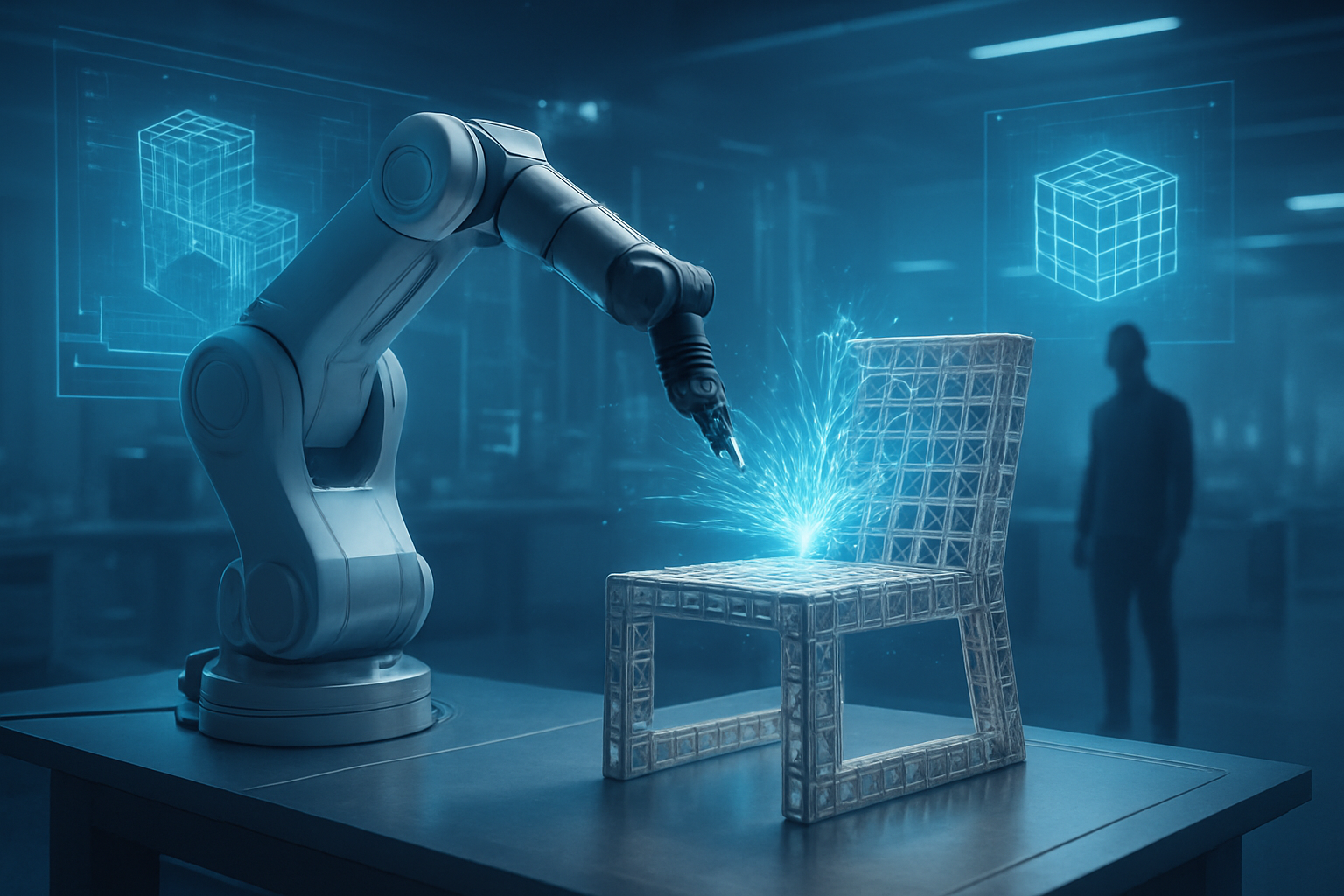
In a landmark demonstration of "Embodied AI," researchers at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) have unveiled a system that allows users to design and manufacture physical furniture using nothing but natural language. The project, titled "Speech to Reality," marks a departure from generative AI’s traditional digital-only outputs, moving the technology into the physical realm where a simple verbal request—"Robot, make me a two-tiered stool"—can result in a finished, functional object in under five minutes.
This breakthrough represents a pivotal shift in the "bits-to-atoms" pipeline, bridging the gap between Large Language Models (LLMs) and autonomous robotics. By integrating advanced geometric reasoning with modular fabrication, the MIT team has created a workflow where non-experts can bypass complex CAD software and manual assembly entirely. As of January 2026, the system has evolved from a laboratory curiosity into a robust platform capable of producing structural, load-bearing items, signaling a new era for on-demand domestic and industrial manufacturing.
The Technical Architecture of Generative Fabrication
The "Speech to Reality" system operates through a sophisticated multi-stage pipeline that translates high-level human intent into low-level robotic motor controls. The process begins with the OpenAI Whisper API, a product of the Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT) partner, which transcribes the user's spoken commands. These commands are then parsed by a custom Large Language Model that extracts functional requirements, such as height, width, and number of surfaces. This data is fed into a 3D generative model, such as Meshy.AI, which produces a high-fidelity digital mesh. However, because raw AI-generated meshes are often structurally unsound, MIT’s critical innovation lies in its "Voxelization Algorithm."
This algorithm discretizes the digital mesh into a grid of coordinates that correspond to standardized, modular lattice components—small cubes and panels that the robot can easily manipulate. To ensure the final product is more than just a pile of blocks, a Vision-Language Model (VLM) performs "geometric reasoning," identifying which parts of the design are structural legs and which are flat surfaces. The physical assembly is then carried out by a UR10 robotic arm from Universal Robots, a subsidiary of Teradyne (NASDAQ: TER). Unlike previous iterations like 2018's "AutoSaw," which used traditional timber and power tools, the 2026 system utilizes discrete cellular structures with mechanical interlocking connectors, allowing for rapid, reversible, and precise assembly.
