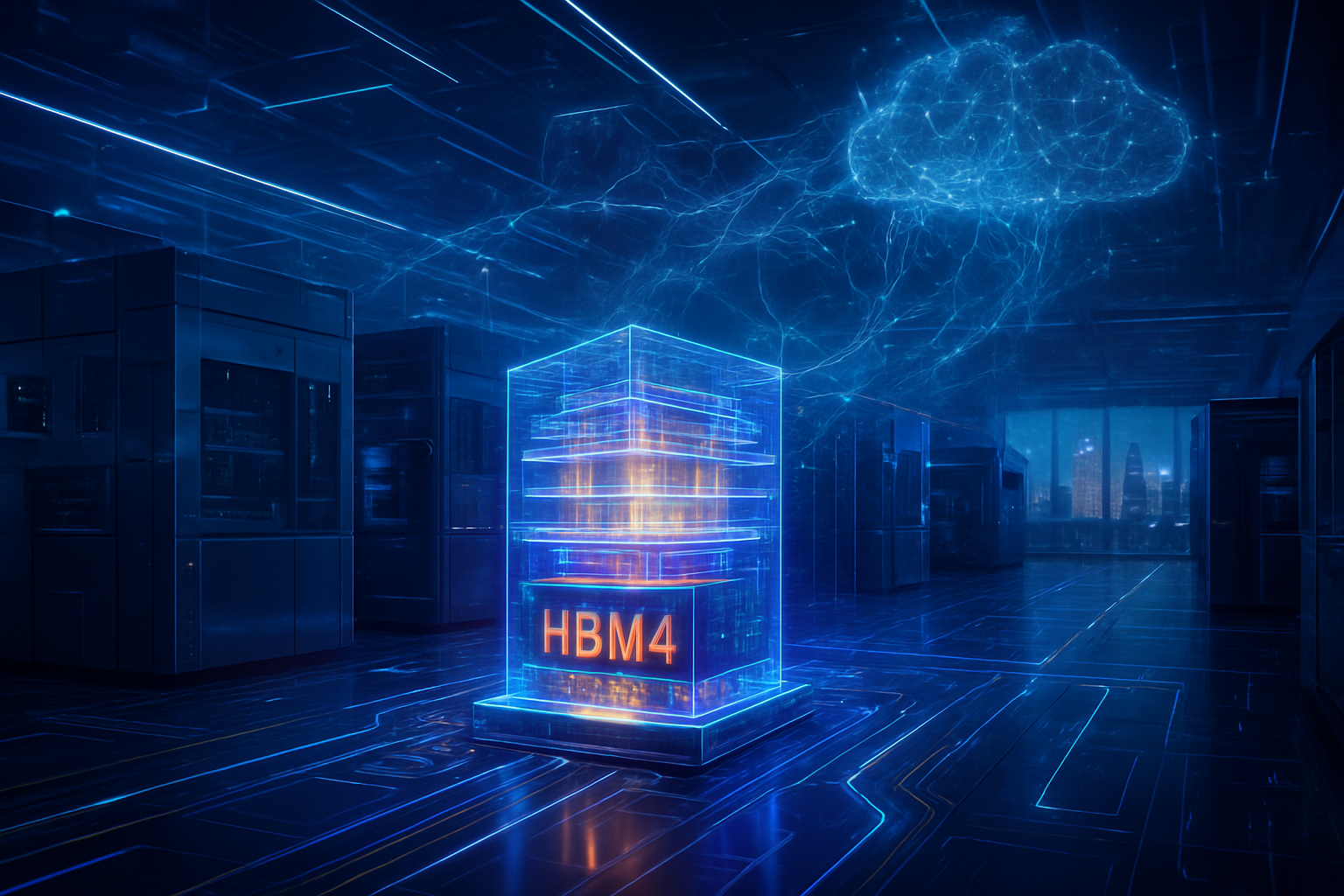
As of January 28, 2026, the artificial intelligence landscape has reached a critical hardware inflection point. The transition from generative chatbots to autonomous "Agentic AI"—systems capable of complex, multi-step reasoning and independent execution—has placed an unprecedented strain on global computing infrastructure. The answer to this crisis has arrived in the form of High Bandwidth Memory 4 (HBM4), which is officially moving into mass production this quarter.
HBM4 is not merely an incremental update; it is a fundamental redesign of how data moves between memory and the processor. As the first memory standard to integrate logic-on-memory technology, HBM4 is designed to shatter the "Memory Wall"—the physical bottleneck where processor speeds outpace the rate at which data can be delivered. With the world's leading semiconductor firms reporting that their entire 2026 capacity is already pre-sold, the HBM4 boom is reshaping the power dynamics of the global tech industry.
