As of January 2, 2026, the artificial intelligence landscape has reached a pivotal turning point with the formal rollout of NVIDIA's (NASDAQ:NVDA) next-generation "Rubin" architecture. Following the unprecedented success of the Blackwell series, which dominated the data center market throughout 2024 and 2025, the Rubin platform represents more than just a seasonal upgrade; it is a fundamental architectural shift designed to move the industry from static large language models (LLMs) toward dynamic, autonomous "World Models" and reasoning agents.
The immediate significance of the Rubin launch lies in its ability to break the "memory wall" that has long throttled AI performance. By integrating the first-ever HBM4 memory stacks and a custom-designed Vera CPU, NVIDIA has effectively doubled the throughput available for the world’s most demanding AI workloads. This transition signals the start of the "AI Factory" era, where trillion-parameter models are no longer experimental novelties but the standard engine for global enterprise automation and physical robotics.
The Engineering Marvel of the R100: 3nm Precision and HBM4 Power
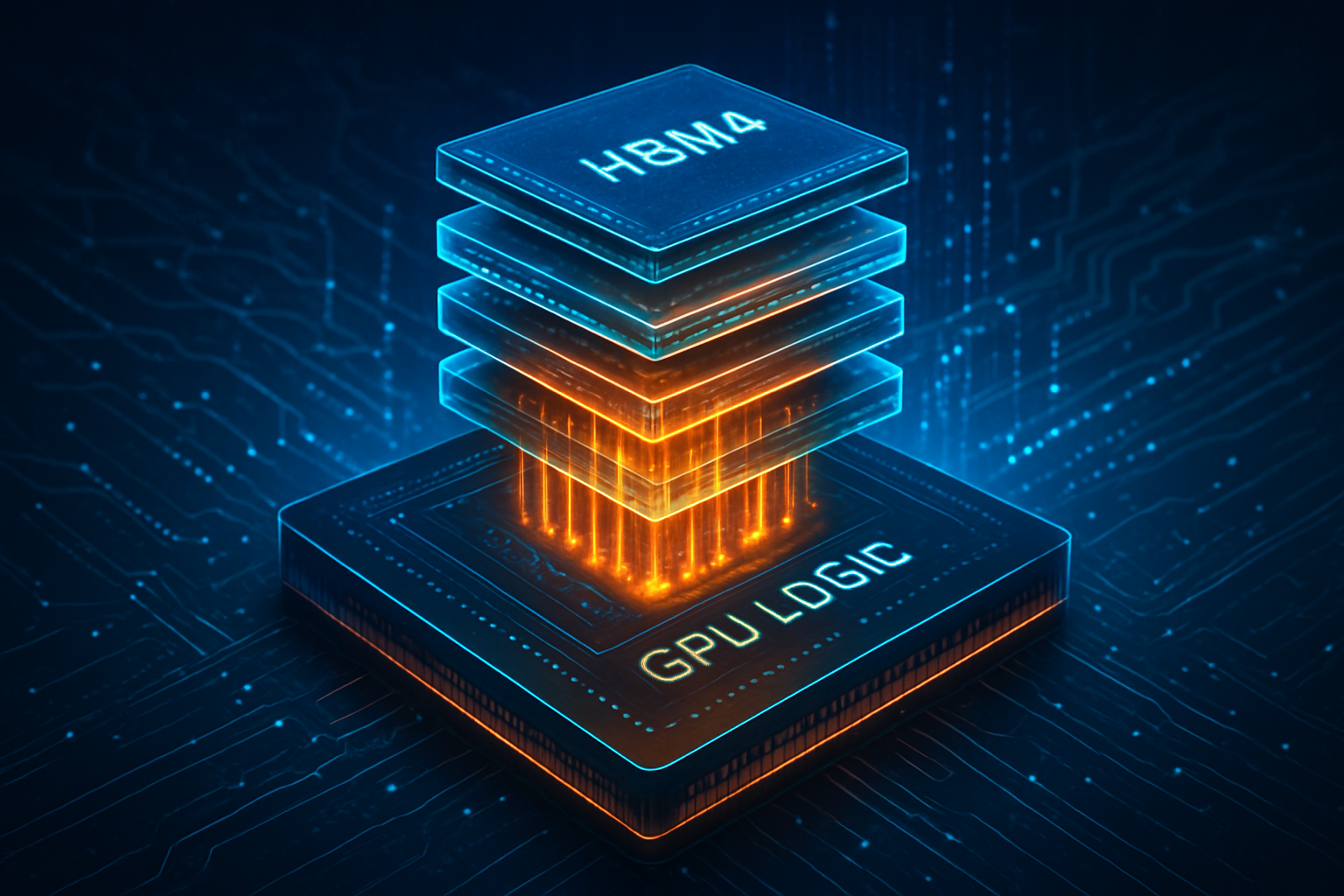
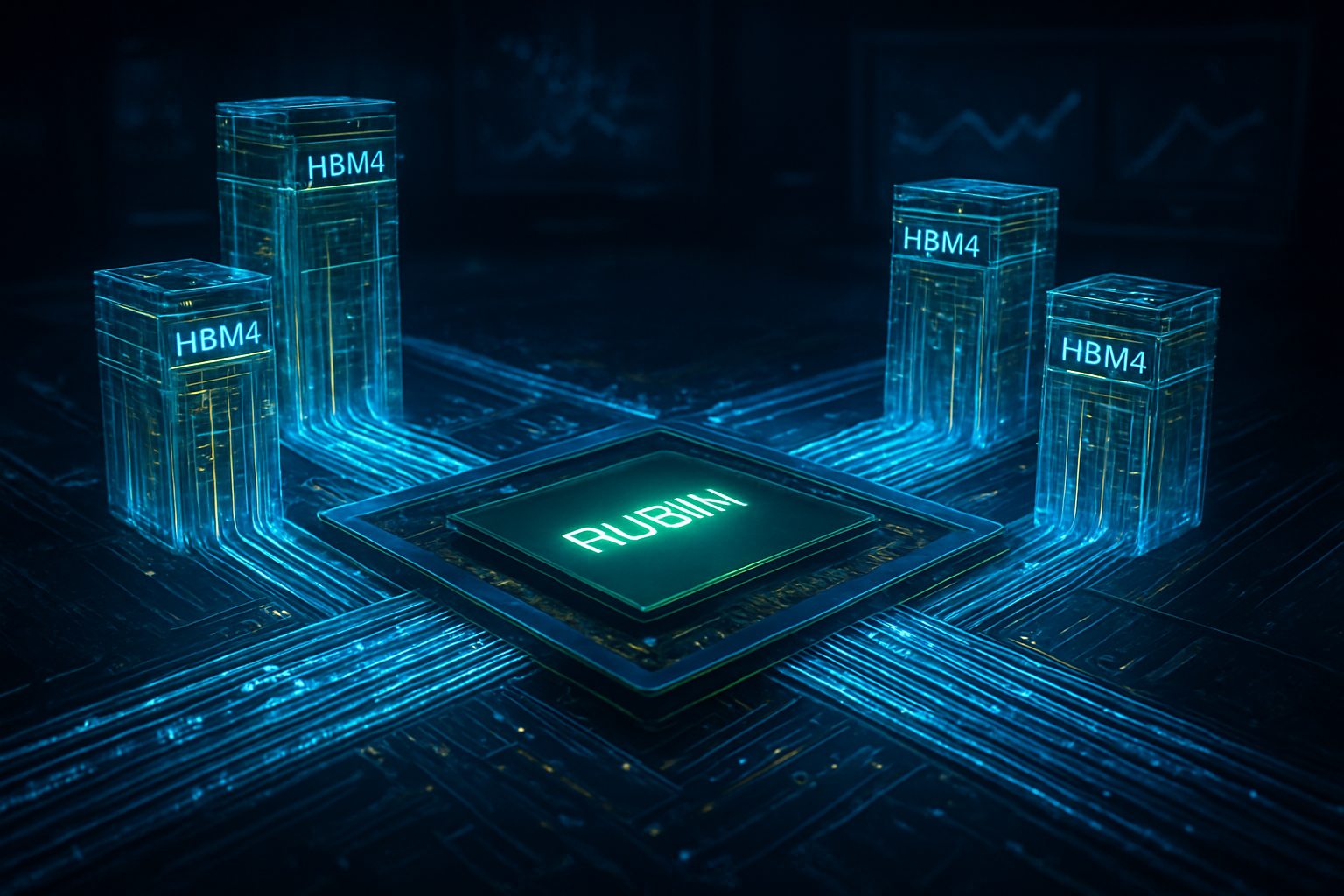
At the heart of the Rubin platform is the R100 GPU, a powerhouse fabricated on Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company’s (NYSE:TSM) enhanced 3nm (N3P) process. This move to the 3nm node allows for a 20% increase in transistor density and a 30% reduction in power consumption compared to the 4nm Blackwell chips. For the first time, NVIDIA has