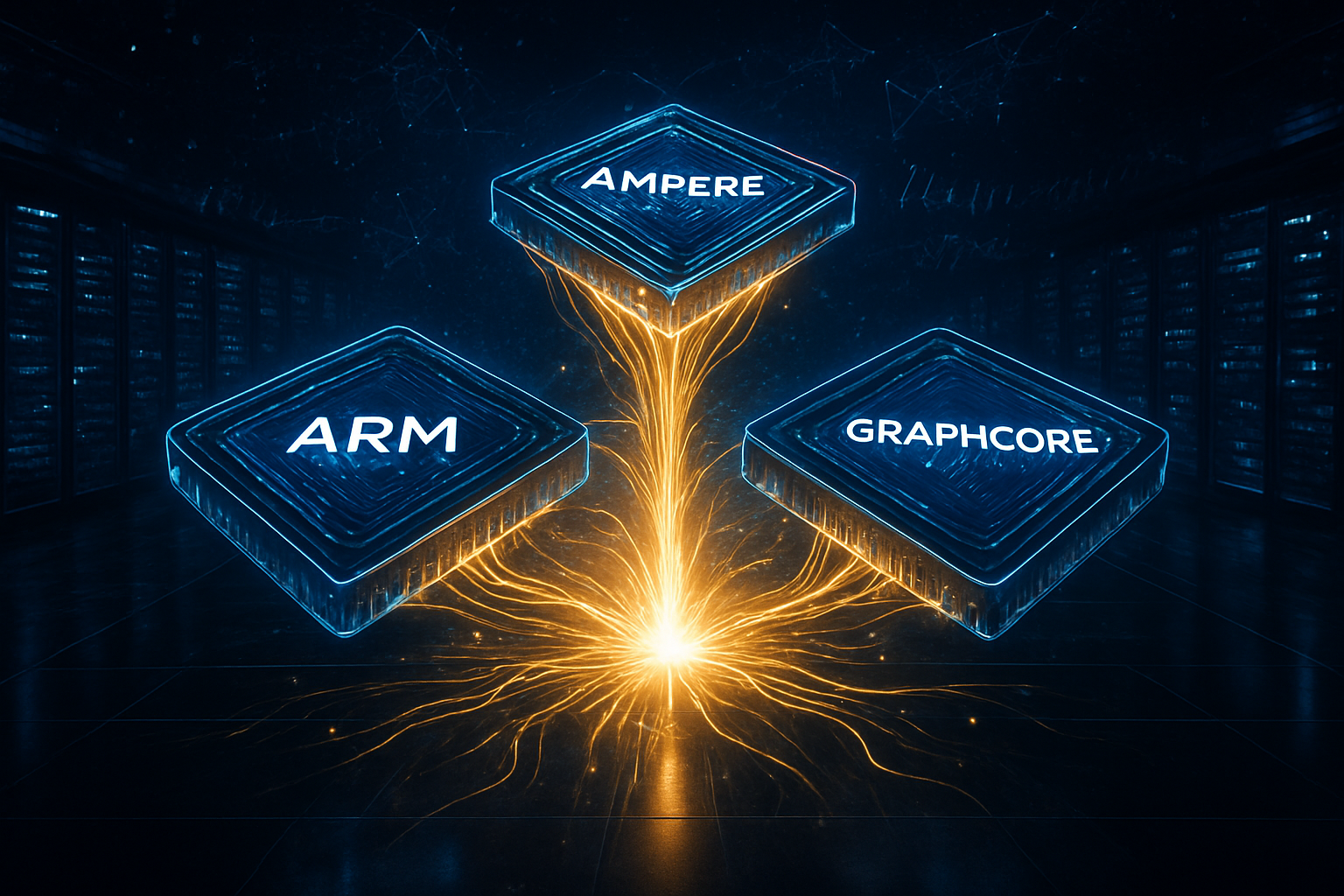
The global landscape of artificial intelligence infrastructure shifted decisively this week as SoftBank Group Corp. (OTC: SFTBY) finalized its $6.5 billion acquisition of Ampere Computing. The deal, which officially closed on November 25, 2025, represents the latest and perhaps most critical piece in Masayoshi Son’s ambitious "Artificial Super Intelligence" (ASI) roadmap. By bringing the world’s leading independent ARM-based server chip designer under its roof, SoftBank has effectively transitioned from a venture capital powerhouse into a vertically integrated industrial giant capable of controlling the hardware that will power the next decade of AI evolution.
The acquisition marks a strategic pivot for SoftBank, which has spent the last year consolidating its grip on the semiconductor supply chain. With the addition of Ampere, SoftBank now owns a formidable "Silicon Trinity" consisting of Arm Holdings plc (Nasdaq: ARM) for architecture, the recently acquired Graphcore for AI acceleration, and Ampere for server-side processing. This integration is designed to solve the massive power and efficiency bottlenecks currently plaguing hyperscale data centers as they struggle to meet the insatiable compute demands of generative AI and emerging autonomous systems.
The Technical Edge: 512 Cores and the Death of x86 Dominance
At the heart of this acquisition is Ampere’s revolutionary "cloud-native" processor architecture. Unlike traditional incumbents like Intel Corporation (Nasdaq: INTC) and Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (Nasdaq: AMD), which have spent decades refining the x86 architecture for general-purpose computing, Ampere built its chips from the ground up using the ARM instruction set. The technical crowning jewel of the deal is the "AmpereOne Aurora," a massive 512-core processor slated for widespread deployment in 2026. This chip utilizes custom-designed cores that prioritize predictable performance and high-density throughput, allowing data centers to pack more processing power into a smaller physical footprint.
