The semiconductor industry stands at the precipice of an unprecedented era of growth and innovation, poised to shatter the $1 trillion market valuation barrier by 2030. This monumental expansion, often termed a "super cycle," is primarily fueled by the insatiable global demand for advanced computing, particularly from the burgeoning field of Artificial Intelligence. As of November 11, 2025, the industry is navigating a complex landscape shaped by relentless technological breakthroughs, evolving market imperatives, and significant geopolitical realignments, all converging to redefine the very foundations of modern technology.
This transformative period is characterized by a dual revolution: the continued push for miniaturization alongside a strategic pivot towards novel architectures and materials. Beyond merely shrinking transistors, manufacturers are embracing advanced packaging, exploring exotic new compounds, and integrating AI into the very fabric of chip design and production. These advancements are not just incremental improvements; they represent fundamental shifts that promise to unlock the next generation of AI systems, autonomous technologies, and a myriad of connected devices, cementing semiconductors as the indispensable engine of the 21st-century economy.
Beyond the Silicon Frontier: Engineering the Next Generation of Intelligence
The relentless pursuit of computational supremacy, primarily driven by the demands of artificial intelligence and high-performance computing, has propelled the semiconductor industry into an era of profound technical innovation. At the core of this transformation are revolutionary advancements in transistor architecture, lithography, advanced packaging, and novel materials, each representing a significant departure from traditional silicon-centric manufacturing.
One of the most critical evolutions in transistor design is the Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistor, exemplified by Samsung's (KRX:005930) Multi-Bridge-Channel FET (MBCFET™) and Intel's (NASDAQ:INTC) upcoming RibbonFET. Unlike their predecessors, FinFETs, where the gate controls the channel from three sides, GAA transistors completely encircle the channel, typically in the form of nanosheets or nanowires. This "all-around" gate design offers superior electrostatic control, drastically reducing leakage currents and mitigating short-channel effects that become prevalent at sub-5nm nodes. Furthermore, GAA nanosheets provide unprecedented flexibility in adjusting channel width, allowing for more precise tuning of performance and power characteristics—a crucial advantage for energy-hungry AI workloads. Industry reception is overwhelmingly positive, with major foundries rapidly transitioning to GAA architectures as the cornerstone for future sub-3nm process nodes.
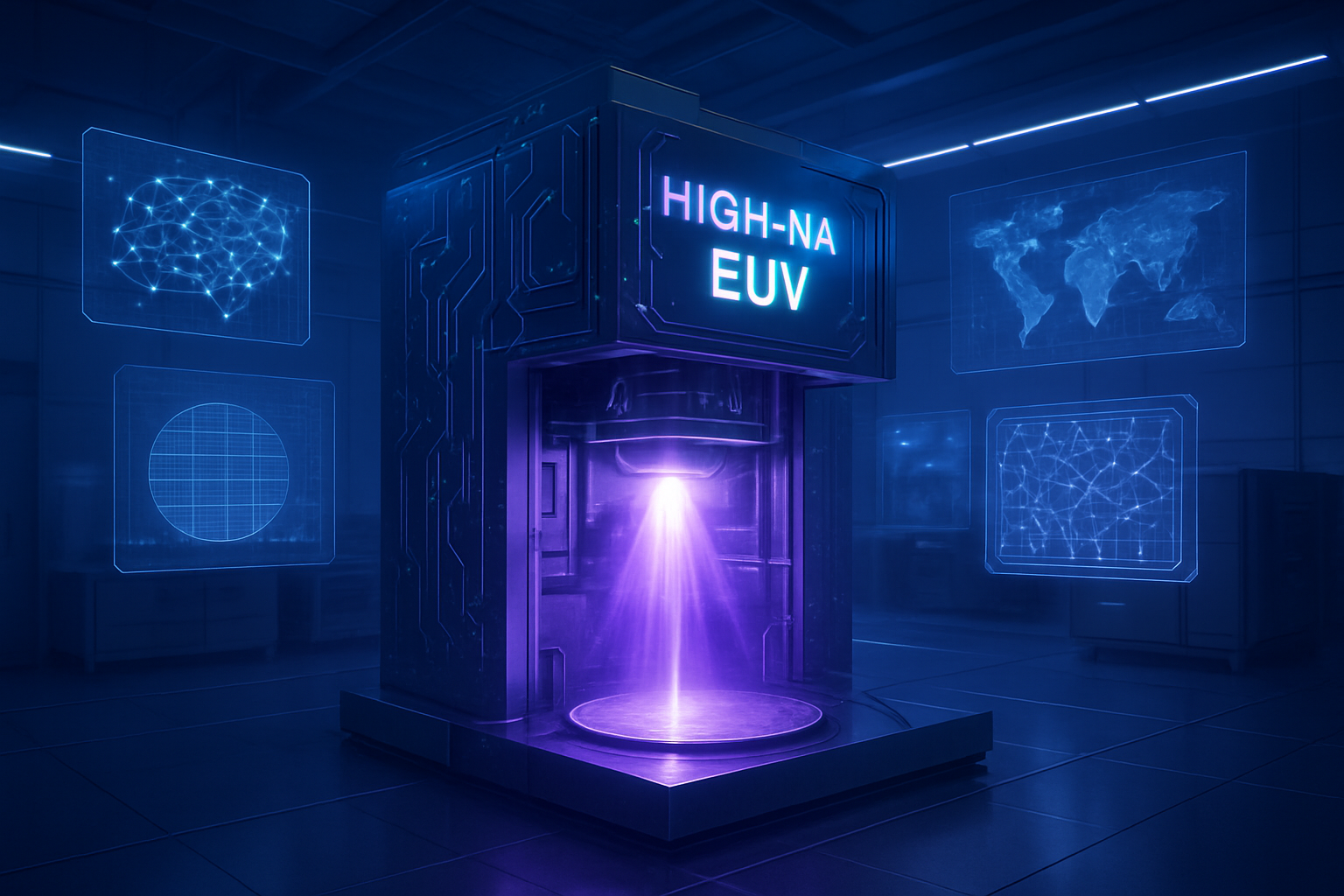
Complementing these transistor innovations is the cutting-edge High-Numerical Aperture (High-NA) Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography. ASML's (AMS:ASML) TWINSCAN EXE:5000, with its 0.55 NA lens, represents a significant leap from current 0.33 NA EUV systems. This higher NA enables a resolution of 8 nm, allowing for the printing of significantly smaller features and nearly triple the transistor density compared to existing EUV. While current EUV is crucial for 7nm and 5nm nodes, High-NA EUV is indispensable