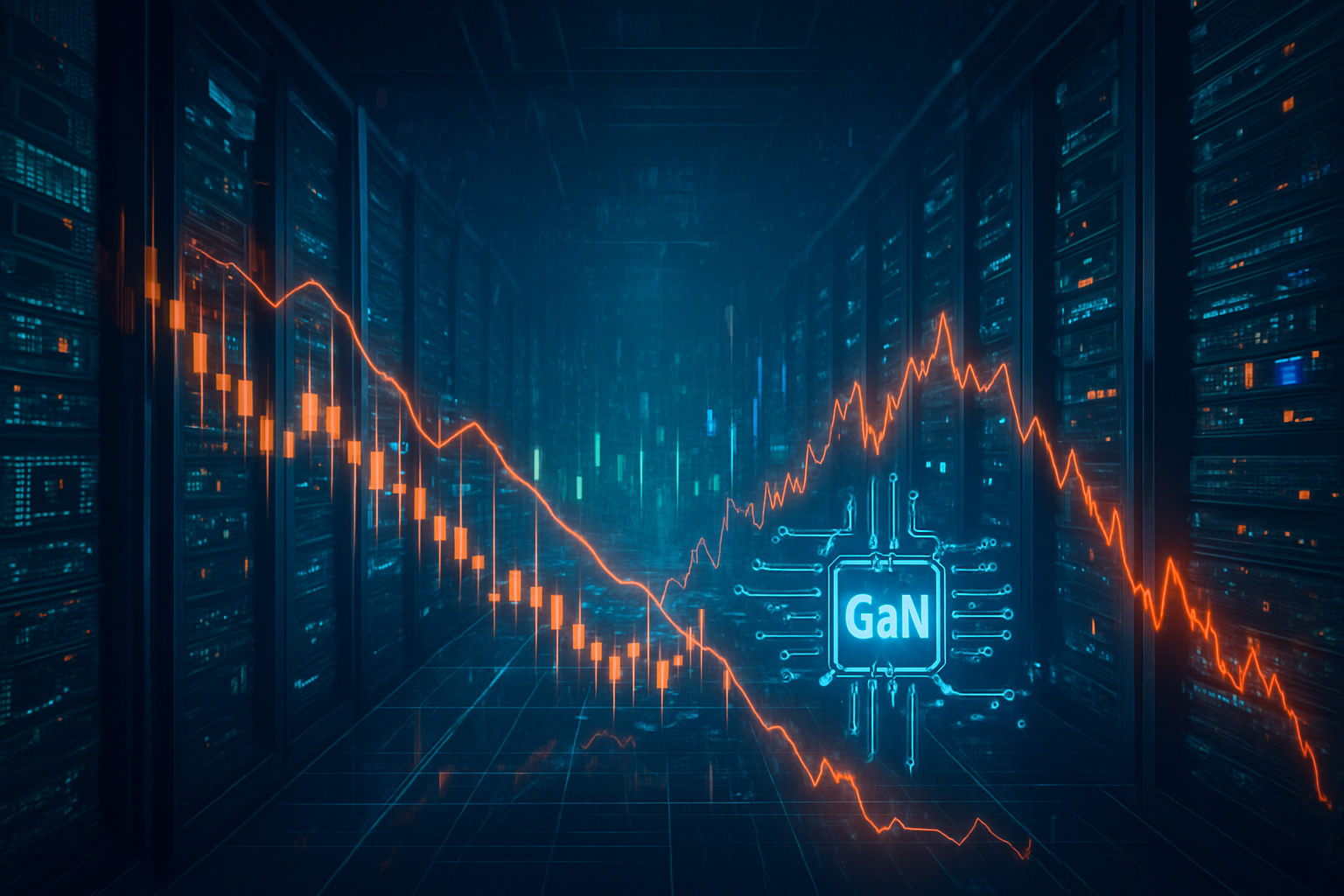
San Francisco, CA – November 5, 2025 – Navitas Semiconductor (NASDAQ: NVTS), a prominent player in gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) power semiconductors, experienced a sharp downturn this week, with its stock plummeting 14.6% following the release of its third-quarter 2025 financial results. The disappointing earnings, announced on Monday, November 3, 2025, have sent ripples through the market, raising questions about investor sentiment in the high-growth, yet highly scrutinized, AI hardware sector. While Navitas is strategically pivoting towards higher-power applications critical for AI data centers, the immediate financial missteps highlight the challenges of translating long-term potential into near-term profitability.