The technical distinction lies in Ampere’s ability to handle "AI inference" workloads—the process of running trained AI models—with significantly higher efficiency than traditional CPUs. While NVIDIA Corporation (Nasdaq: NVDA) GPUs remain the gold standard for training large language models, those GPUs require powerful, energy-efficient CPUs to act as "host" processors to manage data flow. Ampere’s ARM-based designs eliminate the "IO bottleneck" often found in x86 systems, ensuring that expensive AI accelerators aren't left idling while waiting for data.
Industry experts have noted that the AmpereOne Aurora’s performance-per-watt is nearly double that of current-generation x86 server chips. In an era where power availability has become the primary constraint for AI expansion, this efficiency is not just a cost-saving measure but a fundamental requirement for scaling. The AI research community has largely reacted with optimism, noting that a standardized ARM-based server platform could simplify software development for AI researchers who are increasingly moving away from hardware-specific optimizations.
A Strategic Masterstroke in the AI Arms Race
The market implications of this deal are profound, particularly for the major cloud service providers. Oracle Corporation (NYSE: ORCL), an early backer of Ampere, has already integrated these chips deeply into its cloud infrastructure, and the acquisition ensures a stable, SoftBank-backed roadmap for other giants like Microsoft Corporation (Nasdaq: MSFT) and Alphabet Inc. (Nasdaq: GOOGL). By controlling Ampere, SoftBank can now offer a unified hardware-software stack that bridges the gap between the mobile-centric ARM ecosystem and the high-performance computing required for AI.
For competitors like Intel and AMD, the SoftBank-Ampere alliance represents a direct existential threat in the data center market. For years, x86 was the undisputed king of the server room, but the AI boom has exposed its limitations in power efficiency and multi-core scalability. SoftBank’s ownership of Arm Holdings allows for "deep taping out" synergies, where the architectural roadmap of ARM can be co-developed with Ampere’s physical chip implementations. This creates a feedback loop that could allow SoftBank to bring AI-optimized silicon to market months or even years faster than traditional competitors.
Furthermore, the acquisition positions SoftBank as a key player in "Project Stargate," the rumored $500 billion infrastructure initiative aimed at building the world's largest AI supercomputers. With Ampere chips serving as the primary compute host, SoftBank is no longer just a supplier of intellectual property; it is the architect of the physical infrastructure upon which the future of AI will be built. This strategic positioning gives Masayoshi Son immense leverage over the direction of the entire AI industry.
Energy, Sovereignty, and the Broader AI Landscape
Beyond the balance sheets, the SoftBank-Ampere deal addresses the growing global concern over energy consumption in the AI era. As AI models grow in complexity, the carbon footprint of the data centers that house them has come under intense scrutiny. Ampere’s "Sustainable Compute" philosophy aligns with a broader industry trend toward "Green AI." By reducing the power required for inference, SoftBank is positioning itself as the "responsible" choice for governments and corporations under pressure to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) targets.
This acquisition also touches on the sensitive issue of "technological sovereignty." As nations race to build their own domestic AI capabilities, the ability to access high-performance, non-x86 hardware becomes a matter of national security. SoftBank’s global footprint and its base in Japan provide a neutral alternative to the US-centric dominance of Intel and NVIDIA, potentially opening doors for massive infrastructure projects in Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
However, the consolidation of such critical technology under one roof has raised eyebrows among antitrust advocates. With SoftBank owning the architecture (ARM), the server chips (Ampere), and the accelerators (Graphcore), there are concerns about a "walled garden" effect. Critics argue that this level of vertical integration could stifle innovation from smaller chip startups that rely on ARM licenses but now find themselves competing directly with their licensor’s parent company.
The Horizon: From Inference to Autonomy
Looking ahead, the integration of Ampere into the SoftBank ecosystem is expected to accelerate the development of "Edge AI"—bringing powerful AI capabilities out of the data center and into robots, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT devices. The near-term focus will be on the 2026 rollout of the 512-core Aurora chips, but the long-term vision involves a seamless compute fabric where a single architecture scales from a smartwatch to a massive AI supercluster.
The biggest challenge facing SoftBank will be the execution of this integration. Merging the corporate cultures of a British IP firm (ARM), a British AI startup (Graphcore), and a Silicon Valley chip designer (Ampere) under a Japanese conglomerate is a monumental task. Furthermore, the industry is watching closely to see how SoftBank manages its relationship with other ARM licensees who may now view the company as a direct competitor rather than a neutral partner.
A New Era for AI Hardware
The acquisition of Ampere Computing for $6.5 billion is more than just a line item in SoftBank’s portfolio; it is a declaration of intent. It marks the end of the "software-first" era of AI and the beginning of the "infrastructure-first" era. By securing the most efficient server technology on the market, SoftBank has insured itself against the volatility of the AI software market and anchored its future in the physical reality of silicon and power.
As we move into 2026, the industry will be watching for the first "Trinity" systems—servers that combine ARM architecture, Ampere CPUs, and Graphcore accelerators into a single, optimized unit. If Masayoshi Son’s gamble pays off, the "Silicon Trinity" could become the standard blueprint for the AI age, fundamentally altering the power dynamics of the technology world for decades to come.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.