fully embraced a chiplet-based design for its flagship data center GPU, utilizing CoWoS-L (Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate with Local Interconnect) packaging. This modular approach enables the R100 to feature a massive 100x100mm substrate, housing multiple compute dies and high-bandwidth memory stacks with near-zero latency.
The most striking technical specification of the R100 is its memory subsystem. By utilizing the new HBM4 standard, the R100 delivers a staggering 13 to 15 TB/s of memory bandwidth—a nearly twofold increase over the Blackwell Ultra. This bandwidth is supported by a 2,048-bit interface and 288GB of HBM4 memory across eight 12-high stacks, sourced through strategic partnerships with SK Hynix (KRX:000660), Micron (NASDAQ:MU), and Samsung (KRX:005930). This massive pipeline is essential for the "Million-GPU" clusters that hyperscalers are currently constructing to train the next generation of multimodal AI.
Complementing the R100 is the Vera CPU, the successor to the Arm-based Grace CPU. The Vera CPU features 88 custom "Olympus" Arm-compatible cores, supporting 176 logical threads via simultaneous multithreading (SMT). The Vera-Rubin superchip is linked via an NVLink-C2C (Chip-to-Chip) interconnect, boasting a bidirectional bandwidth of 1.8 TB/s. This tight coherency allows the CPU to handle complex data pre-processing and real-time shuffling, ensuring that the R100 is never "starved" for data during the training of trillion-parameter models.
