The consumer electronics landscape shifted seismically this month at CES 2026, marking the definitive end of the "Chatbot Era" and the dawn of the "Agentic Era." For the last two years, the industry teased the potential of the AI PC, but the 2026 showcase in Las Vegas proved that the hardware has finally caught up to the hype. No longer restricted to simple text summaries or image generation, the latest silicon from the world’s leading chipmakers is now capable of running autonomous agents locally—systems that can plan, reason, and execute complex workflows across applications without ever sending a single packet of data to the cloud.
This transition is underpinned by a brutal three-way war between Intel, Qualcomm, and AMD. As these titans unveiled their latest system-on-chips (SoCs), the metrics of success have shifted from raw clock speeds to NPU (Neural Processing Unit) TOPS (Trillions of Operations Per Second) and the ability to sustain high-parameter models on-device. With performance levels now hitting the 60-80 TOPS range for dedicated NPUs, the laptop has been reimagined as a private, sovereign AI node, fundamentally challenging the dominance of cloud-based AI providers.
The Silicon Arms Race: Panther Lake, X2 Elite, and the Rise of 80 TOPS
The technical showdown at CES 2026 centered on three flagship architectures: Intel’s Panther Lake, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X2 Elite, and AMD’s Ryzen AI 400. Intel Corporation (NASDAQ: INTC) took center stage with the launch of Panther Lake, branded as the Core Ultra Series 3. Built on the highly anticipated Intel 18A process node, Panther Lake represents a massive architectural leap, utilizing Cougar Cove performance cores and Darkmont efficiency cores. While its dedicated NPU 5 delivers 50 TOPS, Intel emphasized its "Platform TOPS" approach, leveraging the Xe3 (Celestial) graphics engine to reach a combined 180 TOPS. This allows Panther Lake machines to run Large Language Models (LLMs) with 30 to 70 billion parameters locally, a feat previously reserved for high-end desktop workstations.
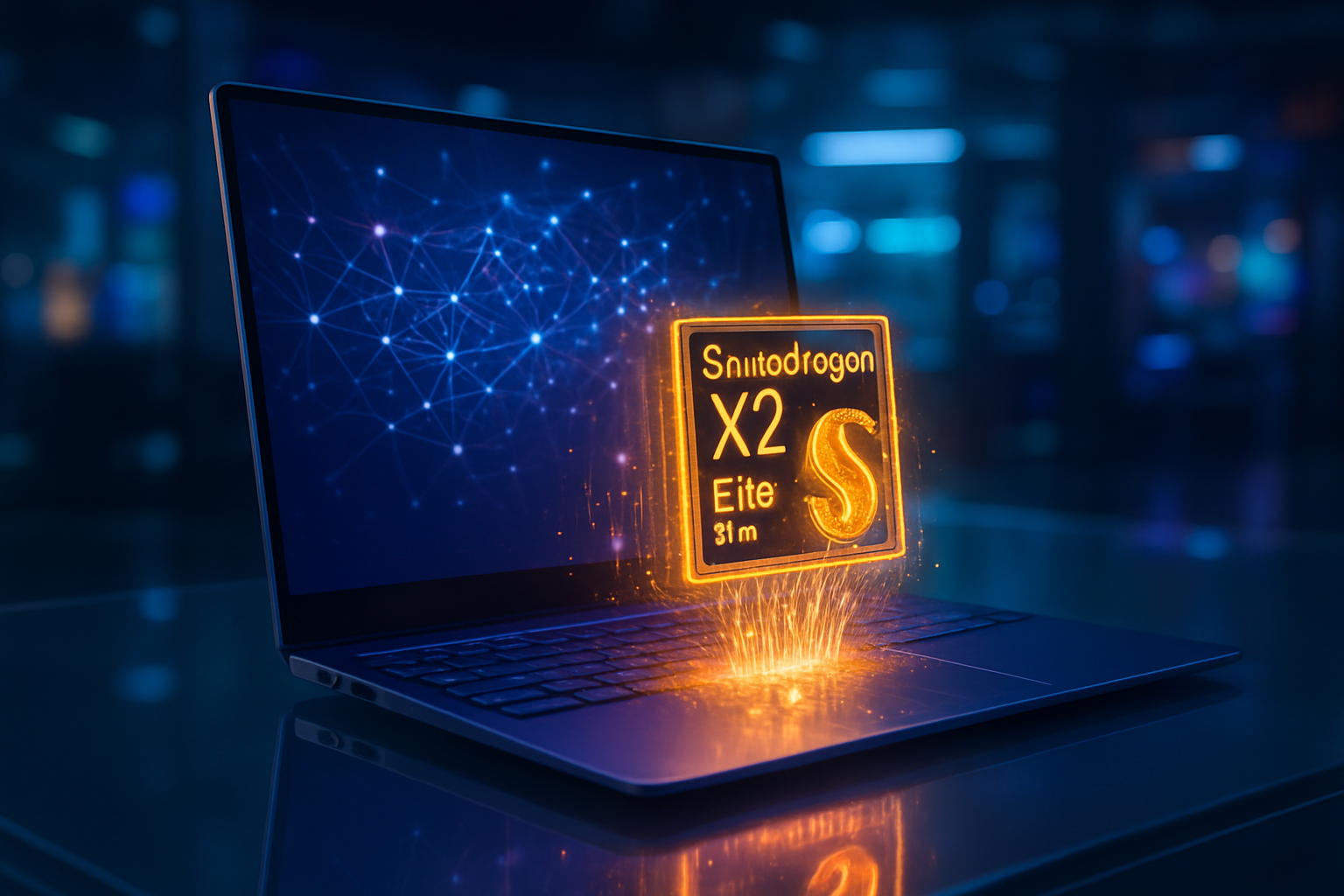
Qualcomm Inc. (NASDAQ: QCOM), however, currently holds the crown for raw NPU throughput. The newly unveiled Snapdragon X2 Elite, powered by the 3rd Generation Oryon CPU, features a Hexagon NPU capable of a staggering 80 TOPS. Qualcomm’s focus remained on power efficiency and "Ambient Intelligence," demonstrating a seamless integration with Google’s Gemini Nano to power proactive assistants. These agents don't wait for a prompt; they monitor user workflows in real-time to suggest actions, such as automatically drafting follow-up emails after a local voice call or organizing files based on the context of an ongoing project.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NASDAQ: AMD) countered with the Ryzen AI 400 series (codenamed Gorgon Point). While its 60 TOPS XDNA 2 NPU sits in the middle of the pack, AMD’s strategy is built on accessibility and software ecosystem integration. By partnering with Nexa AI to launch "Hyperlink," an on-device agentic retrieval system, AMD is positioning itself as the leader in "Private Search." Hyperlink acts as a local version of Perplexity, indexing every document, chat, and file on a user’s hard drive to provide an agentic interface that can answer questions and perform tasks based on a user’s entire digital history without compromising privacy.