The system also includes a "Fabrication Constraints Layer" that solves for real-world physics in real-time. Before the robotic arm begins its first movement, the AI calculates path planning to avoid collisions, ensures that every part is physically attached to the main structure, and confirms that the robot can reach every necessary point in the assembly volume. This "Reachability Analysis" prevents the common "hallucination" issues found in digital LLMs from translating into physical mechanical failures.
Impact on the Furniture Giants and the Robotics Sector
The emergence of automated, prompt-based manufacturing is sending shockwaves through the $700 billion global furniture market. Traditional retailers like IKEA (Ingka Group) are already pivoting; the Swedish giant recently announced strategic partnerships to integrate Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) into their logistics chain. For IKEA, the MIT system suggests a future where "flat-pack" furniture is replaced by "no-pack" furniture—where consumers visit a local micro-factory, describe their needs to an AI, and watch as a robot assembles a custom piece of furniture tailored to their specific room dimensions.
In the tech sector, this development intensifies the competition for "Physical AI" dominance. Amazon (NASDAQ: AMZN) has been a frontrunner in this space with its "Vulcan" robotic arm, which uses tactile feedback to handle delicate warehouse items. However, MIT’s approach shifts the focus from simple manipulation to complex assembly. Meanwhile, companies like Alphabet (NASDAQ: GOOGL) through Google DeepMind are refining Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models like RT-2, which allow robots to understand abstract concepts. MIT’s modular lattice approach provides a standardized "hardware language" that these VLA models can use to build almost anything, potentially commoditizing the assembly process and disrupting specialized furniture manufacturers.
Startups are also entering the fray, with Figure AI—backed by the likes of Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) and Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA)—deploying general-purpose humanoids capable of learning assembly tasks through visual observation. The MIT system provides a blueprint for these humanoids to move beyond simple labor and toward creative construction. By making the "instructions" for a chair as simple as a text string, MIT has lowered the barrier to entry for bespoke manufacturing, potentially enabling a new wave of localized, AI-driven craft businesses that can out-compete mass-produced imports on both speed and customization.
The Broader Significance of Reversible Fabrication
Beyond the convenience of "on-demand chairs," the "Speech to Reality" system addresses a growing global crisis: furniture waste. In the United States alone, over 12 million tons of furniture are discarded annually. Because the MIT system uses modular, interlocking components, it enables "reversible fabrication." A user could, in theory, tell the robot to disassemble a desk they no longer need and use those same parts to build a bookshelf or a coffee table. This circular economy model represents a massive leap forward in sustainable design, where physical objects are treated as "dynamic data" that can be reconfigured as needed.
This milestone is being compared to the "Gutenberg moment" for physical goods. Just as the printing press democratized the spread of information, generative assembly democratizes the creation of physical objects. However, this shift is not without its concerns. Industry experts have raised questions regarding the structural safety and liability of AI-generated designs. If an AI-designed chair collapses, the legal framework for determining whether the fault lies with the software developer, the hardware manufacturer, or the user remains dangerously undefined. Furthermore, the potential for job displacement in the carpentry and manual assembly sectors is a significant social hurdle that will require policy intervention as the technology scales.
The MIT project also highlights the rapid evolution of "Embodied AI" datasets. By using the Open X-Embodiment (OXE) dataset, researchers have been able to train robots on millions of trajectories, allowing them to handle the inherent "messiness" of the physical world. This represents a departure from the "locked-box" automation of 20th-century factories, moving toward "General Purpose Robotics" that can adapt to any environment, from a specialized lab to a suburban living room.
Scaling Up: From Stools to Living Spaces
The near-term roadmap for this technology is ambitious. MIT researchers have already begun testing "dual-arm assembly" through the Fabrica project, which allows robots to perform "bimanual" tasks—such as holding a long beam steady while another arm snaps a connector into place. This will enable the creation of much larger and more complex structures than the current single-arm setup allows. Experts predict that by 2027, we will see the first commercial "Micro-Fabrication Hubs" in urban centers, operating as 24-hour kiosks where citizens can "print" household essentials on demand.
Looking further ahead, the MIT team is exploring "distributed mobile robotics." Instead of a stationary arm, this involves "inchworm-like" robots that can crawl over the very structures they are building. This would allow the system to scale beyond furniture to architectural-level constructions, such as temporary emergency housing or modular office partitions. The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) is also on the horizon, allowing users to "paint" their desired furniture into their physical room using a headset, with the robot then matching the physical build to the digital holographic overlay.
The primary challenge remains the development of a universal "Physical AI" model that can handle non-modular materials. While the lattice-cube system is highly efficient, the research community is striving toward robots that can work with varied materials like wood, metal, and recycled plastic with the same ease. As these models become more generalized, the distinction between "designer," "manufacturer," and "consumer" will continue to blur.
A New Chapter in Human-Machine Collaboration
The "Speech to Reality" system is more than just a novelty for making chairs; it is a foundational shift in how humans interact with the physical world. By removing the technical barriers of CAD and the physical barriers of manual labor, MIT has turned the environment around us into a programmable medium. We are moving from an era where we buy what is available to an era where we describe what we need, and the world reshapes itself to accommodate us.
As we look toward the final quarters of 2026, the key developments to watch will be the integration of these generative models into consumer-facing humanoid robots and the potential for "multi-material" fabrication. The significance of this breakthrough in AI history cannot be overstated—it represents the moment AI finally grew "hands" capable of matching the creativity of its "mind." For the tech industry, the race is no longer just about who has the best chatbot, but who can most effectively manifest those thoughts into the physical world.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.