The 2048-Bit Leap: Engineering the Future of Memory
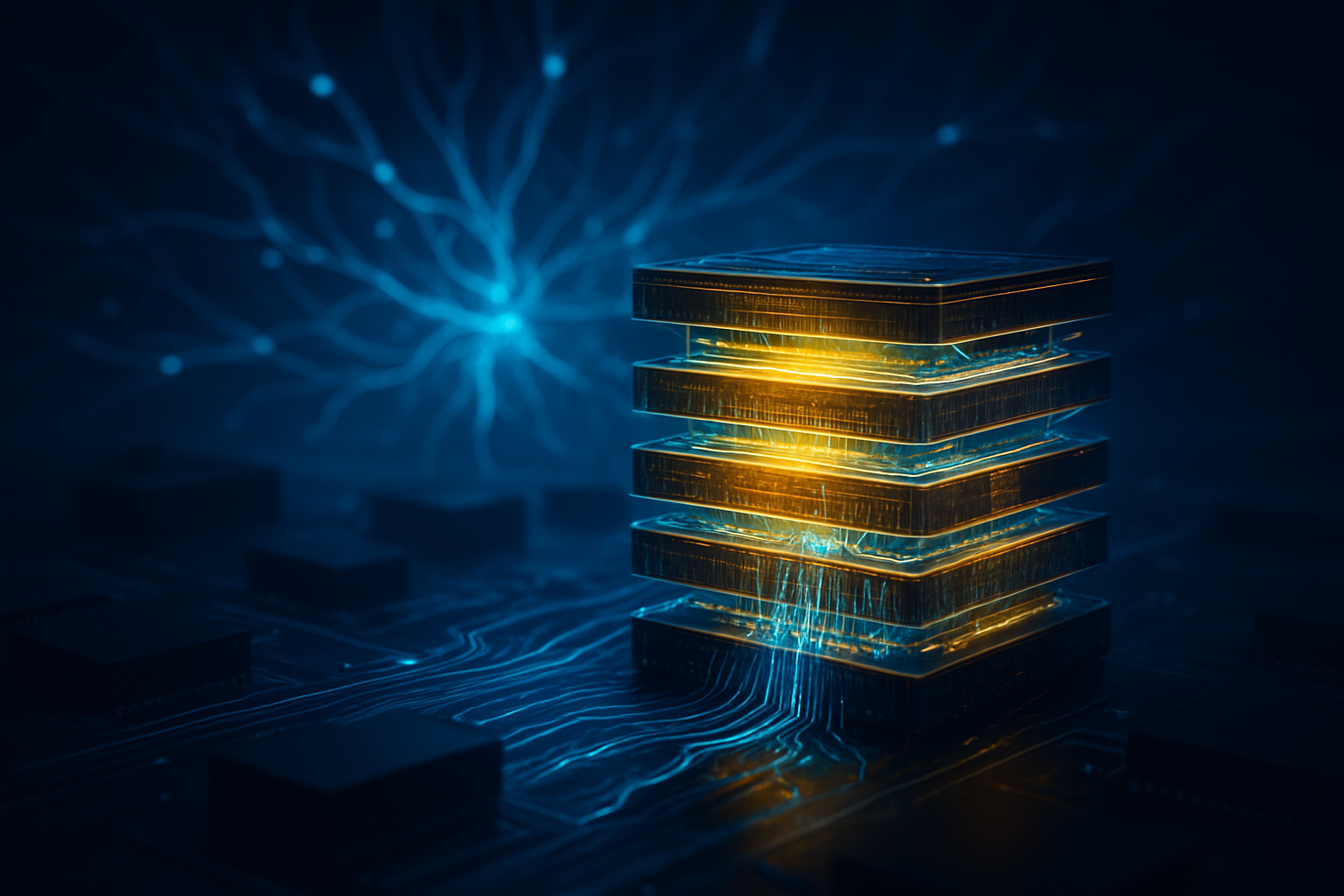
The technical leap from the current HBM3E standard to HBM4 is the most significant in the history of the High Bandwidth Memory category. The most striking advancement is the doubling of the interface width from 1024-bit to 2048-bit per stack. This expanded "data highway" allows for a massive surge in throughput, with individual stacks now capable of exceeding 2.0 TB/s. For next-generation AI accelerators like the NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA) Rubin architecture, this translates to an aggregate bandwidth of over 22 TB/s—nearly triple the performance of the groundbreaking Blackwell systems of 2024.
Density has also seen a dramatic increase. The industry has standardized on 12-high (48GB) and 16-high (64GB) stacks. A single GPU equipped with eight 16-high HBM4 stacks can now access 512GB of high-speed VRAM on a single package. This massive capacity is made possible by the introduction of Hybrid Bonding and advanced Mass Reflow Molded Underfill (MR-MUF) techniques, allowing manufacturers to stack more layers without increasing the physical height of the chip.
Perhaps the most transformative change is the "Logic Die" revolution. Unlike previous generations that used passive base dies, HBM4 utilizes an active logic die manufactured on advanced foundry nodes. SK Hynix (KRX: 000660) and Micron Technology (NASDAQ: MU) have partnered with TSMC (NYSE: TSM) to produce these base dies using 5nm and 12nm processes, while Samsung Electronics (KRX: 005930) is utilizing its own 4nm foundry for a vertically integrated "turnkey" solution. This allows for Processing-in-Memory (PIM) capabilities, where basic data operations are performed within the memory stack itself, drastically reducing latency and power consumption.
