic and user-friendly ecosystem.
In the coming weeks and months, the industry will be closely watching developer adoption rates, the emergence of compelling real-world use cases, and how Analog Devices continues to build out the CodeFusion Studio 2.0 ecosystem with further integrations and updates. The response from competitors and the continued evolution of ADI's "Physical Intelligence" roadmap will also be crucial indicators of the platform's long-term success and its role in shaping the future of embedded intelligence.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.