Industry experts have reacted with awe at the platform's FP4 (4-bit floating point) compute performance. A single R100 GPU delivers approximately 50 Petaflops of FP4 compute. When scaled to a rack-level configuration, such as the Vera Rubin NVL144, the platform achieves 3.6 Exaflops of FP4 inference. This represents a 2.5x to 3.3x performance leap over the previous Blackwell-based systems, making the deployment of massive reasoning models economically viable for the first time in history.
Market Dominance and the Competitive Moat
The transition to Rubin solidifies NVIDIA's position at the top of the AI value chain, creating significant implications for hyperscale customers and competitors alike. Major cloud providers, including Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT), Alphabet (NASDAQ:GOOGL), and Amazon (NASDAQ:AMZN), are already racing to secure the first shipments of Rubin-based systems. For these companies, the 3.3x performance uplift in FP4 compute translates directly into lower "cost-per-token," allowing them to offer more sophisticated AI services at more competitive price points.
For competitors like Advanced Micro Devices (NASDAQ:AMD) and Intel (NASDAQ:INTC), the Rubin architecture sets a high bar for 2026. While AMD’s MI300 and MI400 series have made inroads in the inference market, NVIDIA’s integration of the Vera CPU and R100 GPU into a single, cohesive superchip provides a "full-stack" advantage that is difficult to replicate. The deep integration of HBM4 and the move to 3nm chiplets suggest that NVIDIA is leveraging its massive R&D budget to stay at least one full generation ahead of the rest of the industry.