The significant stock drop underscores a growing cautiousness among investors regarding companies in the AI supply chain that are still in the early stages of securing substantial design wins. Navitas' performance serves as a potent reminder that even amidst the fervent enthusiasm for artificial intelligence, robust financial execution and clear pathways to revenue generation remain paramount. The company's strategic shift is aimed at capitalizing on the burgeoning demand for efficient power solutions in AI infrastructure, but this quarter's results indicate a bumpy road ahead as it navigates this transition.
Financial Misses and Strategic Realignment Drive Market Reaction
Navitas Semiconductor's Q3 2025 financial report painted a challenging picture, missing analyst expectations on both the top and bottom lines. The company reported an adjusted loss per share of -$0.09, wider than the consensus estimate of -$0.05. Revenue for the quarter stood at $10.11 million, falling short of the $10.79 million analyst consensus and representing a substantial 53.4% year-over-year decline from $21.7 million in the same period last year. This dual miss triggered an immediate and severe market reaction, with shares initially dropping 8.2% in after-hours trading, extending to a 9% decline during regular trading on Monday, and ultimately culminating in a more than 14% fall in the extended session.
Several factors contributed to this disappointing performance. Chief among them was a notably weak outlook for the fourth quarter, with Navitas projecting revenue guidance of $7.0 million (plus or minus $0.25 million), significantly below the analysts' average estimate of $10.03 million. Furthermore, the company announced a strategic decision to deprioritize its "low power, lower profit China mobile & consumer business" and reduce channel inventory. This pivot is intended to reorient Navitas towards higher-power revenue streams, particularly in the burgeoning markets of AI data centers, electric vehicles, and energy infrastructure, where its GaN and SiC technologies offer significant efficiency advantages.
However, external pressures also played a role, including adverse impacts from China tariff risks for its silicon carbide business and persistent pricing pressure in the mobile sector, especially within China. While the strategic pivot aligns Navitas with the high-growth AI and electrification trends, the immediate financial consequences underscore the difficulty of executing such a significant shift while maintaining short-term financial stability. The market's reaction suggests that investors are demanding more immediate evidence of this pivot translating into tangible design wins and revenue growth in its target high-power markets.
Investor Sentiment Shifts Amidst AI Hardware Scrutiny
The fallout from Navitas' earnings report has led to a noticeable shift in analyst opinions and broader investor sentiment, particularly concerning companies positioned to benefit from the AI boom. Analyst consensus has generally moved towards a "Hold" rating, reflecting a cautious stance. Rosenblatt, for instance, downgraded Navitas from a "Buy" to a "Neutral" rating and slashed its price target from $12 to $8. This downgrade was largely attributed to "lofty valuation metrics" and a perception that market anticipation for the impact of 800VDC data centers was running ahead of actual design wins.
Conversely, Needham analyst N. Quinn Bolton maintained a "Buy" rating and even increased the price target from $8 to $13, signaling continued optimism despite the recent performance, perhaps focusing on the long-term potential of the strategic pivot. However, other firms like Craig-Hallum expressed skepticism, labeling NVTS stock as overvalued given the absence of significant design wins despite the technological buzz around its 800V architecture. This divergence highlights the ongoing debate within the investment community about how to value companies that promise future AI-driven growth but are currently facing execution challenges.
The broader impact on investor sentiment is one of increased skepticism and a more cautious approach towards AI hardware plays, especially those with high valuations and unproven near-term revenue streams. Macroeconomic uncertainties and ongoing trade tensions, particularly with China, further exacerbate this caution. While Navitas' pivot to AI data centers and energy infrastructure is strategically sound for long-term growth, the immediate negative reaction indicates that investors are becoming more discerning, demanding concrete evidence of design wins and revenue generation rather than solely relying on future potential. This could lead to a re-evaluation of other AI-adjacent semiconductor companies that have seen their valuations soar based on anticipated, rather than realized, contributions to the AI revolution.