for the 2nm node and beyond, potentially eliminating the need for complex and costly multi-patterning techniques. Intel received the first High-NA EUV modules in December 2023, signaling its commitment to leading the charge. While the immense cost and complexity pose challenges—with some reports suggesting TSMC (NYSE:TSM) and Samsung might strategically delay its full adoption for certain nodes—the industry broadly recognizes High-NA EUV as a critical enabler for the next wave of miniaturization essential for advanced AI chips.
As traditional scaling faces physical limits, advanced packaging has emerged as a parallel and equally vital pathway to enhance performance. Techniques like 3D stacking, which vertically integrates multiple dies using Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs), dramatically reduce data travel distances, leading to faster data transfer, improved power efficiency, and a smaller footprint. This is particularly evident in High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), a form of 3D-stacked DRAM that has become indispensable for AI accelerators and HPC due to its unparalleled bandwidth and power efficiency. Companies like SK Hynix (KRX:000660), Samsung, and Micron (NASDAQ:MU) are aggressively expanding HBM production to meet surging AI data center demand. Simultaneously, chiplets are revolutionizing chip design by breaking monolithic System-on-Chips (SoCs) into smaller, modular components. This approach enhances yields, reduces costs by allowing different process nodes for different functions, and offers greater design flexibility. Standards like UCIe are fostering an open chiplet ecosystem, enabling custom-tailored solutions for specific AI performance and power requirements.
Beyond silicon, the exploration of novel materials is opening new frontiers. Wide bandgap semiconductors like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are rapidly replacing silicon in power electronics. GaN, with its superior electron mobility and breakdown strength, enables faster switching, higher power density, and greater efficiency in applications ranging from EV chargers to 5G base stations. SiC, boasting even higher thermal conductivity and breakdown voltage, is pivotal for high-power devices in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Further out, 2D materials such as Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) and Indium Selenide (InSe) are showing immense promise for ultra-thin, high-mobility transistors that could push past silicon's theoretical limits, particularly for future low-power AI at the edge. While still facing manufacturing challenges, recent advancements in wafer-scale fabrication of InSe are seen as a major step towards a post-silicon future.
The AI research community and industry experts view these technical shifts with immense optimism, recognizing their fundamental role in accelerating AI capabilities. The ability to achieve superior computational power, data throughput, and energy efficiency through GAA, High-NA EUV, and advanced packaging is deemed critical for advancing large language models, autonomous systems, and ubiquitous edge AI. However, concerns about the immense cost of development and deployment, particularly for High-NA EUV, hint at potential industry consolidation, where only the leading foundries with significant capital can compete at the cutting edge.