Startups specializing in "Agentic AI" are perhaps the biggest winners of this development. Companies that previously struggled with the latency of "Chain-of-Thought" reasoning can now run multiple hidden reasoning steps in real-time. This capability is expected to disrupt the software-as-a-service (SaaS) industry, as autonomous agents begin to replace traditional static software interfaces. NVIDIA’s market positioning has shifted from being a "chip maker" to becoming the primary infrastructure provider for the "Reasoning Economy."
Scaling Toward World Models and Physical AI
The Rubin architecture is specifically tuned for the rise of "World Models"—AI systems that build internal representations of physical reality. Unlike traditional LLMs that predict the next word in a sentence, World Models predict the next state of a physical environment, understanding concepts like gravity, spatial relationships, and temporal continuity. The 15 TB/s bandwidth of the R100 is the key to this breakthrough, allowing AI to process massive streams of high-resolution video and sensor data in real-time.
This shift has profound implications for the field of robotics and "Physical AI." NVIDIA’s Project GR00T, which focuses on humanoid robot foundations, is expected to be the primary beneficiary of the Rubin platform. With the Vera-Rubin superchip, robots can now perform "on-device" reasoning, planning their movements and predicting the outcomes of their actions before they even move a limb. This move toward autonomous reasoning agents marks a transition from "System 1" AI (fast, intuitive, but prone to error) to "System 2" AI (slow, deliberate, and capable of complex planning).
However, this massive leap in compute power also brings concerns regarding energy consumption and the environmental impact of AI factories. While the 3nm process is more efficient on a per-transistor basis, the sheer scale of the Rubin deployments—often involving hundreds of thousands of GPUs in a single cluster—requires unprecedented levels of power and liquid cooling infrastructure. Critics argue that the race for AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) is becoming a race for energy dominance, potentially straining national power grids.
The Roadmap Ahead: Toward Rubin Ultra and Beyond
Looking forward, NVIDIA has already teased a "Rubin Ultra" variant slated for 2027, which is expected to feature a 1TB HBM4 configuration and bandwidth reaching 25 TB/s. In the near term, the focus will be on the software ecosystem. NVIDIA has paired the Rubin hardware with the Llama Nemotron family of reasoning models and the AI-Q Blueprint, tools that allow developers to build "Agentic AI Workforces" that can autonomously manage complex business workflows.
The next two years will likely see the emergence of "Physical AI" applications that were previously thought to be decades away. We can expect to see Rubin-powered autonomous vehicles that can navigate complex, unmapped environments by reasoning about their surroundings rather than relying on pre-programmed rules. Similarly, in the medical field, Rubin-powered systems could simulate the physical interactions of new drug compounds at a molecular level with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Challenges remain, particularly in the global supply chain. The reliance on TSMC’s 3nm capacity and the high demand for HBM4 memory could lead to supply bottlenecks throughout 2026. Experts predict that while NVIDIA will maintain its lead, the "scarcity" of Rubin chips will create a secondary market for Blackwell and older architectures, potentially leading to a bifurcated AI landscape where only the wealthiest labs have access to true "World Model" capabilities.
A New Chapter in AI History
The transition from Blackwell to Rubin marks the end of the "Chatbot Era" and the beginning of the "Agentic Era." By delivering a 3.3x performance leap and breaking the memory bandwidth barrier with HBM4, NVIDIA has provided the hardware foundation necessary for AI to interact with and understand the physical world. The R100 GPU and Vera CPU represent the pinnacle of current semiconductor engineering, merging chiplet architecture with high-performance Arm cores to create a truly unified AI superchip.
Key takeaways from this launch include the industry's decisive move toward FP4 precision for efficiency, the critical role of HBM4 in overcoming the memory wall, and the strategic focus on World Models. As we move through 2026, the success of the Rubin architecture will be measured not just by NVIDIA's stock price, but by the tangible presence of autonomous agents and reasoning systems in our daily lives.
In the coming months, all eyes will be on the first benchmark results from the "Million-GPU" clusters being built by the tech giants. If the Rubin platform delivers on its promise of enabling real-time, trillion-parameter reasoning, the path to AGI may be shorter than many dared to imagine.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.