Broader Implications for the AI Hardware Ecosystem
Navitas Semiconductor's recent performance and strategic realignment offer a crucial case study within the broader AI hardware landscape. The company's explicit decision to pivot away from lower-profit consumer electronics towards high-power applications like AI data centers and electric vehicles underscores the intensifying race to capture value in the most demanding and lucrative segments of the AI supply chain. This move reflects a wider trend where semiconductor manufacturers are recalibrating their strategies to align with the massive power efficiency requirements of modern AI computational infrastructure, which demands advanced GaN and SiC solutions.
However, the market's negative reaction also highlights potential concerns within this rapidly expanding sector. Is the AI hardware boom sustainable across all segments, or are certain valuations getting ahead of actual design wins and revenue generation? Navitas' struggle to translate its technological prowess into immediate, significant revenue from AI data centers suggests that securing these critical design wins is more challenging and time-consuming than some investors might have anticipated. This could lead to a more discerning investment environment, where companies with tangible, immediate contributions to AI infrastructure are favored over those still positioning themselves.
This event could serve as a reality check for the entire AI hardware ecosystem, distinguishing between companies with robust, immediate AI-driven revenue streams and those still primarily operating on future potential. It emphasizes that while the demand for AI compute power is unprecedented, the underlying hardware market is complex, competitive, and subject to economic and geopolitical pressures. The focus will increasingly shift from mere technological capability to demonstrable market penetration and financial performance in the high-stakes AI infrastructure buildout.
Navigating Future Developments and Challenges
Looking ahead, Navitas Semiconductor has provided a Q4 2025 outlook that anticipates revenue bottoming in the current quarter, with expectations for growth to resume in 2026. This projection is heavily reliant on the successful execution of its strategic pivot towards higher-power, higher-margin applications in AI data centers, electric vehicles, and renewable energy. The company's ability to secure significant design wins with leading customers in these critical sectors will be paramount to validating its new direction and restoring investor confidence.
However, Navitas faces several challenges. Successfully transitioning away from established, albeit lower-margin, consumer markets requires a robust sales and marketing effort to penetrate new, highly competitive industrial and enterprise segments. Managing external pressures, such as ongoing China tariff risks and potential fluctuations in global supply chains, will also be crucial. Furthermore, the company must demonstrate that its GaN and SiC technologies offer a compelling enough advantage in efficiency and performance to overcome the inertia of existing solutions in the demanding AI data center environment.
Experts predict that the coming quarters will bring continued scrutiny of AI hardware companies for tangible results. The market will be watching for concrete announcements of design wins, especially those involving the 800V architecture in data centers, which Navitas has been championing. The ability of companies like Navitas to move beyond promising technology to actual market adoption and significant revenue contribution will define their success in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
A Crucial Moment for AI Hardware Valuation
Navitas Semiconductor's Q3 2025 earnings report and subsequent stock decline mark a significant moment in the ongoing narrative of AI hardware development. The key takeaways are clear: even within the booming AI market, execution, tangible design wins, and justified valuations are critical. While Navitas' strategic pivot towards high-power AI data center applications is a logical move to align with future growth, the immediate financial miss highlights the inherent challenges of such a transition and the market's demand for near-term results.
This development underscores the importance of distinguishing between the immense potential of AI and the practical realities of bringing innovative hardware solutions to market. It serves as a potent reminder that the "AI tide" may lift all boats, but only those with strong fundamentals and clear paths to profitability will maintain investor confidence in the long run. The significance of this event in AI history lies in its potential to temper some of the exuberance around AI hardware valuations, fostering a more disciplined approach to investment in the sector.
In the coming weeks and months, all eyes will be on Navitas' Q4 performance and its progress in securing those elusive, yet critical, design wins in the AI data center space. Its journey will offer valuable insights into the broader health and maturity of the AI hardware ecosystem, providing a litmus test for how quickly and effectively innovative power semiconductor technologies can penetrate and transform the infrastructure powering the artificial intelligence revolution.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.