Corporate Battlegrounds: Who Wins and Loses in the Chip Revolution
The seismic shifts in semiconductor manufacturing are fundamentally reshaping the competitive landscape for tech giants, AI companies, and nimble startups alike. The ability to harness innovations like GAA transistors, High-NA EUV, advanced packaging, and novel materials is becoming the ultimate determinant of market leadership and strategic advantage.
Leading the charge in manufacturing are the pure-play foundries and Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs). Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (NYSE:TSM), already a dominant force, is heavily invested in GAA and advanced packaging technologies like CoWoS and InFO, ensuring its continued pivotal role for virtually all major chip designers. Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (KRX:005930), as both an IDM and foundry, is fiercely competing with TSMC, notably with its MBCFET™ GAA technology. Meanwhile, Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) is making aggressive moves to reclaim process leadership, being an early adopter of ASML's High-NA EUV scanner and developing its own RibbonFET GAA technology and advanced packaging solutions like EMIB. These three giants are locked in a high-stakes "2nm race," where success in mastering these cutting-edge processes will dictate who fabricates the next generation of high-performance chips.
The impact extends profoundly to chip designers and AI innovators. Companies like NVIDIA Corporation (NASDAQ:NVDA), the undisputed leader in AI GPUs, and Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NASDAQ:AMD), a strong competitor in CPUs, GPUs, and AI accelerators, are heavily reliant on these advanced manufacturing and packaging techniques to power their increasingly complex and demanding chips. Tech titans like Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ:GOOGL) and Amazon.com, Inc. (NASDAQ:AMZN), which design their own custom AI chips (TPUs, Graviton, Trainium/Inferentia) for their cloud infrastructure, are major users of advanced packaging to overcome memory bottlenecks and achieve superior performance. Similarly, Apple Inc. (NASDAQ:AAPL), known for its in-house chip design, will continue to leverage state-of-the-art foundry processes for its mobile and computing platforms. The drive for custom silicon, enabled by advanced packaging and chiplets, empowers these tech giants to optimize hardware precisely for their software stacks, reducing reliance on general-purpose solutions and gaining a crucial competitive edge in AI development and deployment.
Semiconductor equipment manufacturers are also seeing immense benefit. ASML Holding N.V. (AMS:ASML) stands as an indispensable player, being the sole provider of EUV lithography and the pioneer of High-NA EUV. Companies like Applied Materials, Inc. (NASDAQ:AMAT), Lam Research Corporation (NASDAQ:LRCX), and KLA Corporation (NASDAQ:KLAC), which supply critical equipment for deposition, etch, and process control, are essential enablers of GAA and advanced packaging, experiencing robust demand for their sophisticated tools. Furthermore, the rise of novel materials is creating new opportunities for specialists like Wolfspeed, Inc. (NYSE:WOLF) and STMicroelectronics N.V. (NYSE:STM), dominant players in Silicon Carbide (SiC) wafers and devices, crucial for the booming electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors.
However, this transformative period also brings significant competitive implications and potential disruptions. The astronomical R&D costs and capital expenditures required for these advanced technologies favor larger companies, potentially leading to further industry consolidation and higher barriers to entry for startups. While agile startups can innovate in niche markets—such as RISC-V based AI chips or optical computing—they remain heavily reliant on foundry partners and face intense talent wars. The increasing adoption of chiplet architectures, while offering flexibility, could also disrupt the traditional monolithic SoC market, potentially altering revenue streams for leading-node foundries by shifting value towards system-level integration rather smarter, smaller dies. Ultimately, companies that can effectively integrate specialized hardware into their software stacks, either through in-house design or close foundry collaboration, will maintain a decisive competitive advantage, driving a continuous cycle of innovation and market repositioning.
A New Epoch for AI: Societal Transformation and Strategic Imperatives
The ongoing revolution in semiconductor manufacturing transcends mere technical upgrades; it represents a foundational shift with profound implications for the broader AI landscape, global society, and geopolitical dynamics. These innovations are not just enabling better chips; they are actively shaping the future trajectory of artificial intelligence itself, pushing it into an era of unprecedented capability and pervasiveness.