Market Disruptions: Breaking the Cloud Chains
This shift toward local Agentic AI has profound implications for the tech hierarchy. For years, the AI narrative was controlled by cloud giants who benefited from massive data center investments. However, the 2026 hardware cycle suggests a potential "de-clouding" of the AI industry. As NPUs become powerful enough to handle sophisticated reasoning tasks, the high latency and subscription costs associated with cloud-based LLMs become less attractive to both enterprises and individual users. Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ: MSFT) has already pivoted to reflect this, announcing "Work IQ," a local memory feature for Copilot+ PCs that stores interaction history exclusively on-device.
The competitive pressure is also forcing PC OEMs to differentiate through proprietary software layers rather than just hardware assembly. Lenovo Group Limited (HKG: 0992) introduced "Qira," a personal AI agent that maintains context across a user's phone, tablet, and PC. By leveraging the 60-80 TOPS available in new silicon, Qira can perform multi-step tasks—like booking a flight based on a calendar entry and an emailed preference—entirely within the local environment. This move signals a shift where the value proposition of a PC is increasingly defined by the quality of its resident "Super Agent" rather than just its screen or keyboard.
For startups and software developers, this hardware opens a new frontier. The emergence of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) as an industry standard allows different local agents to communicate and share data securely. This enables a modular AI ecosystem where a specialized coding agent from a startup can collaborate with a scheduling agent from another provider, all running on a single Intel or Qualcomm chip. The strategic advantage is shifting toward those who can optimize models for NPU-specific execution, potentially disrupting the "one-size-fits-all" model of centralized AI.
Privacy, Sovereignty, and the AI Landscape
The broader significance of the 2026 AI PC war lies in the democratization of privacy. Previous AI breakthroughs, such as the release of GPT-4, required users to surrender their data to remote servers. The Agentic AI PCs showcased at CES 2026 flip this script. By providing 60-80 TOPS of local compute, these machines enable "Data Sovereignty." Users can now utilize the power of advanced AI for sensitive tasks—legal analysis, medical record management, or proprietary software development—without the risk of data leaks or the ethical concerns of training third-party models on their private information.
Furthermore, this hardware evolution addresses the looming energy crisis facing the AI sector. Running agents locally on high-efficiency 3nm and 18A chips is significantly more energy-efficient than the massive overhead required to power hyperscale data centers. This "edge-first" approach to AI could be the key to scaling the technology sustainably. However, it also raises new concerns regarding the "digital divide." As the baseline for a functional AI PC moves toward expensive, high-TOPS silicon, there is a risk that those unable to afford the latest hardware from Intel or AMD will be left behind in an increasingly automated world.
Comparatively, the leap from 2024’s 40 TOPS requirements to 2026’s 80 TOPS peak is more than just a numerical increase; it is a qualitative shift. It represents the move from AI as a "feature" (like a blur-background tool in a video call) to AI as the "operating system." In this new paradigm, the NPU is not a co-processor but the central intelligence that orchestrates the entire user experience.
The Horizon: From 80 TOPS to Humanoid Integration
Looking ahead, the momentum built at CES 2026 shows no signs of slowing. AMD has already teased its 2027 "Medusa" architecture, which is expected to utilize a 2nm process and push NPU performance well beyond the 100 TOPS mark. Intel’s 18A node is just the beginning of its "IDM 2.0" roadmap, with plans to integrate even deeper "Physical AI" capabilities that allow PCs to act as control hubs for household robotics and IoT ecosystems.
The next major challenge for the industry will be memory bandwidth. While NPUs are becoming incredibly fast, the "memory wall" remains a bottleneck for running truly massive models. We expect the 2027 cycle to focus heavily on unified memory architectures and on-package LPDDR6 to ensure that the 80+ TOPS NPUs are never starved for data. As these hardware hurdles are cleared, the applications will evolve from simple productivity agents to "Digital Twins"—AI entities that can truly represent a user's professional persona in meetings or handle complex creative projects autonomously.
Final Thoughts: The PC Reborn
The 2026 AI PC war has effectively rebranded the personal computer. It is no longer a tool for consumption or manual creation, but a localized engine of autonomy. The competition between Intel, Qualcomm, and AMD has accelerated the arrival of Agentic AI by years, moving us into a world where our devices don't just wait for instructions—they participate in our work.
The significance of this development in AI history cannot be overstated. We are witnessing the decentralization of intelligence. As we move into the spring of 2026, the industry will be watching closely to see which "Super Agents" gain the most traction with users. The hardware is here; the agents have arrived. The only question left is how much of our daily lives we are ready to delegate to the silicon sitting on our desks.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.