The HBM Gold Rush: Market Dominance and Strategic Alliances
The commercial implications of HBM4 have created a "Sold Out" economy. Hyperscalers such as Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT), Meta (NASDAQ: META), and Alphabet (NASDAQ: GOOGL) have reportedly engaged in fierce bidding wars to secure 2026 allocations, leaving many smaller AI labs and startups facing lead times of 40 weeks or more. This supply crunch has solidified the dominance of the "Big Three" memory makers—SK Hynix, Samsung, and Micron—who are seeing record-breaking margins on HBM products that sell for nearly eight times the price of traditional DDR5 memory.
In the chip sector, the rivalry between NVIDIA and AMD (NASDAQ: AMD) has reached a fever pitch. NVIDIA’s Vera Rubin (R200) platform, unveiled earlier this month at CES 2026, is the first to be built entirely around HBM4, positioning it as the premium choice for training trillion-parameter models. However, AMD is challenging this dominance with its Instinct MI400 series, which offers a 12-stack HBM4 configuration providing 432GB of capacity—purpose-built to compete in the burgeoning high-memory-inference market.
The strategic landscape has also shifted toward a "Foundry-Memory Alliance" model. The partnership between SK Hynix and TSMC has proven formidable, leveraging TSMC’s CoWoS (Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate) packaging to maintain a slight edge in timing. Samsung, however, is betting on its ability to offer a "one-stop-shop" service, combining its memory, foundry, and packaging divisions to provide faster delivery cycles for custom HBM4 solutions. This vertical integration is designed to appeal to companies like Amazon (NASDAQ: AMZN) and Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA), which are increasingly designing their own custom AI ASICs.
Breaching the Memory Wall: Implications for the AI Landscape
The arrival of HBM4 marks the end of the "Generative Era" and the beginning of the "Agentic Era." Current Large Language Models (LLMs) are often limited by their "KV Cache"—the working memory required to maintain context during long conversations. HBM4’s 512GB-per-GPU capacity allows AI agents to maintain context across millions of tokens, enabling them to handle multi-day workflows, such as autonomous software engineering or complex scientific research, without losing the thread of the project.
Beyond capacity, HBM4 addresses the power efficiency crisis facing global data centers. By moving logic into the memory die, HBM4 reduces the distance data must travel, which significantly lowers the energy "tax" of moving bits. This is critical as the industry moves toward "World Models"—AI systems used in robotics and autonomous vehicles that must process massive streams of visual and sensory data in real-time. Without the bandwidth of HBM4, these models would be too slow or too power-hungry for edge deployment.
However, the HBM4 boom has also exacerbated the "AI Divide." The 1:3 capacity penalty—where producing one HBM4 wafer consumes the manufacturing resources of three traditional DRAM wafers—has driven up the price of standard memory for consumer PCs and servers by over 60% in the last year. For AI startups, the high cost of HBM4-equipped hardware represents a significant barrier to entry, forcing many to pivot away from training foundation models toward optimizing "LLM-in-a-box" solutions that utilize HBM4's Processing-in-Memory features to run smaller models more efficiently.
Looking Ahead: Toward HBM4E and Optical Interconnects
As mass production of HBM4 ramps up throughout 2026, the industry is already looking toward the next horizon. Research into HBM4E (Extended) is well underway, with expectations for a late 2027 release. This future standard is expected to push capacities toward 1TB per stack and may introduce optical interconnects, using light instead of electricity to move data between the memory and the processor.
The near-term focus, however, will be on the 16-high stack. While 12-high variants are shipping now, the 16-high HBM4 modules—the "holy grail" of current memory density—are targeted for Q3 2026 mass production. Achieving high yields on these complex 16-layer stacks remains the primary engineering challenge. Experts predict that the success of these modules will determine which companies can lead the race toward "Super-Intelligence" clusters, where tens of thousands of GPUs are interconnected to form a single, massive brain.
A New Chapter in Computational History
The rollout of HBM4 is more than a hardware refresh; it is the infrastructure foundation for the next decade of AI development. By doubling bandwidth and integrating logic directly into the memory stack, HBM4 has provided the "oxygen" required for the next generation of trillion-parameter models to breathe. Its significance in AI history will likely be viewed as the moment when the "Memory Wall" was finally breached, allowing silicon to move closer to the efficiency of the human brain.
As we move through 2026, the key developments to watch will be Samsung’s mass production ramp-up in February and the first deployment of NVIDIA's Rubin clusters in mid-year. The global economy remains highly sensitive to the HBM supply chain, and any disruption in these critical memory stacks could ripple across the entire technology sector. For now, the HBM4 boom continues unabated, fueled by a world that has an insatiable hunger for memory and the intelligence it enables.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.