At its core, the advancement in GAA transistors, High-NA EUV lithography, advanced packaging, and novel materials directly underpins the exponential growth of AI. These technologies provide the indispensable computational power, energy efficiency, and miniaturization necessary for training and deploying increasingly complex AI models, from colossal large language models to hyper-efficient edge AI applications. The synergy is undeniable: AI's insatiable demand for processing power drives semiconductor innovation, while these advanced chips, in turn, accelerate AI development, creating a powerful, self-reinforcing cycle. This co-evolution is manifesting in the proliferation of specialized AI chips—GPUs, ASICs, FPGAs, and NPUs—optimized for parallel processing, which are crucial for pushing the boundaries of machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. The shift towards advanced packaging, particularly 2.5D and 3D integration, is singularly vital for High-Performance Computing (HPC) and data centers, allowing for denser interconnections and faster data exchange, thereby accelerating the training of monumental AI models.
The societal impacts of these advancements are vast and transformative. Economically, the burgeoning AI chip market, projected to reach hundreds of billions by the early 2030s, promises to spur significant growth and create entirely new industries across healthcare, automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. More powerful and efficient chips will enable breakthroughs in areas such as precision diagnostics and personalized medicine, truly autonomous vehicles, next-generation 5G and 6G networks, and sustainable energy solutions. From smarter everyday devices to more efficient global data centers, these innovations are integrating advanced computing into nearly every facet of modern life, promising a future of enhanced capabilities and convenience.
However, this rapid technological acceleration is not without its concerns. Environmentally, semiconductor manufacturing is notoriously resource-intensive, consuming vast amounts of energy, ultra-pure water, and hazardous chemicals, contributing to significant carbon emissions and pollution. The immense energy appetite of large-scale AI models further exacerbates these environmental footprints, necessitating a concerted global effort towards "green AI chips" and sustainable manufacturing practices. Ethically, the rise of AI-powered automation, fueled by these chips, raises questions about workforce displacement. The potential for bias in AI algorithms, if trained on skewed data, could lead to undesirable outcomes, while the proliferation of connected devices powered by advanced chips intensifies concerns around data privacy and cybersecurity. The increasing role of AI in designing chips also introduces questions of accountability and transparency in AI-driven decisions.
Geopolitically, semiconductors have become strategic assets, central to national security and economic stability. The highly globalized and concentrated nature of the industry—with critical production stages often located in specific regions—creates significant supply chain vulnerabilities and fuels intense international competition. Nations, including the United States with its CHIPS Act, are heavily investing in domestic production to reduce reliance on foreign technology and secure their technological futures. Export controls on advanced semiconductor technology, particularly towards nations like China, underscore the industry's role as a potent political tool and a flashpoint for international tensions.
In comparison to previous AI milestones, the current semiconductor innovations represent a more fundamental and pervasive shift. While earlier AI eras benefited from incremental hardware improvements, this period is characterized by breakthroughs that push beyond the traditional limits of Moore's Law, through architectural innovations like GAA, advanced lithography, and sophisticated packaging. Crucially, it marks a move towards specialized hardware designed explicitly for AI workloads, rather than AI adapting to general-purpose processors. This foundational shift is making AI not just more powerful, but also more ubiquitous, fundamentally altering the computing paradigm and setting the stage for truly pervasive intelligence across the globe.
The Road Ahead: Next-Gen Chips and Uncharted Territories
Looking towards the horizon, the semiconductor industry is poised for an exhilarating period of continued evolution, driven by the relentless march of innovation in manufacturing processes and materials. Experts predict a vibrant future, with the industry projected to reach an astounding $1 trillion valuation by 2030, fundamentally reshaping technology as we know it.
In the near term, the widespread adoption of Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistors will solidify. Samsung has already begun GAA production, and both TSMC and Intel (with its 18A process incorporating GAA and backside power delivery) are expected to ramp up significantly in 2025. This transition is critical for delivering the enhanced power efficiency and performance required for sub-2nm nodes. Concurrently, High-NA EUV lithography is set to become a cornerstone technology. With TSMC reportedly receiving its first High-NA EUV machine in September 2024 for its A14 (1.4nm) node and Intel anticipating volume production around 2026, this technology will enable the mass production of sub-2nm chips, forming the bedrock for future data centers and high-performance edge AI devices.
The role of advanced packaging will continue to expand dramatically, moving from a back-end process to a front-end design imperative. Heterogeneous integration and 3D ICs/chiplet architectures will become standard, allowing for the stacking of diverse components—logic, memory, and even photonics—into highly dense, high-bandwidth systems. The demand for High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM), crucial for AI applications, is projected to surge, potentially rivaling data center DRAM in market value by 2028. TSMC is aggressively expanding its CoWoS advanced packaging capacity to meet this insatiable demand, particularly from AI-driven GPUs. Beyond this, advancements in thermal management within advanced packages, including embedded cooling, will be critical for sustaining performance in increasingly dense chips.
Longer term, the industry will see further breakthroughs in novel materials. Wide-bandgap semiconductors like GaN and SiC will continue their revolution in power electronics, driving more efficient EVs, 5G networks, and renewable energy systems. More excitingly, two-dimensional (2D) materials such as molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) and graphene are being explored for ultra-thin, high-mobility transistors that could potentially offer unprecedented processing speeds, moving beyond silicon's fundamental limits. Innovations in photoresists and metallization, exploring materials like cobalt and ruthenium, will also be vital for future lithography nodes. Crucially, AI and machine learning will become even more deeply embedded in the semiconductor manufacturing process itself, optimizing everything from predictive maintenance and yield enhancement to accelerating design cycles and even the discovery of new materials.
These developments will unlock a new generation of applications. AI and machine learning will see an explosion of specialized chips, particularly for generative AI and large language models, alongside the rise of neuromorphic chips that mimic the human brain for ultra-efficient edge AI. The automotive industry will become even more reliant on advanced semiconductors for truly autonomous vehicles and efficient EVs. High-Performance Computing (HPC) and data centers will continue their insatiable demand for high-bandwidth, low-latency chips. The Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing will proliferate with powerful, energy-efficient chips, enabling smarter devices and personalized AI companions. Beyond these, advancements will feed into 5G/6G communication, sophisticated medical devices, and even contribute foundational components for nascent quantum computing.
However, significant challenges loom. The immense capital intensity of leading-edge fabs, exceeding $20-25 billion per facility, means only a few companies can compete at the forefront. Geopolitical fragmentation and the need for supply chain resilience, exacerbated by export controls and regional concentrations of manufacturing, will continue to drive efforts for diversification and reshoring. A projected global shortage of over one million skilled workers by 2030, particularly in AI and advanced robotics, poses a major constraint. Furthermore, the industry faces mounting pressure to address its environmental impact, requiring a concerted shift towards sustainable practices, energy-efficient designs, and greener manufacturing processes. Experts predict that while dimensional scaling will continue, functional scaling through advanced packaging and materials will become increasingly dominant, with AI acting as both the primary driver and a transformative tool within the industry itself.
The Future of Semiconductor Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Outlook
The semiconductor industry, currently valued at hundreds of billions and projected to reach a trillion dollars by 2030, is navigating an era of unprecedented innovation and strategic importance. Key takeaways from this transformative period include the critical transition to Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistors for sub-2nm nodes, the indispensable role of High-NA EUV lithography for extreme miniaturization, the paradigm shift towards advanced packaging (2.5D, 3D, chiplets, and HBM) to overcome traditional scaling limits, and the exciting exploration of novel materials like GaN, SiC, and 2D semiconductors to unlock new frontiers of performance and efficiency.
These developments are more than mere technical advancements; they represent a foundational turning point in the history of technology and AI. They are directly fueling the explosive growth of generative AI, large language models, and pervasive edge AI, providing the essential computational horsepower and efficiency required for the next generation of intelligent systems. This era is defined by a virtuous cycle where AI drives demand for advanced chips, and in turn, AI itself is increasingly used to design, optimize, and manufacture these very chips. The long-term impact will be ubiquitous AI, unprecedented computational capabilities, and a global tech landscape fundamentally reshaped by these underlying hardware innovations.
In the coming weeks and months, as of November 2025, several critical developments bear close watching. Observe the accelerated ramp-up of GAA transistor production from Samsung (KRX:005930), TSMC (NYSE:TSM) with its 2nm (N2) node, and Intel (NASDAQ:INTC) with its 18A process. Key milestones for High-NA EUV will include ASML's (AMS:ASML) shipments of its next-generation tools and the progress of major foundries in integrating this technology into their advanced process development. The aggressive expansion of advanced packaging capacity, particularly TSMC's CoWoS and the adoption of HBM4 by AI leaders like NVIDIA (NASDAQ:NVDA), will be crucial indicators of AI's continued hardware demands. Furthermore, monitor the accelerated adoption of GaN and SiC in new power electronics products, the impact of ongoing geopolitical tensions on global supply chains, and the effectiveness of government initiatives like the CHIPS Act in fostering regional manufacturing resilience. The ongoing construction of 18 new semiconductor fabs starting in 2025, particularly in the Americas and Japan, signals a significant long-term capacity expansion that will be vital for meeting future demand for these indispensable components of the modern world.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.